Abstract
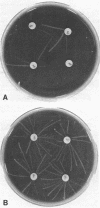
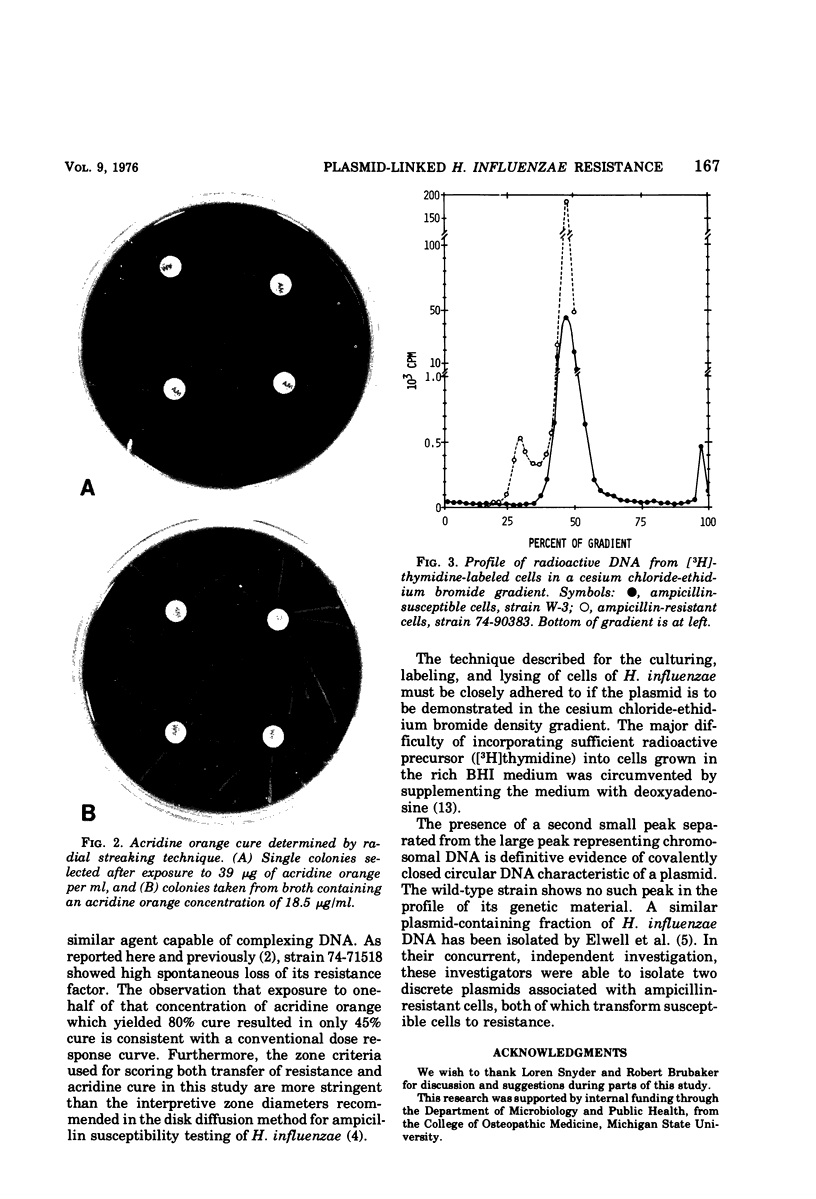
The genetic mechanisms associated with ampicillin resistance in strains of Haemophilus influenzae type b were investigated. In experiments concerned with transfer of total deoxyribonucleic acid in vitro, expression of resistance by wild-type strains occurred at a frequency of about 10%. The minimum inhibitory concentration of ampicillin for the transformed strains was similar to that of the resistant donor strains, and resistance in transformants was associated with acquisition of the ability to produce beta-lactamase. Exposure to 39 μg of acridine per ml for 18 h cured resistance at a frequency of 80%, and there was spontaneous loss of resistance after repeated subculture of some strains. Analysis by cesium chloride-ethidium bromide density gradient centrifugation demonstrated the presence of extrachromosomal deoxyribonucleic acid in the resistant strains, providing further evidence that the resistance factor is plasmid mediated.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrett F. F., Taber L. H., Morris C. R., Stephenson W. B., Clark D. J., Yow M. D. A 12 year review of the antibiotic management of Hemophilus influenzae meningitis. Comparison of ampicillin and conventional therapy including chloramphenicol. J Pediatr. 1972 Aug;81(2):370–377. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(72)80316-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catlin B. W. Iodometric detection of Haemophilus influenzae beta-lactamase: rapid presumptive test for ampicillin resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Mar;7(3):265–270. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.3.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elwell L. P., De Graaff J., Seibert D., Falkow S. Plasmid-linked ampicillin resistance in haempohilus influenza type b. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):404–410. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.404-410.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar W. E., Jr, O'Dell N. M. Beta-lactamase activity in ampicillin-resistant Haemophilus influenzae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Nov;6(5):625–629. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.5.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunn B. A., Woodall J. B., Jones J. F., Thornsberry C. Letter: Ampicillin-resistant haemophilus influenzae. Lancet. 1974 Oct 5;2(7884):845–845. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91113-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haltalin K. C., Smith J. B. Reevaluation of ampicillin therapy for Hemophilus influenzae meningitis. An appraisal based on a review of cases of persistent or recurrent infection. Am J Dis Child. 1971 Oct;122(4):328–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotchkiss R. D., Gabor M. Bacterial transformation, with special reference to recombination process. Annu Rev Genet. 1970;4:193–224. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.04.120170.001205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juni E., Janik A. Transformation of Acinetobacter calco-aceticus (Bacterium anitratum). J Bacteriol. 1969 Apr;98(1):281–288. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.1.281-288.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz S. L. Ampicillin-resistant Hemophilus influenzae type b: a status report. Pediatrics. 1975 Jan;55(1):6–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan W., Ross S., Rodriguez W., Controni G., Saz A. K. Haemophilus influenzae type B resistant to ampicillin. A report of two cases. JAMA. 1974 Jul 15;229(3):298–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett P. S. Plasmid in Bacillus pumilus and the enhanced sporulation of plasmid-negative variants. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jul;115(1):291–298. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.1.291-298.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medeiros A. A., O'Brien T. F. Ampicillin-resistant Haemophilus influenzae type B possessing a TEM-type beta-lactamase but little permeability barrier to ampicillin. Lancet. 1975 Mar 29;1(7909):716–719. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91630-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson J. D. Editorial: Should ampicillin be abandoned for treatment of Haemophilus influenzae disease? JAMA. 1974 Jul 15;229(3):322–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond M. H., Sykes R. B. The beta-lactamases of gram-negative bacteria and their possible physiological role. Adv Microb Physiol. 1973;9:31–88. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60376-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorne G. M., Farrar W. E., Jr Transfer of ampicillin resistance between strains of Haemophilus influenzae type B. J Infect Dis. 1975 Sep;132(3):276–281. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.3.276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornsberry C., Kirven L. A. Ampicillin resistance in Haemophilus influenzae as determined by a rapid test for beta-lactamase production. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Nov;6(5):653–654. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.5.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]