Abstract
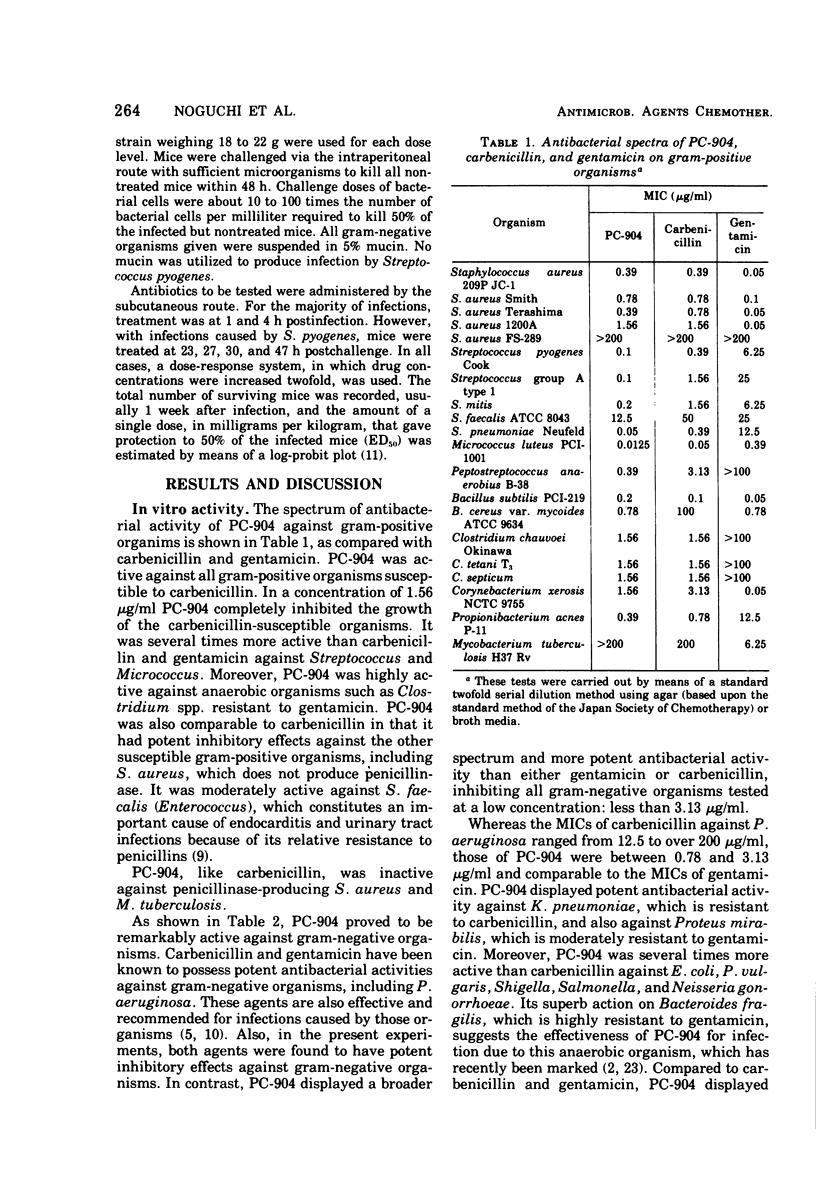
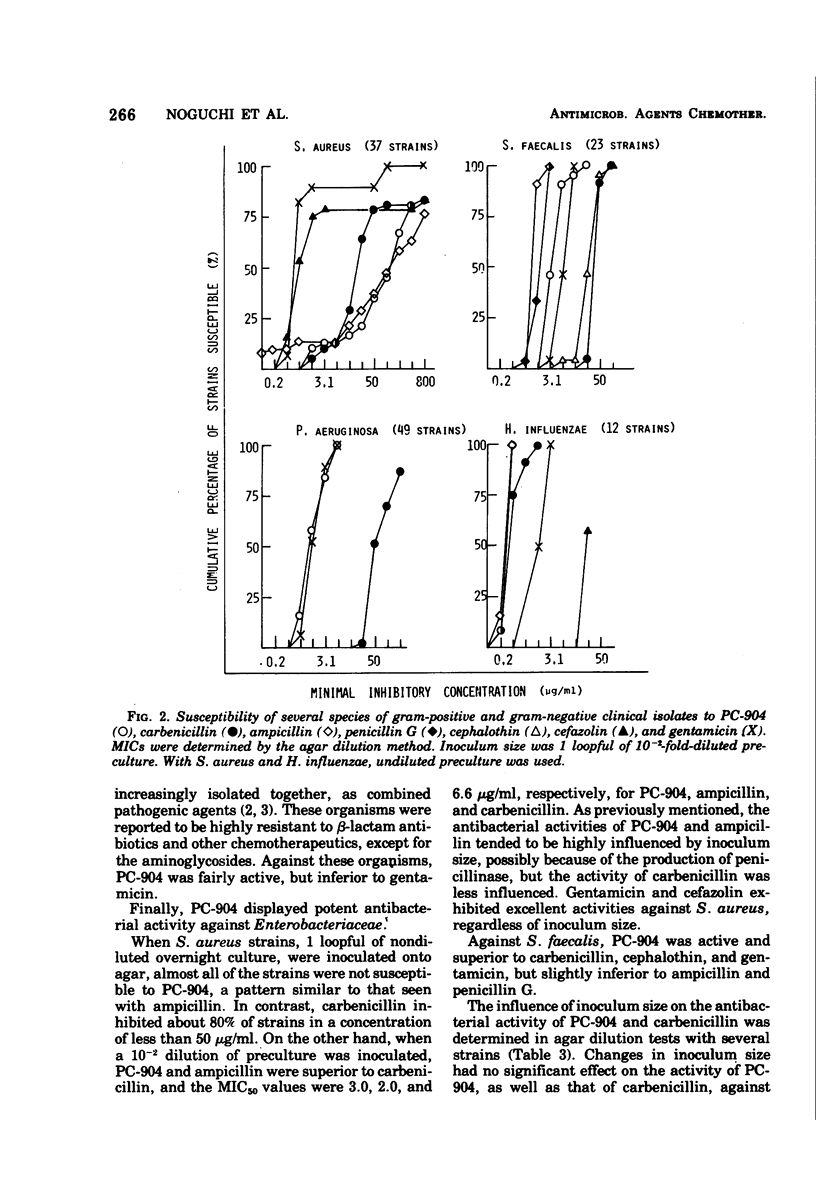
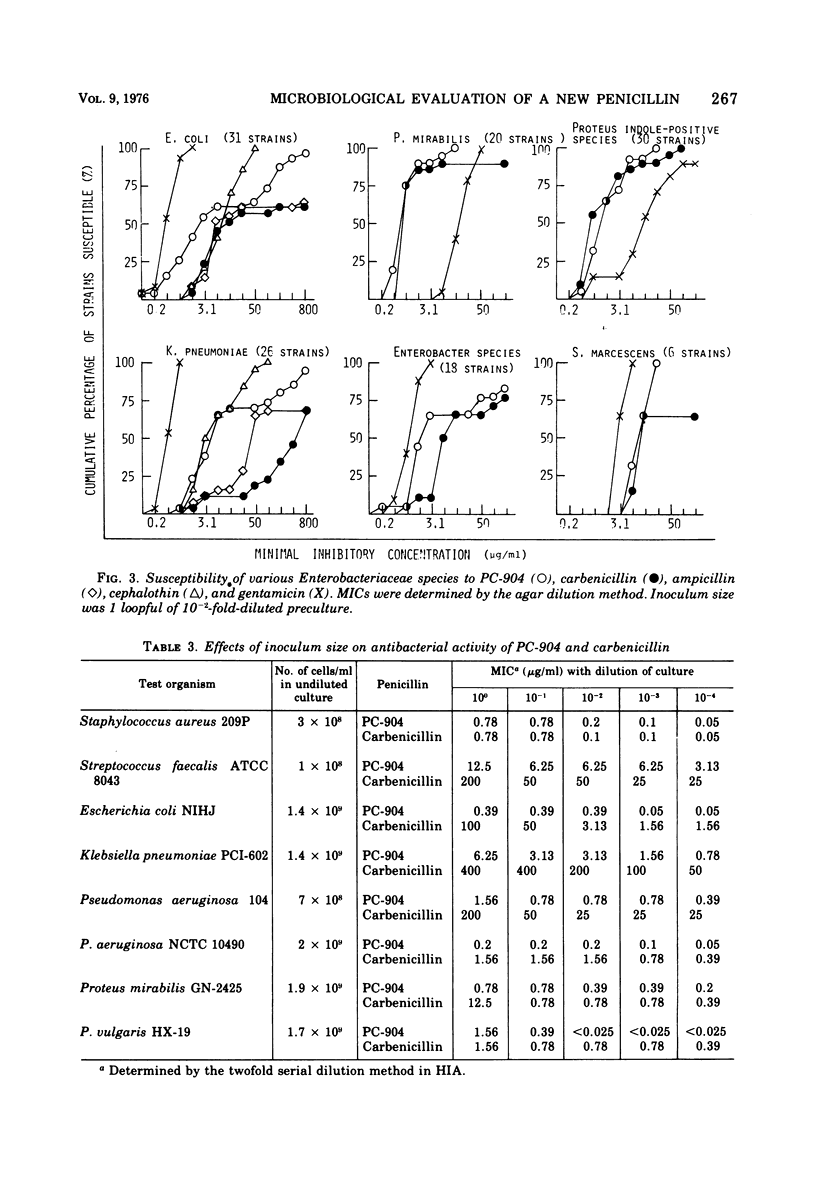
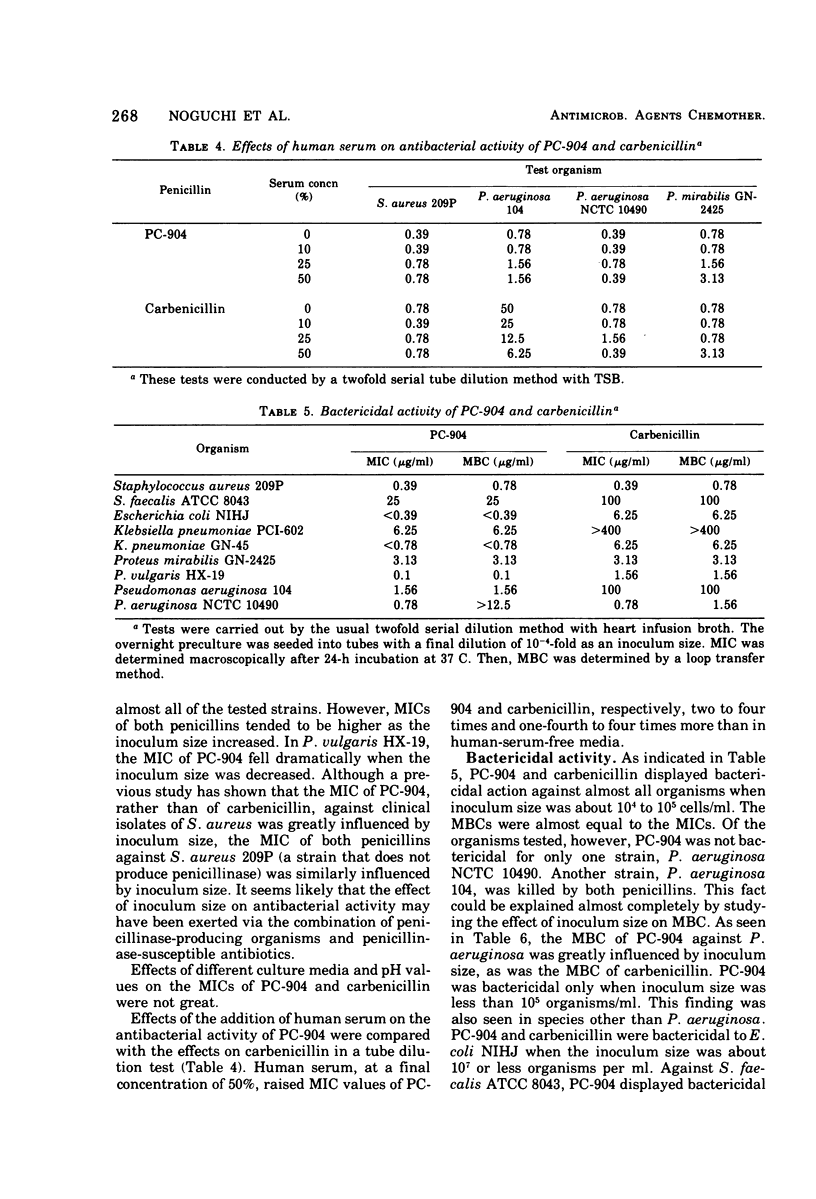
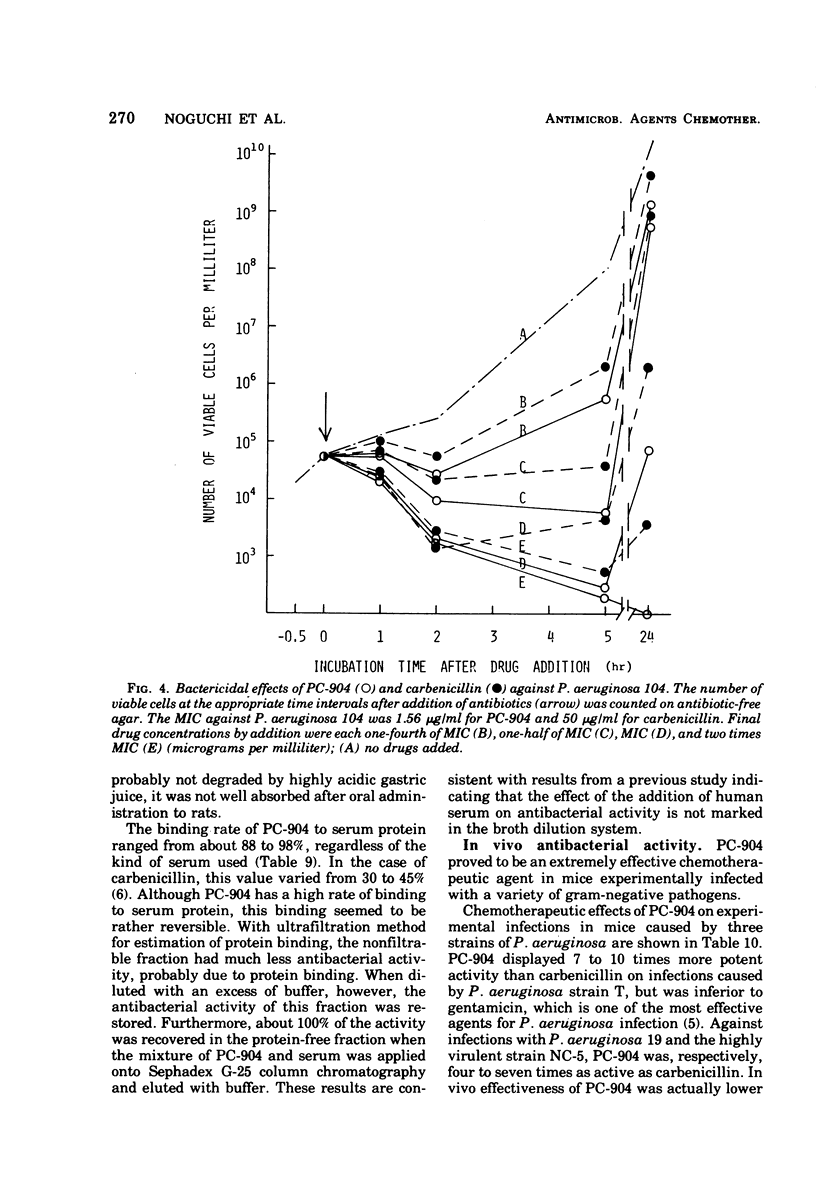
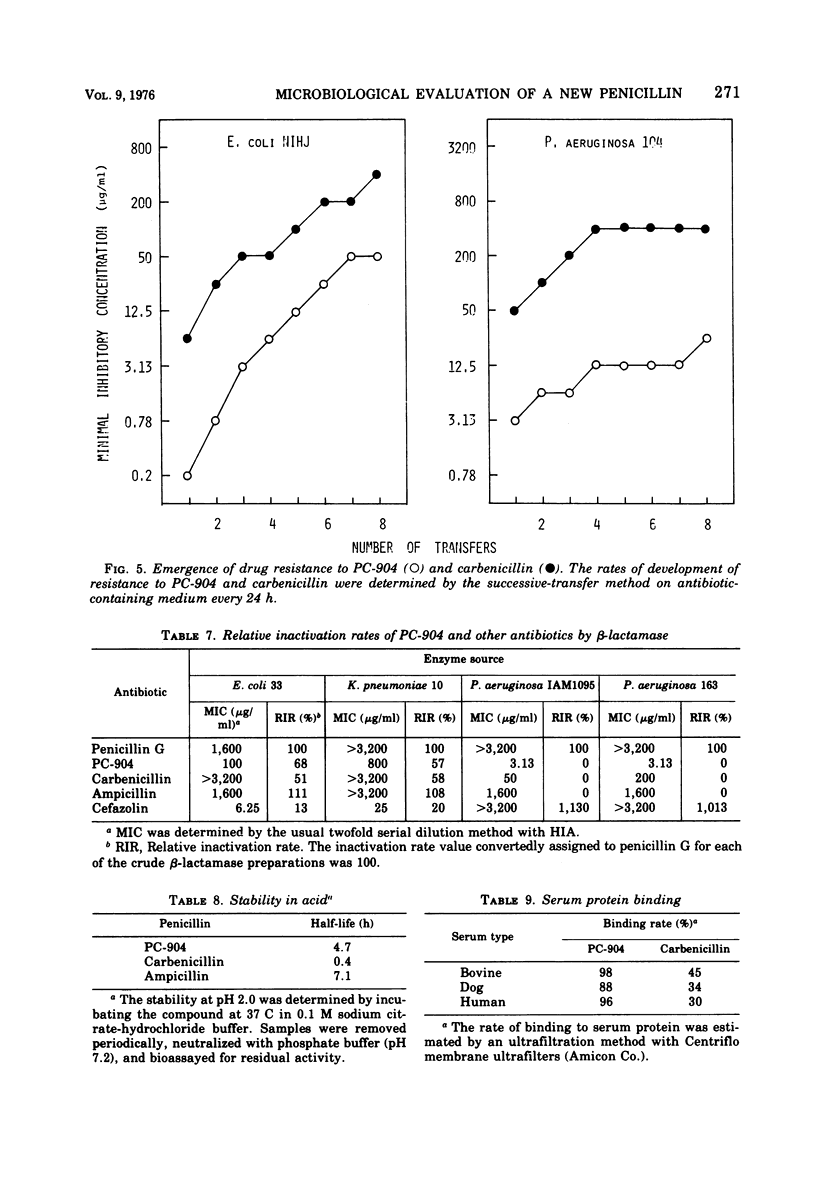
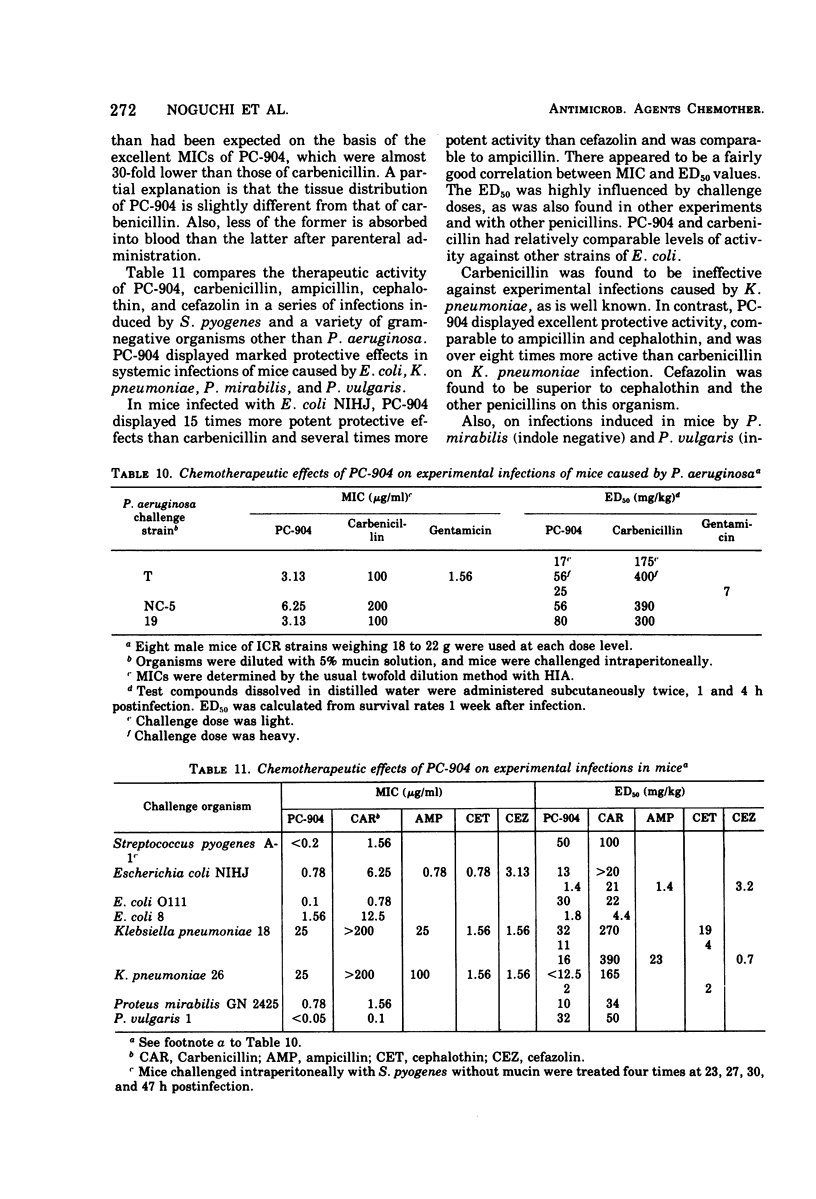
PC-904, sodium 6-{d(−)-α-(4-hydroxy-1,5-naphthyridine-3-carboxamido) phenylacetamido}-penicillanate, is a novel semisynthetic penicillin derivative that possesses a broad spectrum of in vitro and in vivo antibacterial activities. In low concentrations, PC-904 inhibits growth against large proportions of the gram-positive and gram-negative organisms susceptible to carbenicillin and gentamicin. In addition, PC-904 is several times more potent than carbenicillin against organisms such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Escherichia