Abstract
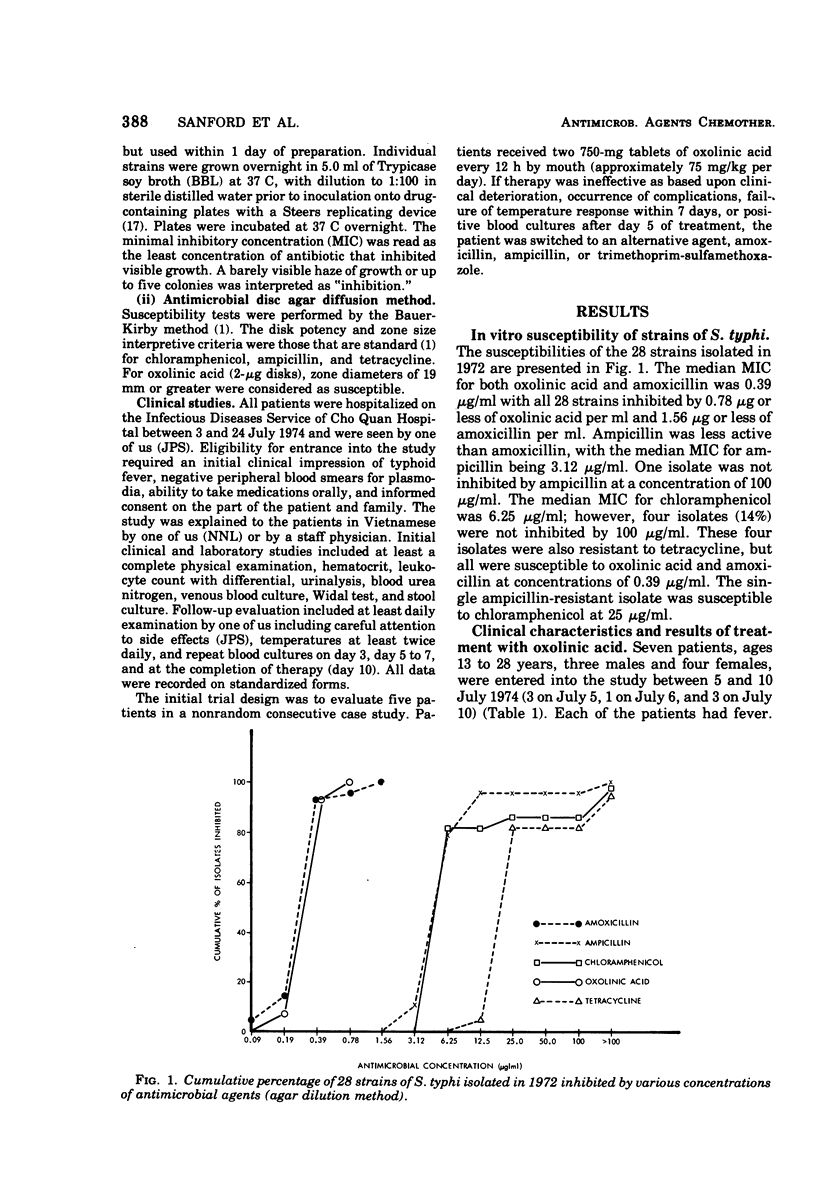
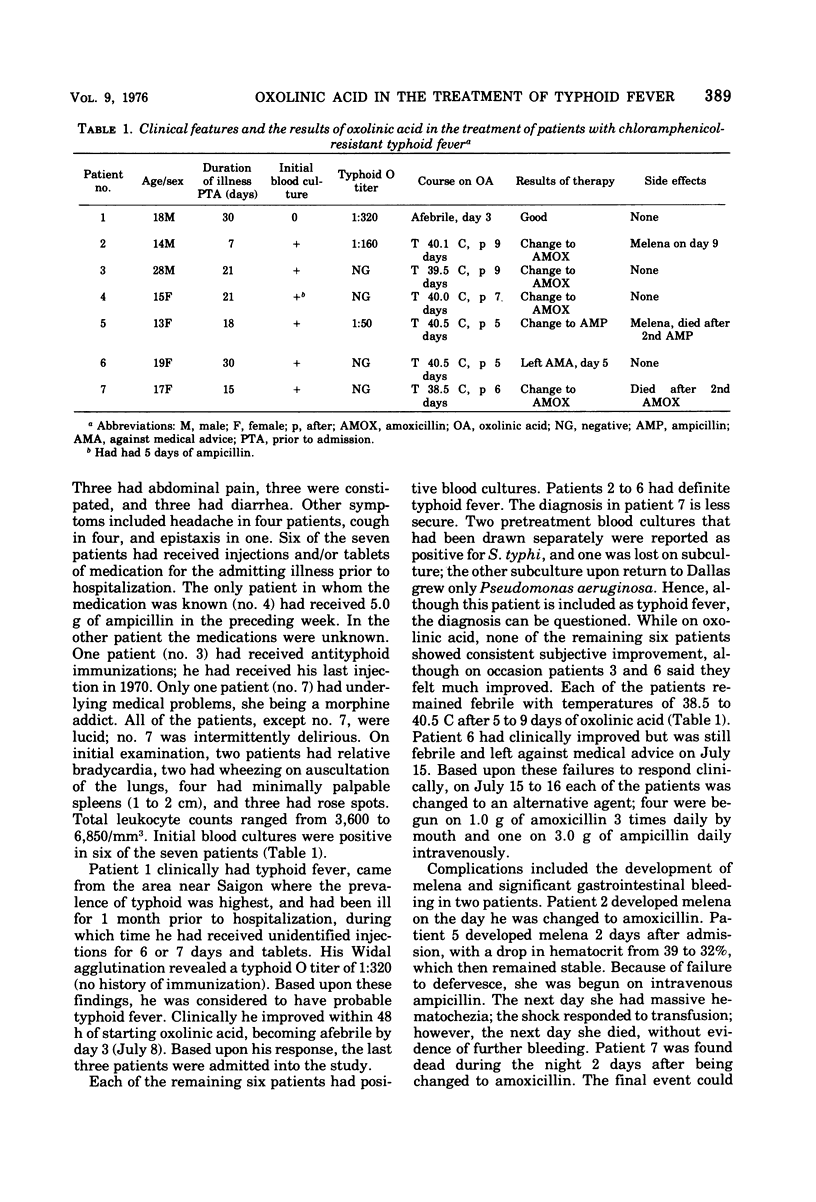
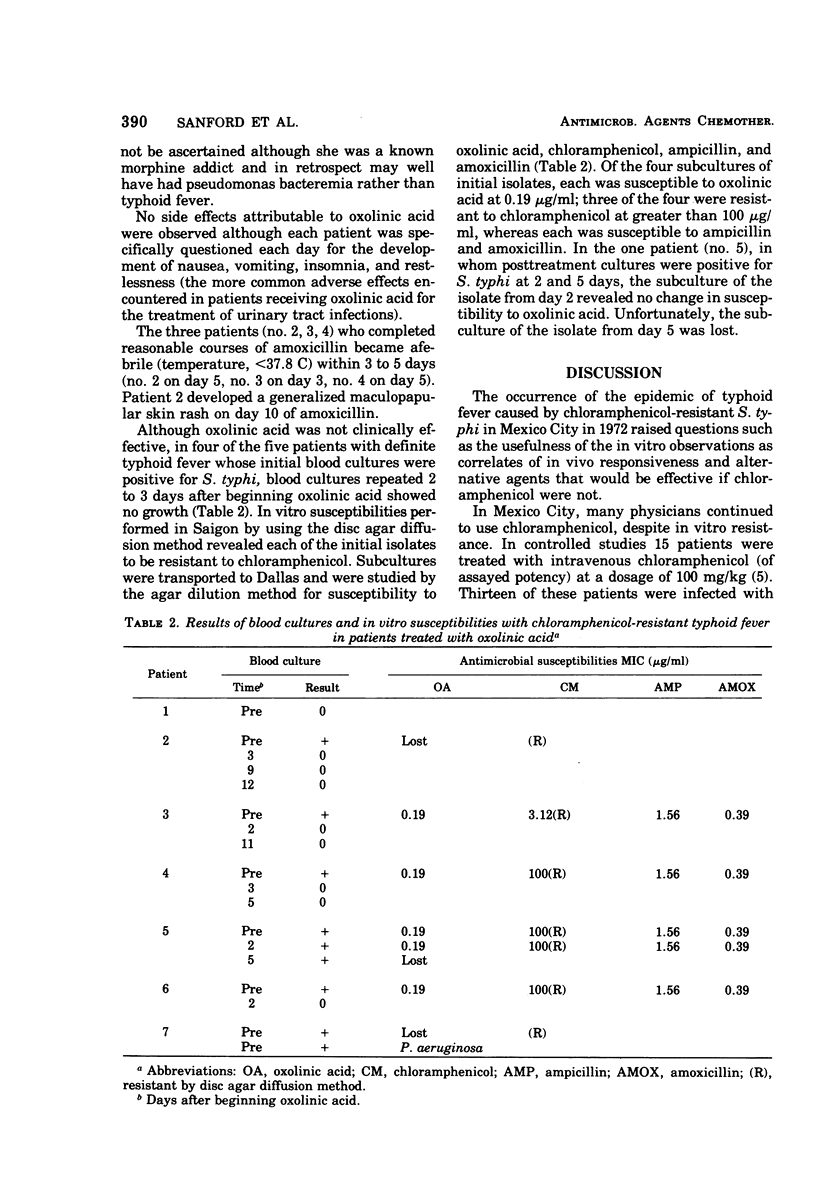
Of 28 strains of Salmonella typhosa collected in late 1972 in Vietnam, 4 had minimum inhibitory concentrations to chloramphenicol of >100 μg/ml. Median minimum inhibitory concentrations of all strains to oxolinic acid were 0.39 μg/ml; ampicillin, 6.25 μg/ml; amoxicillin, 0.39 μg/ml. Widespread typhoid fever appeared in mid-1973 with more than three-fourths of strains found to be resistant to chloramphenicol. Peak serum concentrations of oxolinic acid average 3.0 μg/ml after the oral ingestion of 1.0 g. In July 1974, a pilot study was begun to evaluate the efficacy of oxolinic acid in vivo, recognizing the discrepancy between in vitro and in vivo results with many agents evaluated in the treatment of typhoid fever. Seven patients with typhoid fever, six with positive blood cultures, were treated with oxolinic acid (1.5 g twice daily by mouth, a daily dose that averaged 75 mg/kg per day) for 5 to 12 days. In four of six patients, blood cultures became negative at 2 to 3 days, with another being negative at 6 days. Despite negative blood cultures, all but one patient remained clinically ill with temperatures of >39.5 C at 4 to 9 days. All strains were susceptible to 0.19 μg of oxolinic acid per ml, and resistant strains did not occur. One patient died after being changed to ampicillin, one left against advice, three responded to amoxicillin, and one died with pseudomonas bacteremia. Toxicity to oxolinic acid did not occur.