Abstract
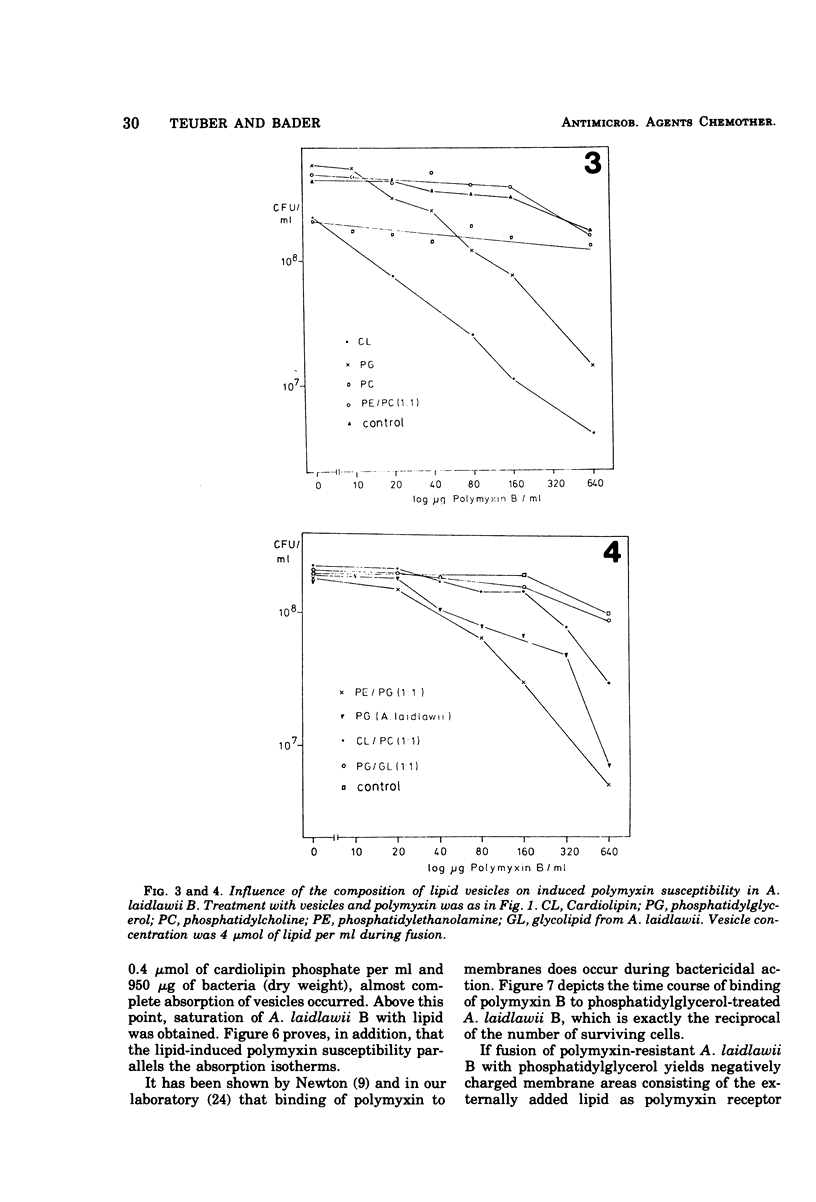
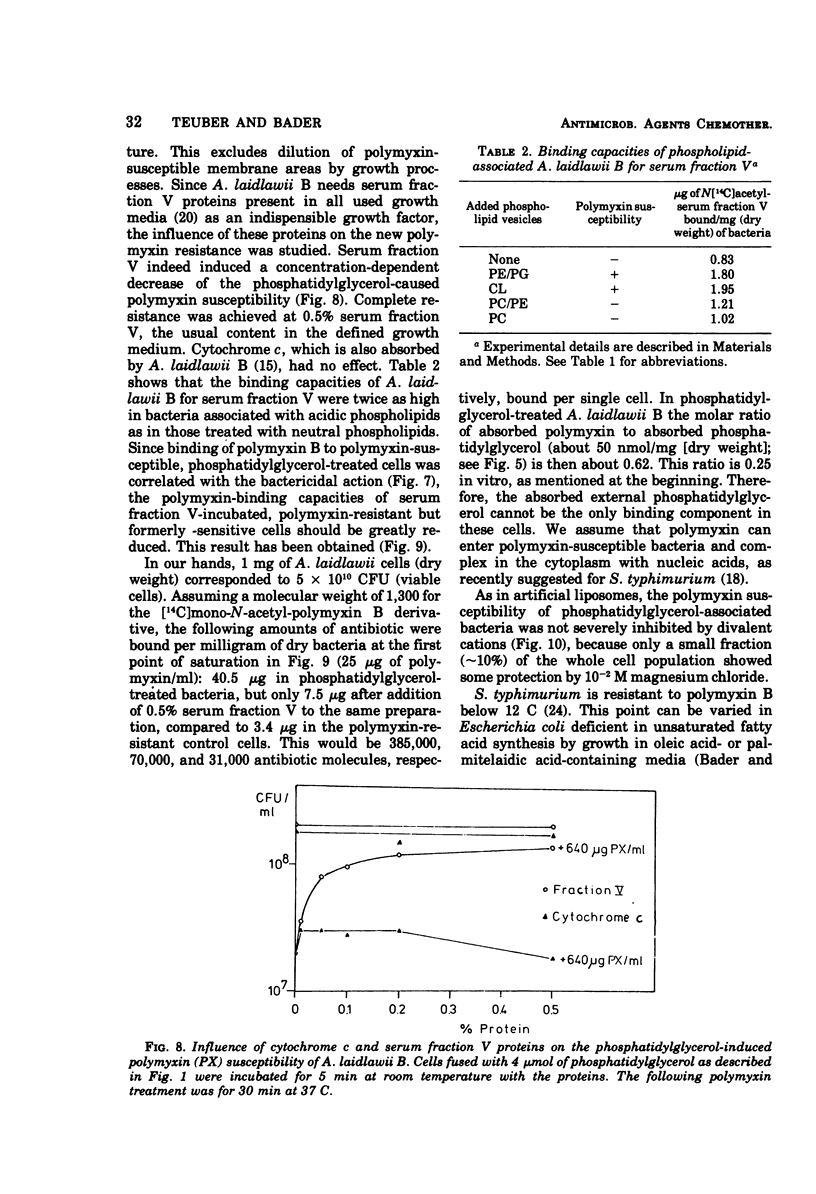
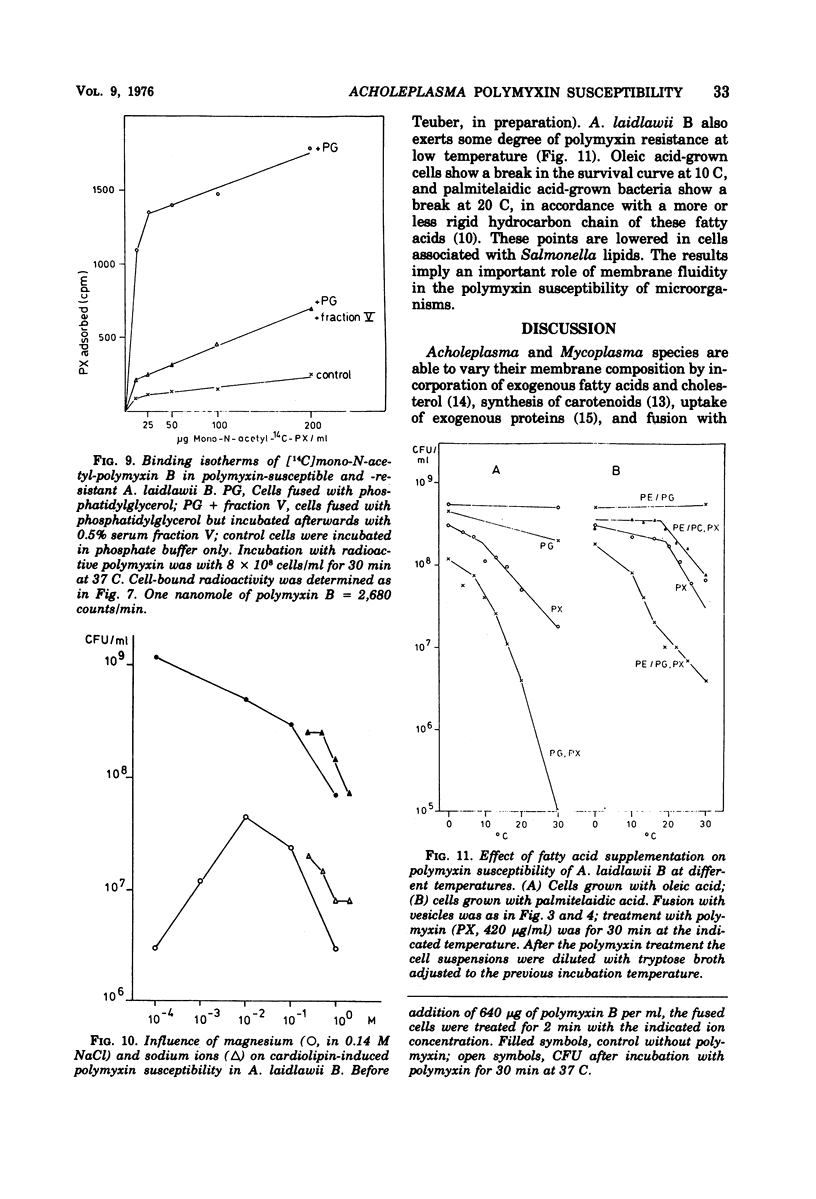
To identify the polymyxin receptor molecules in the membranes of living microorganisms, fusion of intact Acholeplasma laidlawii B with lipid vesicles was investigated according to the procedure of Grant and McConnell (1973). The naturally polymyxin-resistant A. laidlawii B was treated with phospholipid vesicles prepared from purified phospholipids of the polymyxin-susceptible Salmonella typhimurium G30. A. laidlawii B absorbed between 15 and 45% of its own lipid content of the added tritium-labeled phospholipids without loss of viability. Association with the acidic components phosphatidylglycerol and cardiolipin produced a 10- to 30-fold increase in polymyxin susceptibility, which was not obtained with egg-phosphatidylcholine and mixed phosphatidylcholine-phosphatidylethanolamine vesicles. The polymyxin-sensitized cells bound 12 times more radioactive antibiotic than resistant cells. The phosphatidylglycerol-induced susceptibility was abolished by serum fraction V (Cohn) proteins.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- FEW A. V. The interaction of polymyxin E with bacterial and other lipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1955 Jan;16(1):137–145. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(55)90191-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold D. S., HsuChen C. C., Sud I. J. Basis for the selectivity of action of the polymyxin antibiotics on cell membranes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 May 10;235(0):480–492. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb43285.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant C. W., McConnell H. M. Fusion of phospholipid vesicles with viable Acholeplasma laidlawii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Apr;70(4):1238–1240. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.4.1238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai M., Inoue K., Nojima S. Effect of polymyxin B on liposomal membranes derived from Escherichia coli lipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jan 14;375(1):130–137. