Abstract
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are the most commonly used medications for pain control in dentistry. The reported adverse effects include gastrointestinal and cardiovascular events, alterations in renal function, and effects on blood pressure, hepatic injury, and platelet inhibition which can lead to increased bleeding. This case report describes an unusual rare adverse event of the use of ibuprofen for pain control post restorative treatment. A 26-year-old, otherwise healthy Saudi male reported an unusual side effect of increased libido and erectile function post use of ibuprofen. The medical and laboratory tests have failed to identify a link between this rare adverse event and either underlying conditions or possibly related etiology. This case represented a puzzling challenge with no clear explanation.
Keywords: Erectile, ibuprofen, side effects
Introduction
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are the most commonly used medications during the dental treatment for their creditable efficacy in reducing pain and inflammation.1,2 However, the burden of their unwanted side effects is high particularly with traditional NSAIDs.1,2 This is more likely due to chronic use and reflecting the fact that NSAIDs are used extensively in the more vulnerable elderly population.1 The reported adverse effects include gastrointestinal and cardiovascular events, alterations in renal function, effects on blood pressure, hepatic injury, and platelet inhibition which can lead to increased bleeding.1
This case report describes an unusual rare adverse event of the use of ibuprofen for pain control post restorative treatment.
Case Report
A 26-year-old, otherwise healthy male has reported to the restorative clinic at Al-Farabi College, Riyadh for investigation and management of pain affecting the posterior left region of the maxilla. His history of chief complaint showed typical presentation of severe pain due to advanced buccal cervical carious lesion.
Based on clinical findings, radiographic interpretation, and vitality tests, a diagnosis of acute pulpitis of upper left first molar was made. No periapical diagnosis was identified. Routine endodontic therapy was planned. Local anesthesia using 2% lignocaine with 1:80,000 epinephrine was administered. Standard routine root canal procedure was performed under rubber dam isolation. The carious lesion was removed and replaced by composite material (Filtek™ P90, 3M). The endodontic access opening was prepared. Working length was established. In addition, cleaning and shaping were performed using crown down technique with ProTaper rotary instruments (dentsply). In addition, obturation was done with lateral compaction. A root canal completion radiograph confirmed the correct root canal therapy. A single dose of 600 mg ibuprofen was prescribed to control postendodontic pain. The patient reported to has an increased erectile function and libido after 2 h from taking the ibuprofen tablet. He has reported that has done three sexual intercourses with his wife at that day. On the next day, he was curious, and he repeated taking the ibuprofen tablet. Surprisingly, he had the same experience of his first use of ibuprofen of having increased libido and erectile function that has lasted for at nearly 6 h. He contacted us to question this unusual experience. His medical history was re-reviewed thoroughly with an endocrinologist, and nothing was mentioned. Furthermore, tests for complete blood count, testosterone, thyroid stimulating hormone, cholesterol pre and post ibuprofen intake were assessed, and all results came up as normal. He also reported to have the same previous experience during the test period. A gynecological ultrasound test was also negative for pathological findings.
Discussion
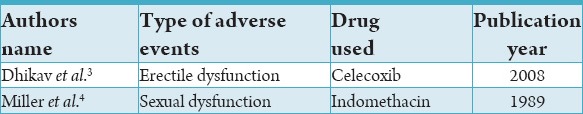
Cyclo-oxygenase inhibitors are widely used in pain control in dentistry. Ibuprofen is one of the most recommended over-the-counter drug. The unwanted side effects are well-reported. To our knowledge, this is the first report to present an unusual side effect of increased libido and erectile function post use of ibuprofen. The clear medical history and normal findings of the clinical tests puzzled us. We searched the literature using MedLine, accessed via the National Library of MedicinePubMed interface (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed), for articles relating to the existence of reports of adverse events of erectile dysfunction in relation to the use of ibuprofen or NSAIDS written in English from 1966 to September 2014. We used the following MeSH terms (NSAIDS, Ibuprofen, erectile dysfunction, libido, and adverse event). Two relevant reports were found and presented in Table 1. These included studies reported sporadic erectile or sexual dysfunction associated with the use of different types of NSAIDS. In an animal model study, Uqochukwu et al. (2011) found that the treatment with nimesulide has an impact on the testosterone and estradiol levels. However, at the doses studied, there were no significant changes in testicular architecture except for mild degenerative changes.5 The most recent study showed that the aspirin was effective in improving lithium-related sexual dysfunction in men with stable bipolar affective disorder.6 With no doubt, we cannot speculate that ibuprofen can improve sexual dysfunction, but NSAIDs could have a role in treating such patients. Further studies are warranted.
Table 1.
The studies that found in the MedLine from 1966 to 2014.
Footnotes
Source of Support: Nil
Conflict of Interest: None
References
- 1.Ong CK, Lirk P, Tan CH, Seymour RA. An evidence-based update on nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Clin Med Res. 2007;5(1):19–34. doi: 10.3121/cmr.2007.698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ong CK, Seymour RA. An evidence-based update of the use of analgesics in dentistry. Periodontol 2000. 2008;46:143–64. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0757.2008.00225.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Dhikav V, Gupta S, Anand KS. Erectile dysfunction induced probably by celecoxib. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2008;17(2):211–2. doi: 10.1002/pds.1539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Miller LG, Rogers JC, Swee DE. Indomethacin-associated sexual dysfunction. J Fam Pract. 1989;29(2):210–1. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ugochukwu AP, Ebere OO, Okwuoma A. Effects of nimesulide on testicular functions in prepubertal albino rats. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2011;22(4):137–40. doi: 10.1515/JBCPP.2011.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Saroukhani S, Emami-Parsa M, Modabbernia A, Ashrafi M, Farokhnia M, Hajiaghaee R, et al. Aspirin for treatment of lithium-associated sexual dysfunction in men: Randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study. Bipolar Disord. 2013;15(6):650–6. doi: 10.1111/bdi.12108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


