Abstract
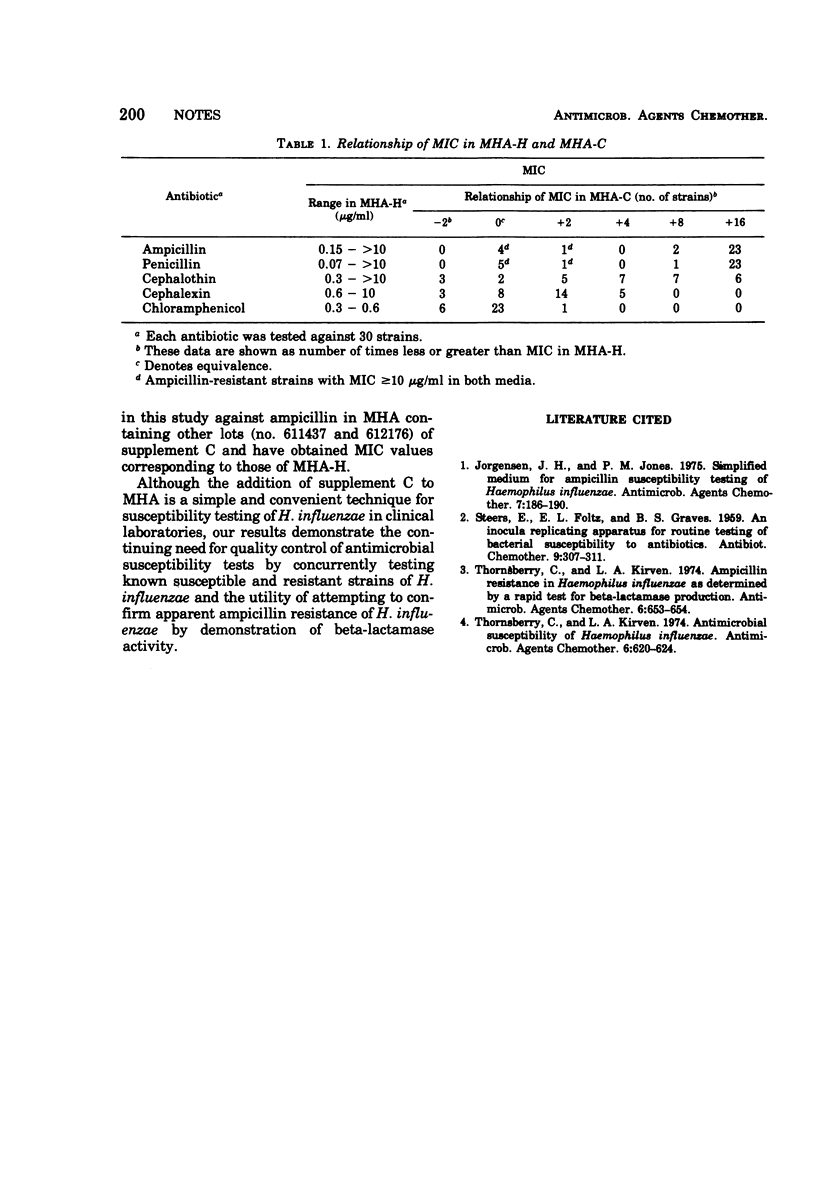
Ampicillin resistance (minimal inhibitory concentration ≥10 μg/ml) in the absence of beta-lactamase activity by Haemophilus influenzae was noted in tests performed with Mueller-Hinton agar containing one lot of supplement C. All strains, except five with known resistance due to beta-lactamase activity, were inhibited by 0.6 μg or less of ampicillin per ml of chocolatized blood agar.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Jorgensen J. H., Jones P. M. Simplified medium for ampicillin susceptibility testing of Haemophilus influenzae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Feb;7(2):186–190. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.2.186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornsberry C., Kirven L. A. Ampicillin resistance in Haemophilus influenzae as determined by a rapid test for beta-lactamase production. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Nov;6(5):653–654. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.5.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornsberry C., Kirven L. A. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Haemophilus influenzae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Nov;6(5):620–624. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.5.620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