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90078-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McElhaney R. N., Tourtellotte M. E. The relationship between fatty acid structure and the positional distribution of esterified fatty acids in phosphatidyl glycerol from Mycoplasma laidlawii B. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Feb 10;202(1):120–128. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(70)90223-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEWTON B. A. The properties and mode of action of the polymyxins. Bacteriol Rev. 1956 Mar;20(1):14–27. doi: 10.1128/br.20.1.14-27.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overath P., Schairer H. U., Stoffel W. Correlation of in vivo and in vitro phase transitions of membrane lipids in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Oct;67(2):606–612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.2.606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papahadjopoulos D., Miller N. Phospholipid model membranes. I. Structural characteristics of hydrated liquid crystals. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Sep 9;135(4):624–638. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(67)90094-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAZIN S., ROTTEM S. FATTY ACID REQUIREMENTS OF MYCOPLASMA LAIDLAWII. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Dec;33:459–470. doi: 10.1099/00221287-33-3-459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S., Rottem S. Role of carotenoids and cholesterol in the growth of Mycoplasma laidlawii. J Bacteriol. 1967 Mar;93(3):1181–1182. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.3.1181-1182.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S., Tourtellotte M. E., McElhaney R. N., Pollack J. D. Influence of lipid components of Mycoplasma laidlawii membranes on osmotic fragility of cells. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):609–616. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.609-616.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottem S., Hasin M., Razin S. Binding of proteins to mycoplasma membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 16;298(4):876–886. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90392-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottem S., Hasin M., Razin S. Differences in susceptibility to phospholipase C of free and membrane-bound phospholipids of Mycoplasma hominis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Nov 16;323(4):520–531. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90160-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH P. F. THE CAROTENOID PIGMENTS OF MYCOPLASMA. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Sep;32:307–319. doi: 10.1099/00221287-32-3-307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiefer H. G., Gerhardt U., Brunner H. Immunological studies on the localization of phosphatidylglycerol in the membranes of Mycoplasma hominis. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1975 May;356(5):559–565. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1975.356.1.559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler P. R., Teuber M. Action of polymyxin B on bacterial membranes: morphological changes in the cytoplasm and in the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli B. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Jul;8(1):95–104. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teuber M., Bader J. Quantitative correlation of uptake with antibiotic activity of polymyxin B in Salmonella typhimurium. FEBS Lett. 1971 Aug 15;16(3):195–197. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80131-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teuber M. Preparation of biologically active mono-N-acetyl (14C)-derivatives of the membrane-specific polypeptide antibiotic polymyxin B. Z Naturforsch B. 1970 Jan;25(1):117–117. doi: 10.1515/znb-1970-0137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIBULL C., HAMMARBERG K. Catalase activity of Proteus L forms and normal Proteus bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1963 Feb;85:498–498. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.2.498-498.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



