Abstract
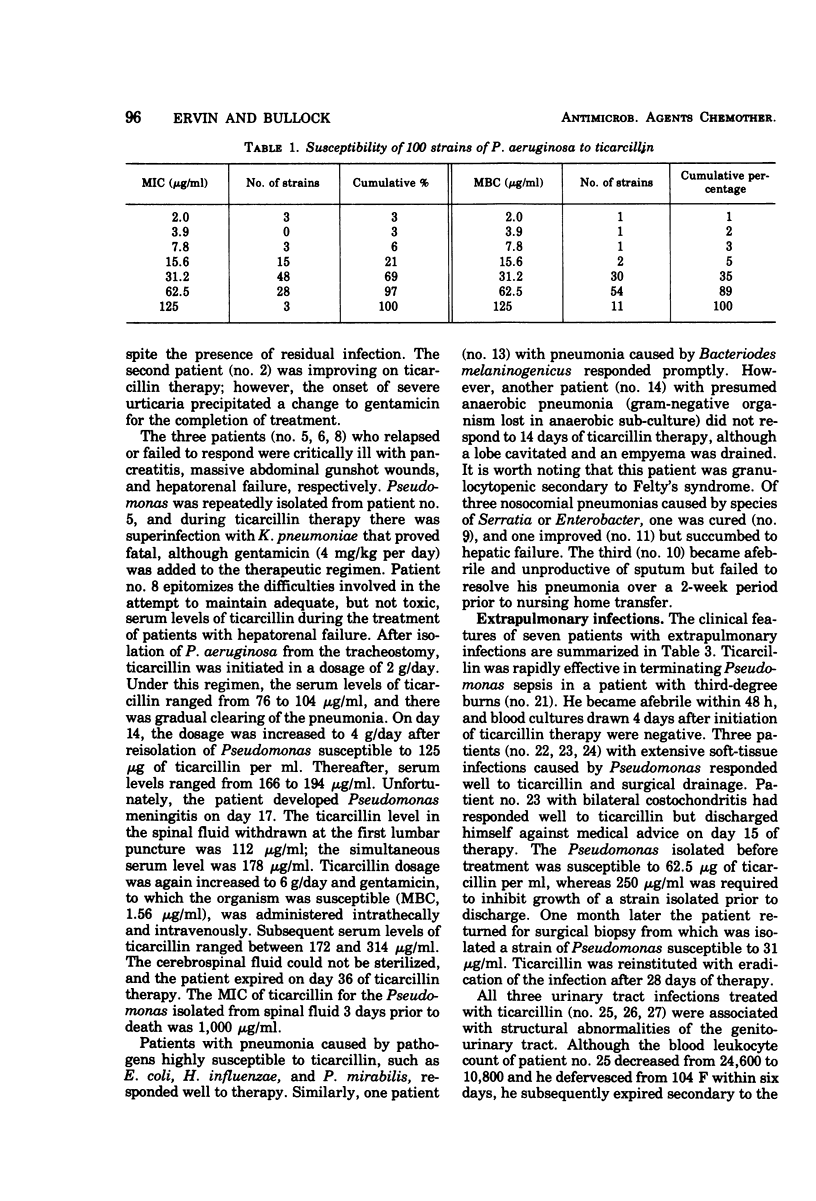
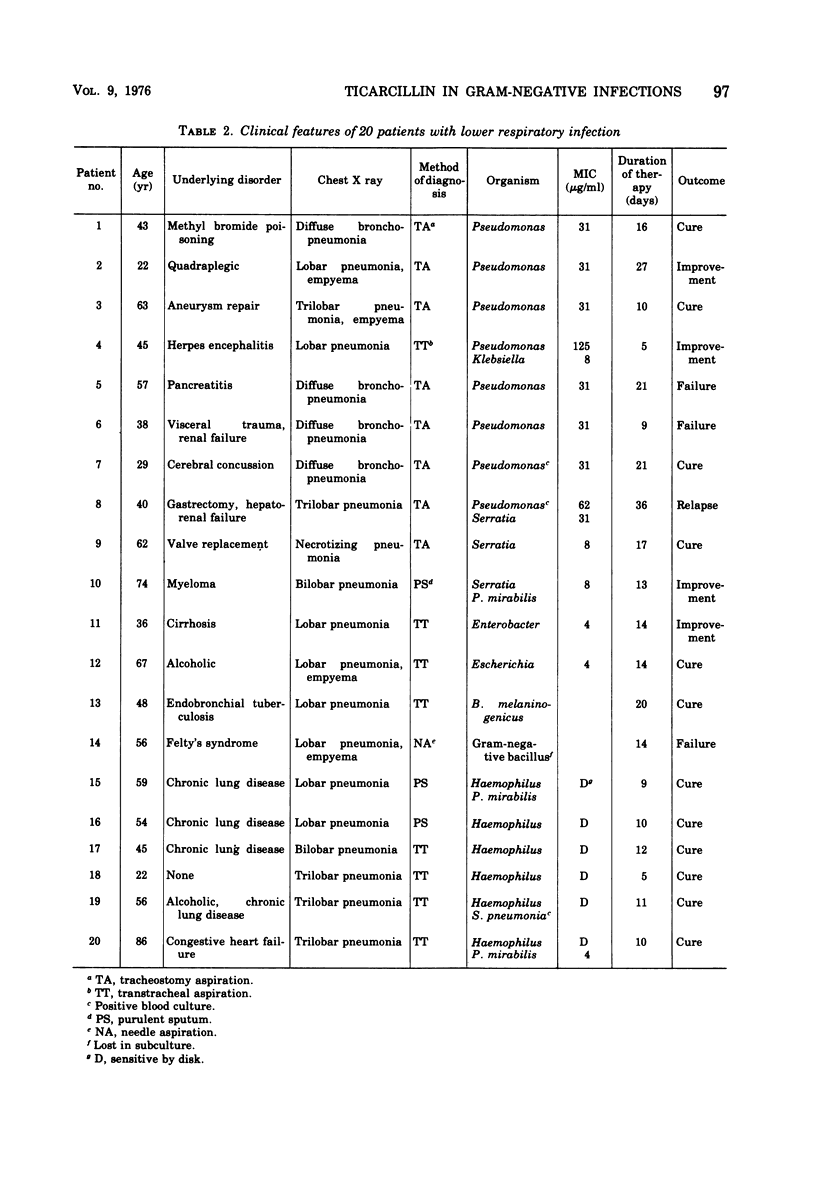
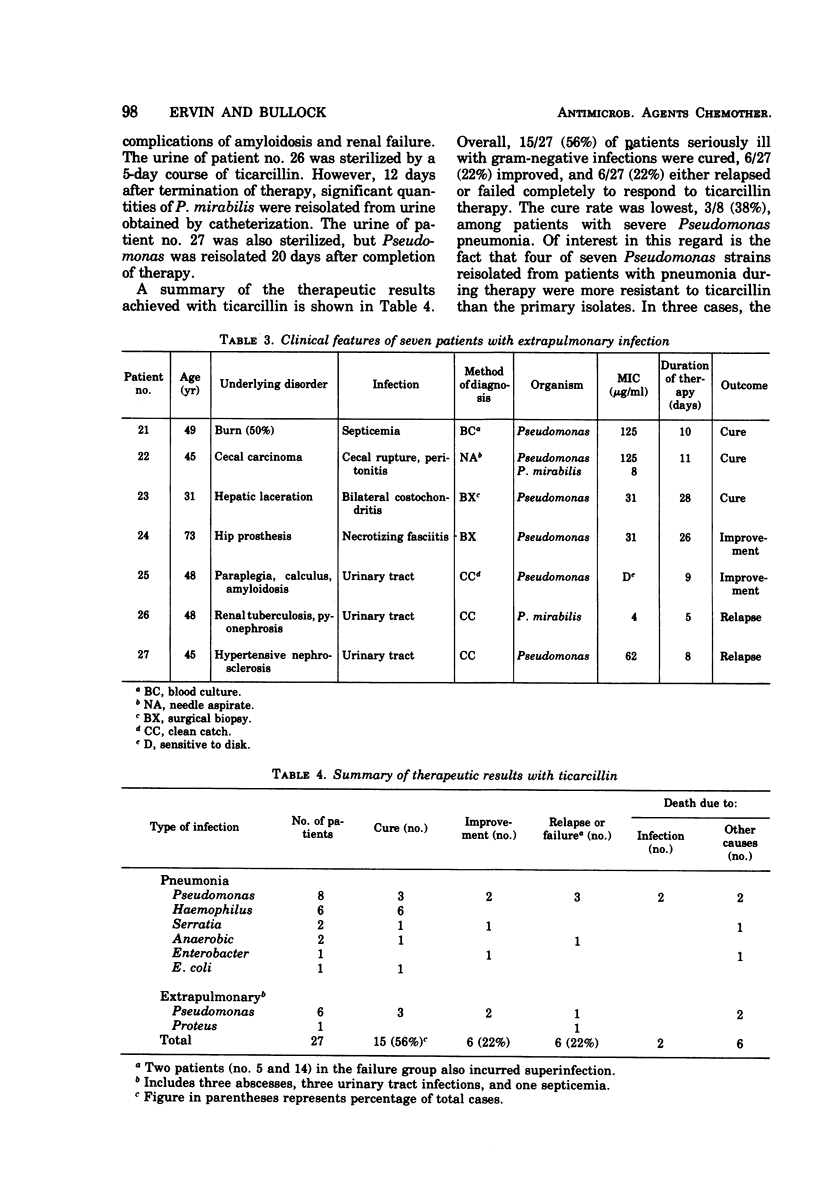
Twenty-seven patients with serious gram-negative infections were treated with ticarcillin in an average daily dosage of 237 mg/kg (range, 174 to 307 mg/kg). Ticarcillin was bactericidal for all infecting organisms in concentrations ranging from 31.2 to 125 μg/ml. Five of 8 patients (62%) with overwhelming Pseudomonas pneumonia were cured or improved, and 9 of 12 (75%) were cured of pneumonia caused by other gram-negative organisms. Of six extrapulmonary infections caused by Pseudomonas, five (83%) were cured or improved. In seven cases, the infecting organism reisolated during therapy was more resistant to ticarcillin than the primary isolate. The serum half-life of ticarcillin in three patients with renal failure was 11.2 ± 1.0 h, and during hemodialysis it decreased to 6.3 ± 1.8 h. There were two episodes of superinfection with resistant organisms. Thirteen patients (48%) manifested eosinophilia, one of whom had severe urticaria. Prolongation of bleeding time was attributable to ticarcillin in two patients. Ticarcillin appears to be effective for therapy of serious gram-negative infections in dosages 30 to 50% less than those recommended for carbenicillin.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bodey G. P., Whitecar J. P., Jr, Middleman E., Rodriguez V. Carbenicillin therapy for pseudomonas infections. JAMA. 1971 Oct 4;218(1):62–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. H., 3rd, Natelson E. A., Bradshaw W., Williams T. W., Jr, Alfrey C. P., Jr The hemostatic defect produced by carbenicillin. N Engl J Med. 1974 Aug 8;291(6):265–270. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197408082910601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darrell J. H., Waterworth P. M. Carbenicillin resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa from clinical material. Br Med J. 1969 Jul 19;3(5663):141–143. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5663.