Abstract
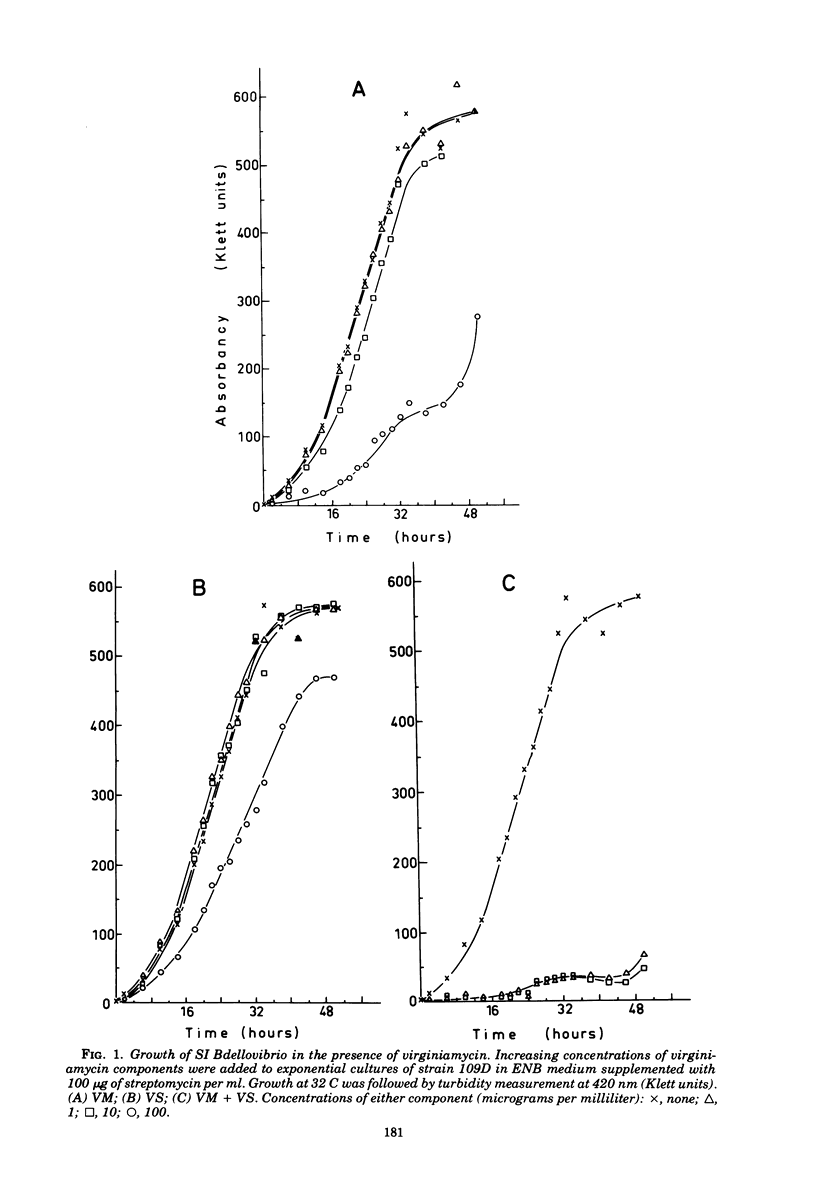
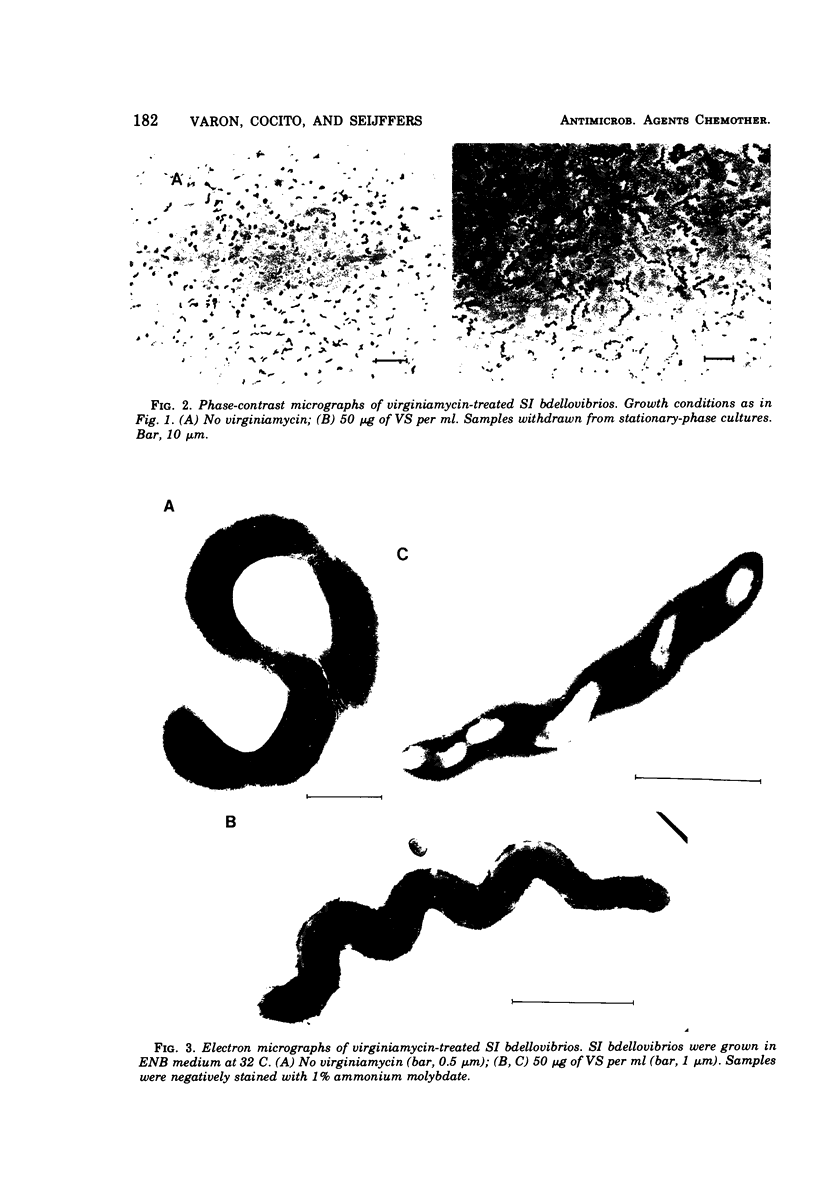
The two components of virginiamycin, virginiamycin M (VM) and virginiamycin S (VS), were used to explore the life cycle of symbiosis-dependent and -independent strains of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus during multiplication in a two-membered system with either living or heat-inactivated Escherichia coli or in axenic cultures. Relatively high concentrations of these inhibitors separately were required to stop growth under all the conditions, but the minimum inhibitory concentration of the single components was reduced 1,000-fold by the association of VM and VS. No dissociation between mass growth and cell division was observed with VM; VS specifically halted cell division without affecting the kinetics of macromolecules formation and overall growth. This effect on cell division was only obtained when the antibiotic was added during the first half of the multiplication cycle and was reversible at any time.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burnham J. C., Hashimoto T., Conti S. F. Ultrastructure and cell division of a facultatively parasitic strain of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. J Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;101(3):997–1004. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.3.997-1004.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocito C. Formation and decay of polyribosomes and ribosomes during the inhibition of protein synthesis and recovery. Biochimie. 1971;53(9):987–1000. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(71)80067-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocito C. Formation of ribosomal particles in virginiamycin sensitive and resistant mutants of Bacillus subtilis. Biochimie. 1973;55(2):153–161. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(73)80387-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocito C., Fraselle G. The properties of virginiamycin-resistant mutants of Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 May;76(1):115–125. doi: 10.1099/00221287-76-1-115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocito C., Kaji A. Virginiamycin M, a specific inhibitor of the acceptor site of ribosomes. Biochimie. 1971;53(6):763–770. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(71)80117-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocito C. Metabolism of macromolecules in bacteria treated with virginiamycin. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Aug;57(2):179–194. doi: 10.1099/00221287-57-2-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocito C., Shilo M. Macromolecule metabolism and photosynthetic functions in blue-green algae treated with virginiamycin, an inhibitor of protein synthesis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Aug;6(2):136–143. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.2.136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocito C., Voorma H. O., Bosch L. Interference of virginiamycin M with the initiation and the elongation of peptide chains in cell-free systems. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Mar 27;340(3):285–298. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(74)90274-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grover N. B., Naaman J., Ben-Sasson S., Doljanski F. Electrical sizing of particles in suspensions. 3. Rigid spheroids and red blood cells. Biophys J. 1972 Sep;12(9):1099–1117. