Abstract
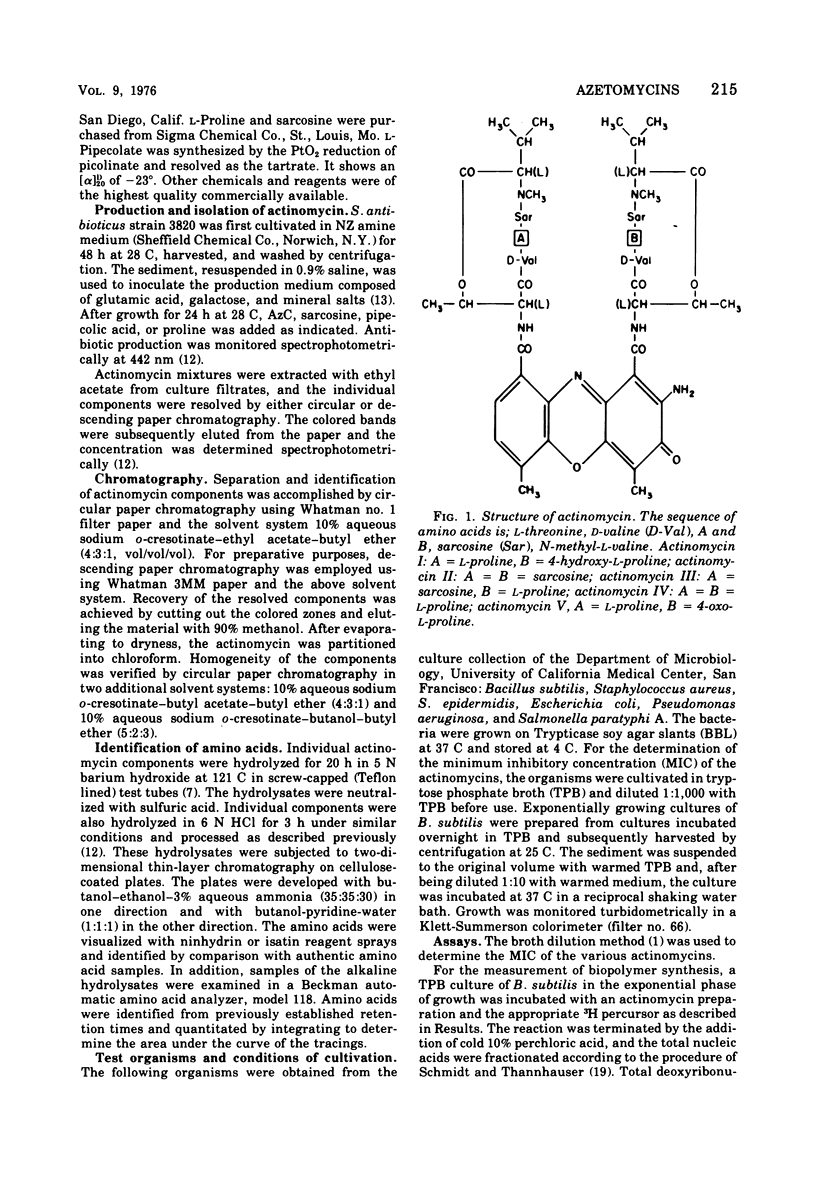
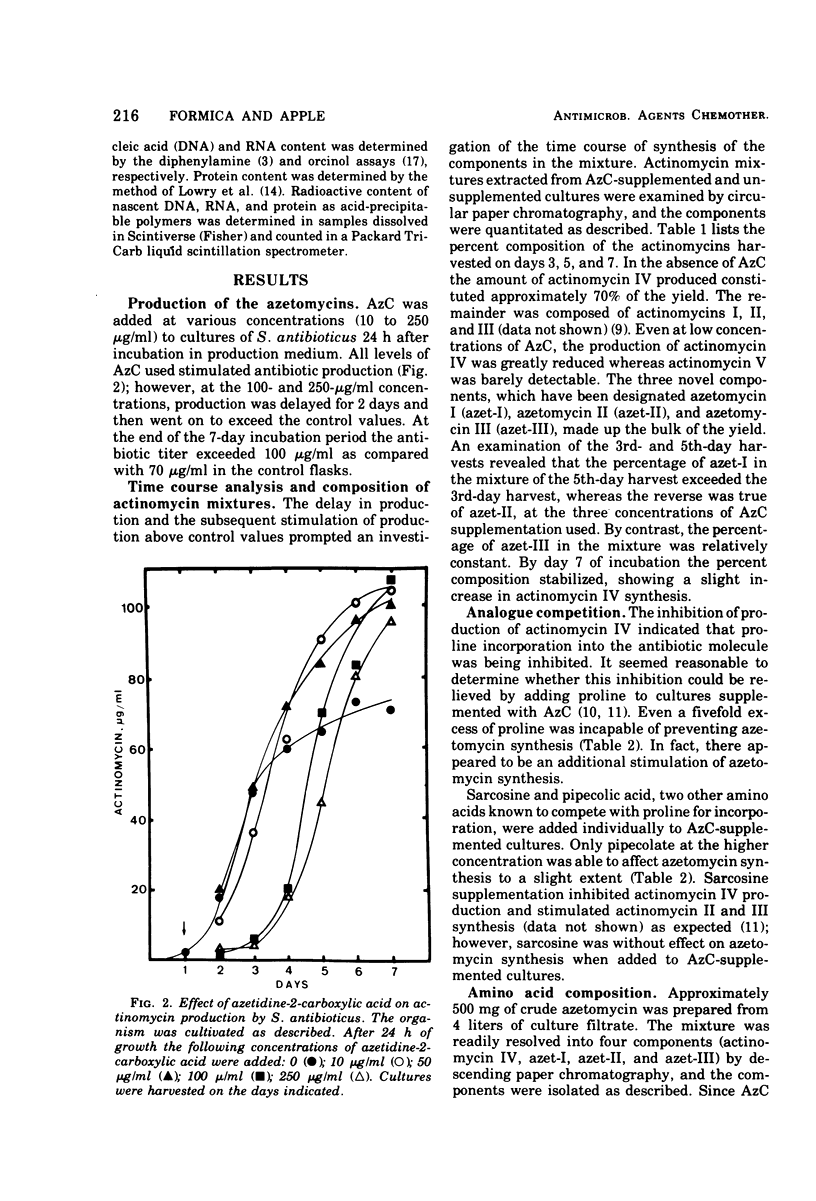
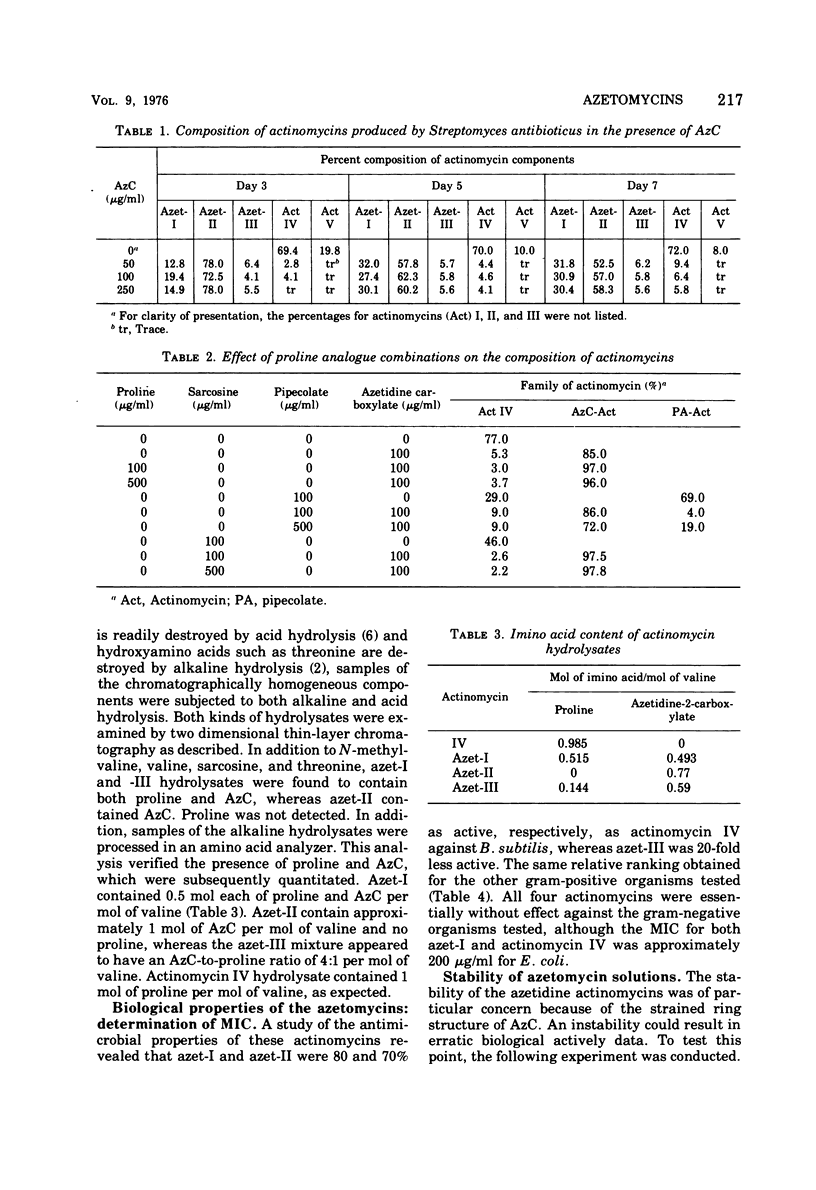
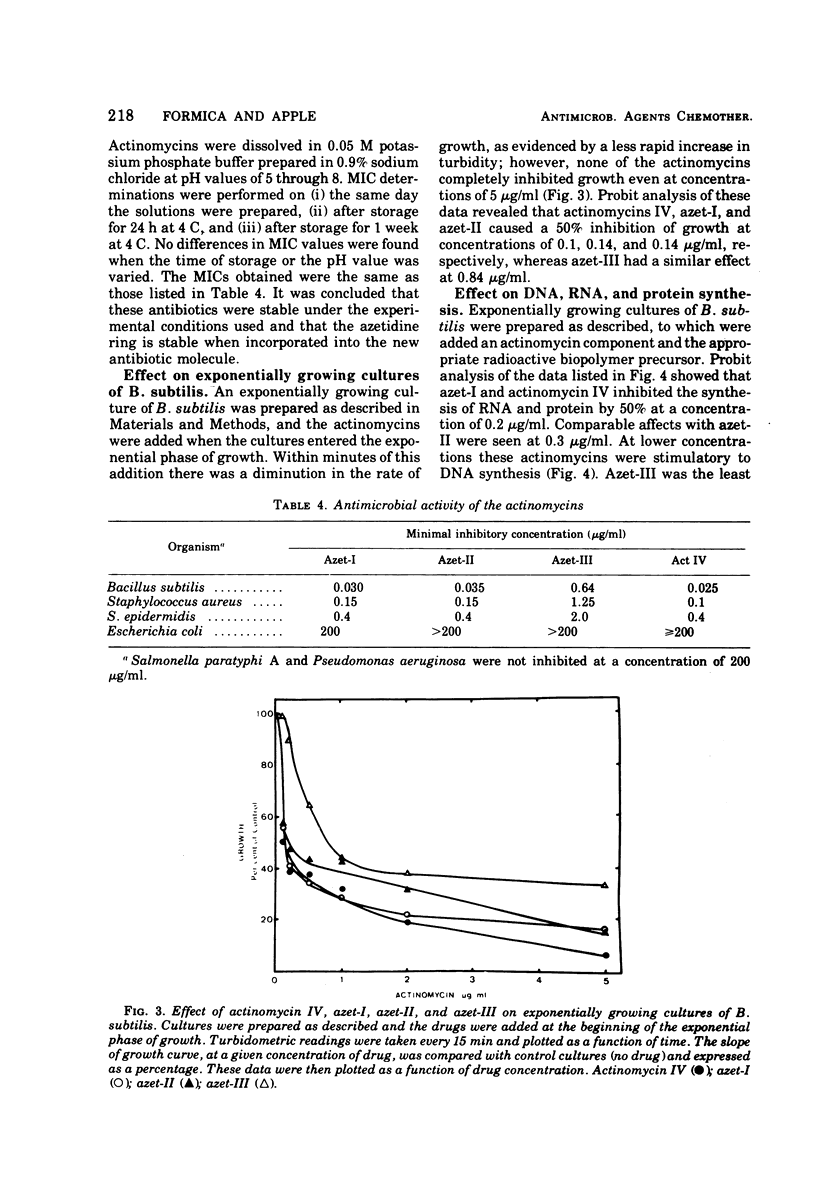
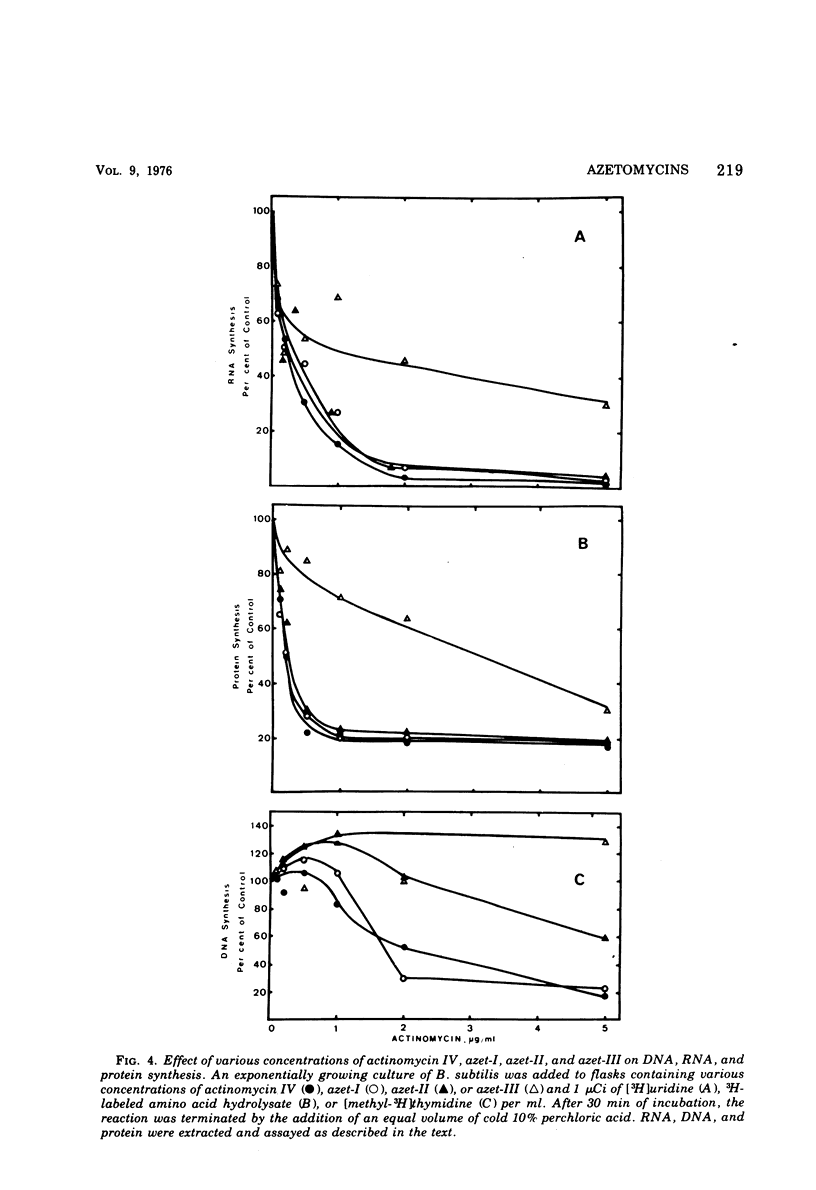
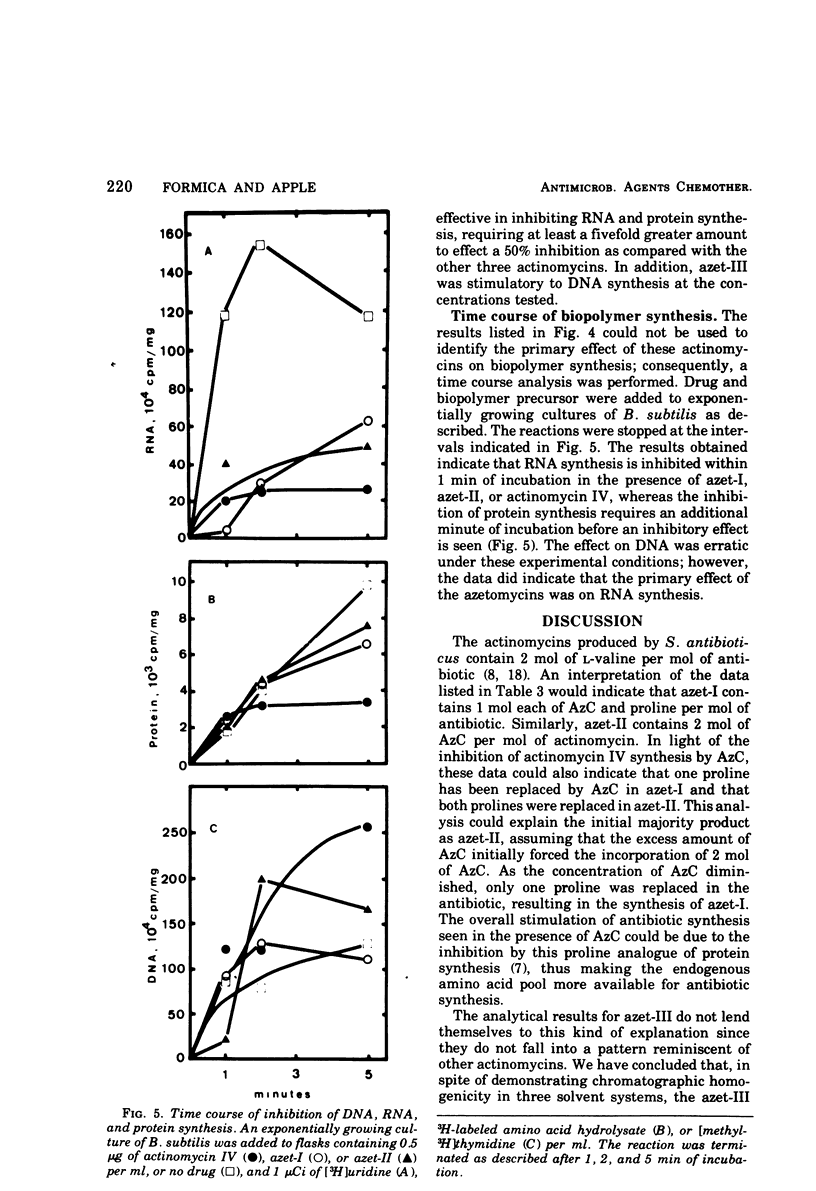
Streptomyces antibioticus synthesizes five actinomycins that differ in the “proline site” of the molecule. When cultured in the presence of azetidine-2-carboxylic acid (AzC), antibiotic synthesis was stimulated 40 to 50%, synthesis of actinomycin IV was inhibited, and one or both prolines were replaced by AzC. AzC incorporation could not be reversed by concomitant supplementation with proline or sarcosine, and only pipecolic acid affected a minor reversal of AzC incorporation. AzC-containing actinomycins were isolated and designated azet-I and