coli, Proteus vulgaris, Shigella, Salmonella, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, and Bacteroides fragilis. Most striking are the inhibitory effects of PC-904 against P. aeruginosa and K. pneumoniae. Against these two clinical isolates, PC-904 is, respectively, 35 and 100 times more active than carbenicillin. The minimum inhibitory concentrations of PC-904 against P. aeruginosa are comparable to those of gentamicin. PC-904 acts bactericidally. The effect of inoculum size on the antibacterial activity is often small and generally comparable to carbenicillin. The rate of binding to serum protein is high (88 to 98%), but the effect of the addition of serum on the drug's activity is not marked, because such binding is reversible. It is confirmed that PC-904 has a very potent in vivo antibacterial activity against gram-negative and gram-positive organisms. Against systemic infections with P. aeruginosa, K. pneumoniae, and E. coli in mice, PC-904 is 7 to 10 times, over 8 times, and 2 to 15 times more active than carbenicillin, respectively.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acred P., Brown D. M., Knudsen E. T., Rolinson G. N., Sutherland R. New semi-synthetic penicillin active against Pseudomonas pyocyanea. Nature. 1967 Jul 1;215(5096):25–30. doi: 10.1038/215025a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altemeier W. A., Hummel R. P., Hill E. O., Lewis S. Changing patterns in surgical infections. Ann Surg. 1973 Oct;178(4):436–445. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197310000-00006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodey G. P., Rodriguez V., Smith J. P. Serratia sp. infections in cancer patients. Cancer. 