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies M., Morgan J. R., Anand C. Interactions of carbenicillin and ticarcillin with gentamicin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Apr;7(4):431–434. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.4.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eknoyan G., Wacksman S. J., Glueck H. I., Will J. J. Platelet function in renal failure. N Engl J Med. 1969 Mar 27;280(13):677–681. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196903272801301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwick H. J., Weiss P., Fekety F. R., Jr Application of microtitration techniques to bacteriostatic and bactericidal antibiotic susceptibility testing. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 Sep;72(3):511–516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman T. A., Bullock W. E. Carbenicillin therapy of Pseudomonas and other gram-negative bacillary infections. Ann Intern Med. 1970 Aug;73(2):165–171. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-73-2-165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNIN C. M., FINLAND M. Demethylchlortetracycline; a new tetracycline antibiotic that yields greater and more sustained antibacterial activity. N Engl J Med. 1958 Nov 20;259(21):999–1005. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195811202592102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klastersky J., Vanderklen B., Daneau D., Mathiew M. Carbenicillin and hypokalemia. Ann Intern Med. 1973 May;78(5):774–775. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-78-5-774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowbury E. J., Lilly H. A., Kidson A., Ayliffe G. A., Jones R. J. Sensitivity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to antibiotics: emergence of strains highly resistant to carbenicillin. Lancet. 1969 Aug 30;2(7618):448–452. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90163-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynn B. Administration of carbenicillin and ticarcillin--pharmaceutical aspects. Eur J Cancer. 