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown J. D., Duong Hong M. o., Rhoades E. R. Chloramphenicol-resistant Salmonella typhi in Saigon. JAMA. 1975 Jan 13;231(2):162–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler T., Linh N. N., Arnold K., Pollack M. Chloramphenicol-resistant typhoid fever in Vietnam associated with R factor. Lancet. 1973 Nov 3;302(7836):983–985. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91086-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderon E. Amoxicillin in the treatment of typhoid fever due to chloramphenicol-resistance Salmonella typhi. J Infect Dis. 1974 Jun;129(0):suppl–suppl:S221. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.supplement_2.s219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderón E., Gilman R. H., Snyder M. J., Vázquez V., Barreto D. G., Legorreta J., Rodríguez R., Martínez E., Hornick R. B., Woodward T. E. A controlled clinical trial of chloramphenicol in chloramphenicol-resistant typhoid fever. Rev Latinoam Microbiol. 1974 Jul-Sep;16(3):131–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuPont H. L., Hornick R. B. Clinical approach to infectious diarrheas. Medicine (Baltimore) 1973 Jul;52(4):265–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geddes A. M., Goodall J. A. Chloramphenicol resistance in the typhoid bacillus. Br Med J. 1972 Aug 26;3(5825):525–525. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5825.525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haltalin K. C., Nelson J. D., Hinton L. V., Kusmiesz H. T., Sladoje M. Comparison of orally absorbable and nonabsorbable antibiotics in shigellosis. A double-blind study with ampicillin and neomycin. J Pediatr. 1968 May;72(5):708–720. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(68)80021-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyruey M. H., Goudineau J. A., Germain M. Fièvres typhoïdes résistantes au chloramphénicol Saigon. Nouv Presse Med. 1973 May 26;2(21):1455–1455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen Ngoc Linh Letter: Typhoid fever treated with chloramphenicol and co-trimoxazole. Lancet. 1974 Jun 15;1(7868):1222–1222. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91025-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pillay N., Adams E. B., North-Coombes D. Comparative trial of amoxycillin and chloramphenicol in treatment of typhoid fever in adults. Lancet. 1975 Aug 23;2(7930):333–334. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92776-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOODWARD T. E., SMADEL J. E. MANAGEMENT OF TYPHOID FEVER AND ITS COMPLICATIONS. Ann Intern Med. 1964 Jan;60:144–157. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-60-1-144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOODWARD T. E., SMADEL J. E., PARKER R. T., WISSEMAN C. L., Jr Treatment of typhoid fever with antibiotics. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1952 Dec 30;55(6):1043–1055. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1952.tb22663.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