azet-II; a third unresolved component or mixture was called azet-III. The molar ratio of AzC to proline was: azet-I, 1:1; azet-II, 2:0. Azet-III was equivocal. These azetidine actinomycins (azetomycins) were found to be potently inhibitory to the growth of selected gram-positive but not as potent to the growth of gram-negative organisms. The relative inhibitory affect against growth and ribonucleic acid synthesis in Bacillus subtilis was: actinomycin IV ⋝ azet-I > azet-II >>> azet-III. Protein synthesis was affected similarly; however, kinetic studies with B. subtilis revealed that ribonucleic acid synthesis was inhibited rapidly followed by an inhibition of protein synthesis. At concentrations less than 1 μg/ml, deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis was stimulated by these actinomycins.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOWDEN L. Azetidine-2-carboxylic acid: a new cyclic imino acid occurring in plants. Biochem J. 1956 Oct;64(2):323–332. doi: 10.1042/bj0640323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Formica J. V., Katz E. Isolation, purification, and characterization of pipecolic acid-containing actinomycins, Pip 2, Pip 1 , and Pip 1 . J Biol Chem. 1973 Mar 25;248(6):2066–2071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Formica J. V., Shatkin A. J., Katz E. Actinomycin analogues containing pipecolic acid: relationship of structure to biological activity. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2139–2150. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2139-2150.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON A. W., MAUGER A. B. The isolation and structure of actinomycins II and III. Biochem J. 1959 Nov;73:535–538. doi: 10.1042/bj0730535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ E. Biogenesis of the actinomycins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Oct 5;89:304–322. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb20154.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ E., GOSS W. A. Controlled biosynthesis of actinomycin with sarcosine. Biochem J. 1959 Nov;73:458–465. doi: 10.1042/bj0730458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ E., GOSS W. A. Influence of amino-acids of actinomycin biosynthesis. Nature. 1958 Dec 13;182(4650):1668–1669. doi: 10.1038/1821668b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ E., WEISSBACH H. Incorporation of C14-labeled amino acids into actinomycin and protein by Streptomyces antibioticus. J Biol Chem. 1963 Feb;238:666–675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meienhofer J., Atherton E. Structure-activity relationships in the actinomycins. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1973;16:203–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W., Crothers D. M. Studies of the binding of actinomycin and related compounds to DNA. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jul 28;35(2):251–290. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(68)80024-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobell H. M. The stereochemistry of actinomycin binding to DNA. Cancer Chemother Rep. 1974 Jan-Feb;58(1):101–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