1973 Jun;9(6):425–433. doi: 10.1016/0014-2964(73)90107-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mai K., Bülow B. Activity of carbenicillin and ticarcillin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa compared by paired in vitro tests. Infection. 1974;2(1):12–14. doi: 10.1007/BF01642217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks M. I., Eickhoff T. C. Carbenicillin: a clinical and laboratory evaluation. Ann Intern Med. 1970 Aug;73(2):179–187. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-73-2-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mielke C. H., Jr, Kaneshiro M. M., Maher I. A., Weiner J. M., Rapaport S. I. The standardized normal Ivy bleeding time and its prolongation by aspirin. Blood. 1969 Aug;34(2):204–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennington J. E., Reynolds H. Y., Carbone P. P. Pseudomonas pneumonia. A retrospective study of 36 cases. Am J Med. 1973 Aug;55(2):155–160. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(73)90163-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riff L. J., Jackson G. G. Laboratory and clinical conditions for gentamicin inactivation by carbenicillin. Arch Intern Med. 1972 Dec;130(6):887–891. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez V., Bodey G. P., Horikoshi N., Inagaki J., McCredie K. B. Ticarcillin therapy of infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Oct;4(4):427–431. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.4.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whelton A., Carter G. G., Garth M. A., Darwish M. O., Walker W. G. Carbenicillin-induced acidosis and seizures. JAMA. 1971 Dec 27;218(13):1942–1943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R., Reeves D. S. Clinical and laboratory investigations on ticarcillin, an anti-pseudomonal antibiotic. Chemotherapy. 1974;20(1):45–51. doi: 10.1159/000221790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