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(72)86147-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz A. T., Kessel M., Shilo M. Growth cycle of predacious Bdellovibrios in a host-free extract system and some properties of the host extract. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jan;117(1):270–282. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.1.270-282.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingram L. O., Fisher W. D. Novel mutant impaired in cell division: evidence for a positive regulating factor. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):999–1005. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.999-1005.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. C., Donachie W. D. Chromosome replication, transcription and control of cell division in Escherichia coli. Nat New Biol. 1973 May 23;243(125):100–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai K., Tamura G. Mutant of Escherichia coli with thermosensitive protein in the process of cellular division. J Bacteriol. 1972 Nov;112(2):959–966. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.2.959-966.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeve J. N., Clark D. J. Cell division of Escherichia coli BUG-6: effect of varying the length of growth at the nonpermissive temperature. J Bacteriol. 1972 Apr;110(1):117–121. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.1.117-121.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenberg S. C. Nonidentity of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus strains 109D and 109J. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jan;109(1):432–433. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.1.432-433.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. S., Pardee A. B. Accumulation of a protein required for division during the cell cycle of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;101(3):901–909. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.3.901-909.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr M. P. Bdellovibrio as symbiont; the associations of Bdellovibrios with other bacteria interpreted in terms of a generalized scheme for classifying organismic associations. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1975;(29):93–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Pel B., Bronchart R., Kebers F., Cocito C. Structure and function of cytoplasmic organelles in transiently and permanently bleached Euglena. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Mar 30;78(1):103–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90043-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Pel B., Cocito C. Formation of chloroplast ribosomes and ribosomal RNA in Euglena incubated with protein inhibitors. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Mar 30;78(1):111–117. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90044-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varon M., Shilo M. Interaction of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus and host bacteria. II. Intracellular growth and development of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus in liquid cultures. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jul;99(1):136–141. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.1.136-141.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zusman D. R., Inouye M., Pardee A. B. Cell division in Escherichia coli: evidence for regulation of septation by effector molecules. J Mol Biol. 1972 Aug 14;69(1):119–136. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90027-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]