1970 Jan;25(1):199–205. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197001)25:1<199::aid-cncr2820250128>3.0.co;2-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodey G. P., Stewart D. In vitro studies of semisynthetic alpha-(substituted-ureido) penicillins. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Apr;21(4):710–717. doi: 10.1128/am.21.4.710-717.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darrell J. H., Waterworth P. M. Dosage of gentamicin for pseudomonas infections. Br Med J. 1967 May 27;2(5551):535–537. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5551.535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferres H., Basker M. J., O'Hanlon P. J. Beta-lactam antibiotics. I. Comparative structure--activity relationships of 6-acylaminopenicillanic acid derivatives and their 6-(D-alpha-acylaminophenylacetamido) penicillanic acid analogues. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1974 Dec;27(12):922–930. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.27.922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finland M. Changing ecology of bacterial infections as related to antibacterial therapy. J Infect Dis. 1970 Nov;122(5):419–431. doi: 10.1093/infdis/122.5.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewitt W. L., Seligman S. J., Deigh R. A. Kinetics of the synergism of penicillin-streptomycin and penicillin-kanamycin for enterococci and its relationship to L-phase variants. J Lab Clin Med. 1966 May;67(5):792–807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. J., Lowbury E. J. Prophylaxis and therapy for Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection with carbenicillin and with gentamicin. Br Med J. 1967 Jul 8;3(5557):79–82. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5557.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto S., Nomura H., Fugono T., Azuma T., Minami J. Semisynthetic -lactam antibiotics. 2. Synthesis and properties of D- and L- -sulfobenzylpenicillins. J Med Chem. 1972 Nov;15(11):1108–1111. doi: 10.1021/jm00281a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price K. E., Chisholm D. R., Leitner F., Misiek M., Gourevitch A. Antipseudomonal activity of alpha-sulfoaminopenicillins. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Jun;17(6):881–887. doi: 10.1128/am.17.6.881-887.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond M. H., Sykes R. B. The beta-lactamases of gram-negative bacteria and their possible physiological role. Adv Microb Physiol. 1973;9:31–88. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60376-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez V., Inagaki J., Bodey G. P. Clinical pharmacology of ticarcillin (alpha-carboxyl-3-thienylmethyl penicillin, BRL-2288). Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Jul;4(1):31–36. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suginaka H., Blumberg P. M., Strominger J. L. Multiple penicillin-binding components in Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus cereus, Staphylococcus aureus, and Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1972 Sep 10;247(17):5279–5288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson W. R., Martin W. J., Wilkowske C. J., Washington J. A., 2nd Anaerobic bacteremia. Mayo Clin Proc. 1972 Sep;47(9):639–646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



