Abstract
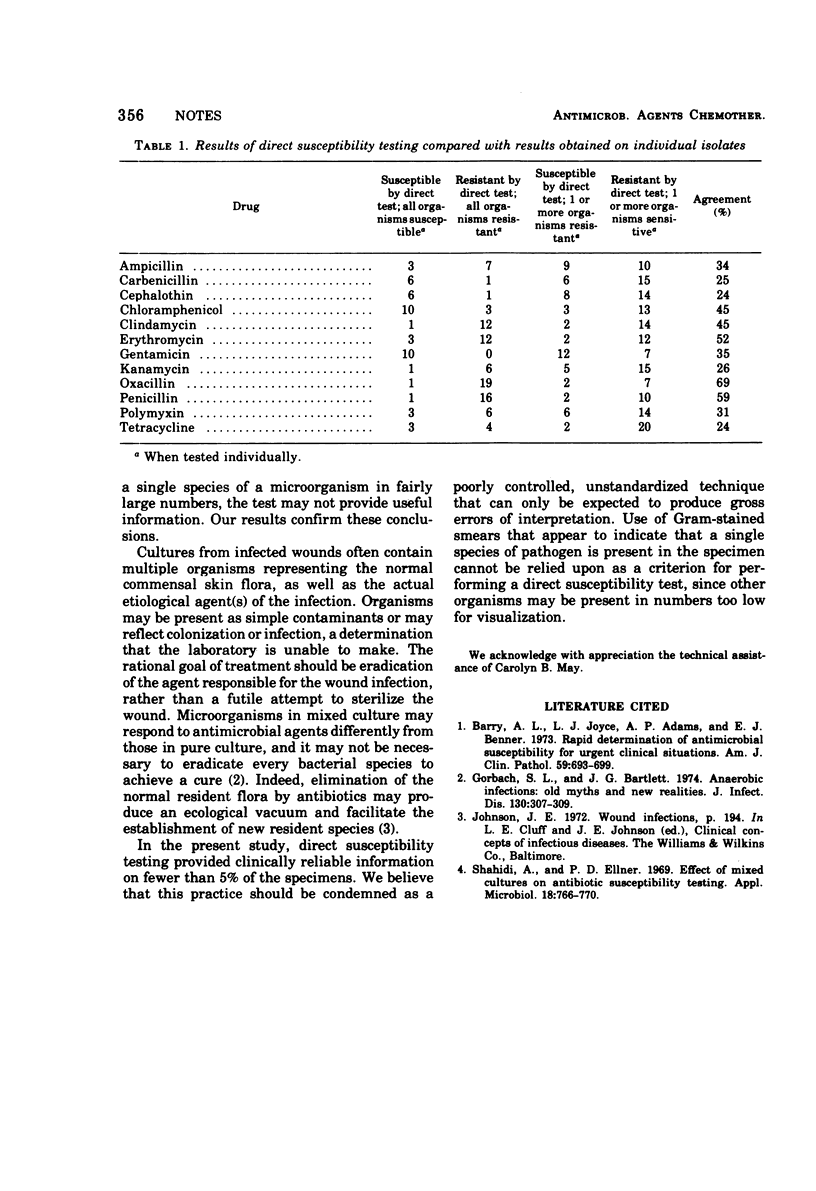
Direct susceptibility testing was performed on 110 specimens of wound exudates. Growth was inadequate in 76 of these specimens. Of the remaining 34 specimens, only 5 produced results corresponding to those obtained by testing individual bacterial isolates by the Kirby-Bauer technique. This study confirms that direct susceptibility testing of wound exudates may provide misleading and clinically unreliable information on more than 95% of specimens.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barry A. L., Joyce L. J., Adams A. P., Benner E. J. Rapid determination of antimicrobial susceptibility for urgent clinical situations. Am J Clin Pathol. 1973 May;59(5):693–699. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/59.5.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbach S. L., Bartlett J. G. Editorial: Anaerobic infections: old myths and new realities. J Infect Dis. 1974 Sep;130(3):307–310. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.3.307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shahidi A., Ellner P. D. Effect of mixed cultures on antibiotic susceptibility testing. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Nov;18(5):766–770. doi: 10.1128/am.18.5.766-770.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



