Abstract
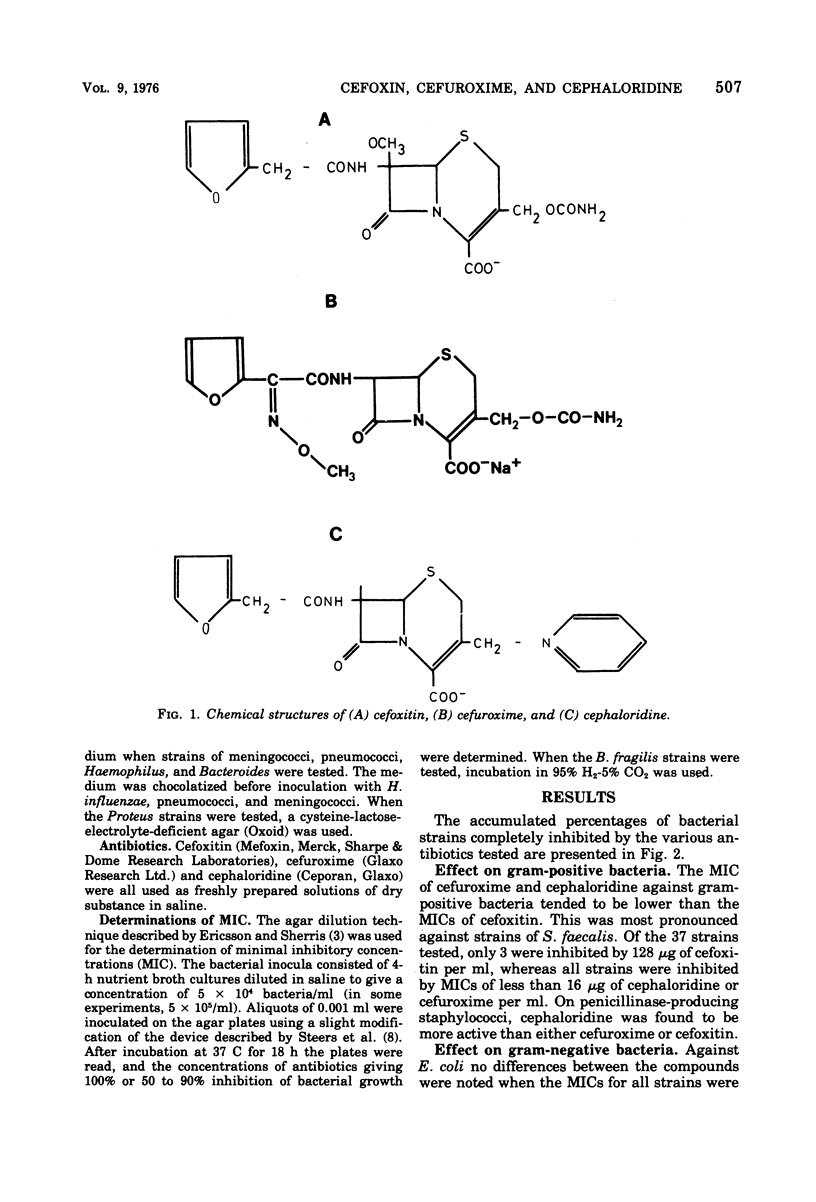
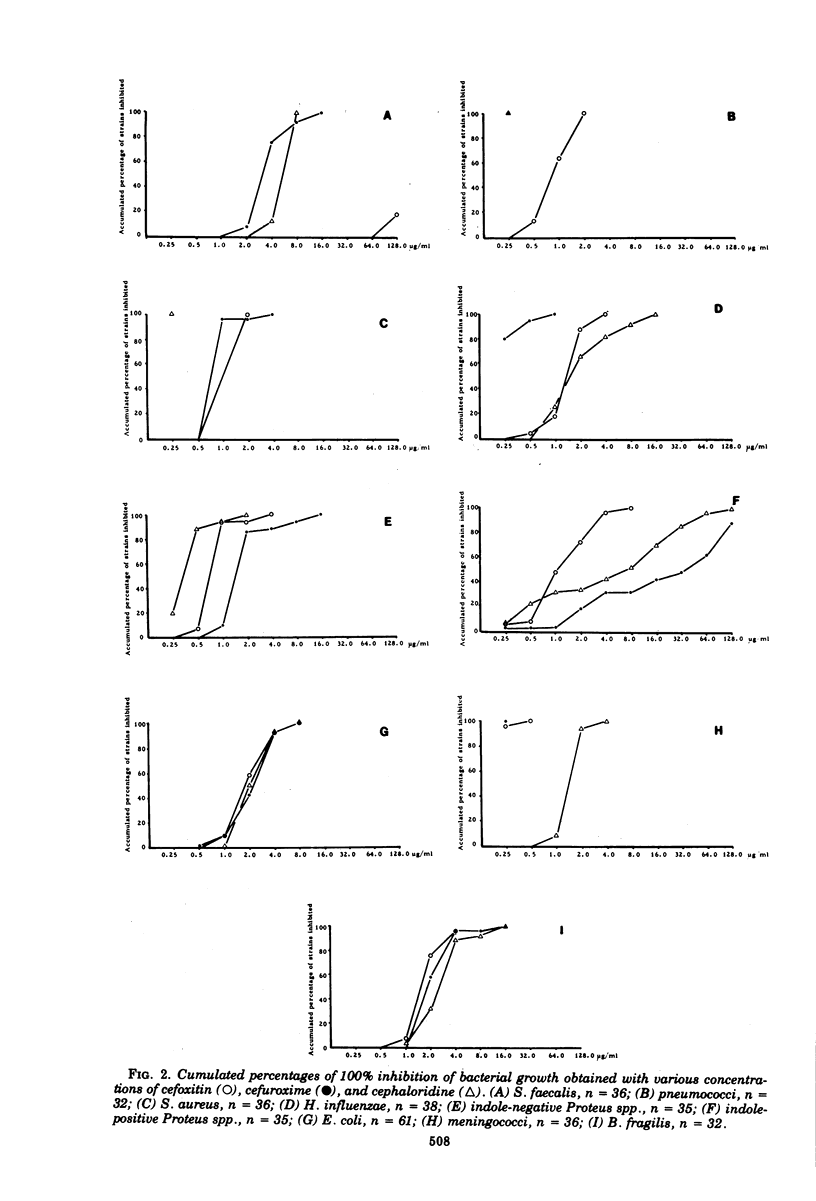
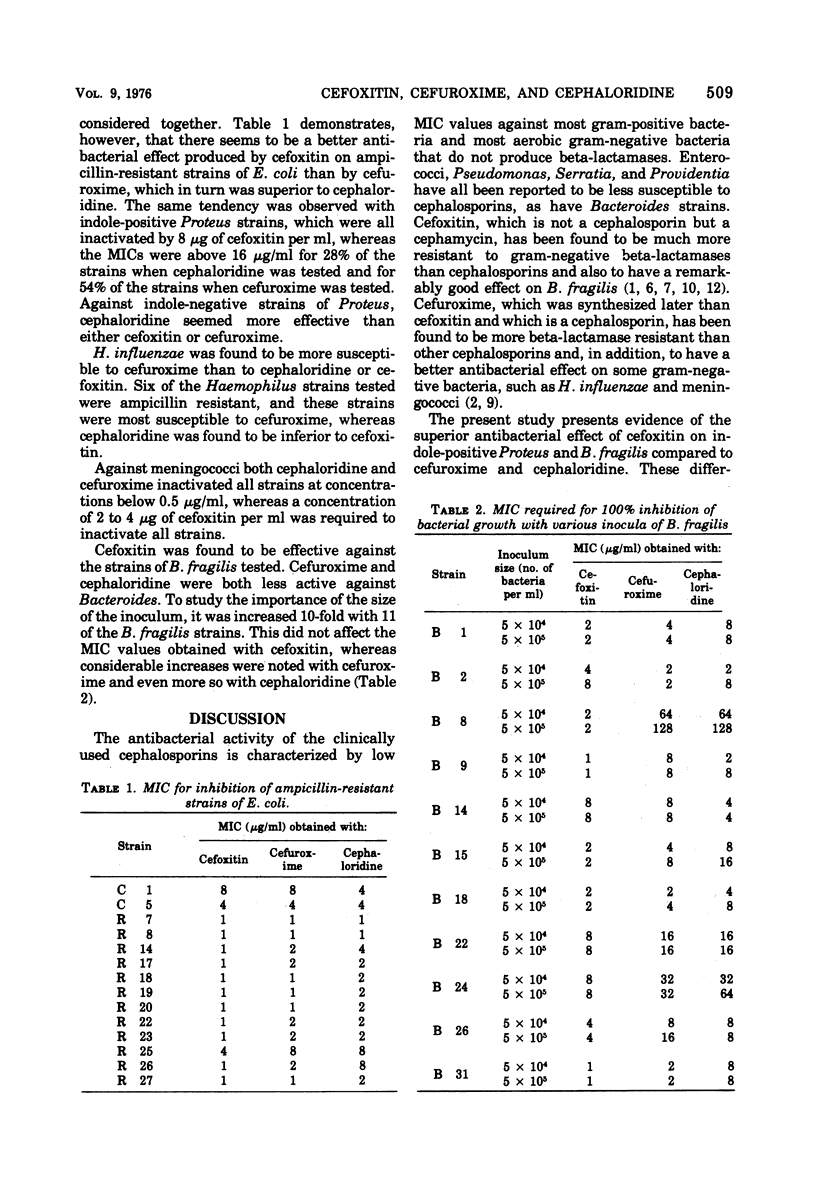
The in vitro antibacterial effects of cefoxitin, a semisynthetic cephamycin, cefuroxime, a new cephalosporin antibiotic, and cephaloridine were compared. With gram-positive bacteria, marked differences were found only in the effects against Streptococcus faecalis, where cephaloridine and cefuroxime were superior to cefoxitin. With gram-negative aerobic bacteria, cefoxitin, which is known to be more resistant to beta-lactamases from gram-negative bacteria than any cephalosporin, was found to be more effective than cefuroxime and cephaloridine against ampicillin-resistant strains of Escherichia coli and indole-positive strains of Proteus. Haemophilus influenzae was found to be more susceptible to cefuroxime than to cefoxitin and cephaloridine. When ampicillin-resistant strains of H. influenzae were tested, markedly higher minimal inhibitory concentration values were obtained with cephaloridine in comparison to those obtained with ampicillin-susceptible strains. These increases in the minimal inhibitory concentration values were not observed with cefoxitin and cefuroxime, probably due to the resistance of these two compounds to beta-lactamases. Strains of Bacteroides fragilis were found to be much more susceptible to cefoxitin than to cefuroxime, which in turn was superior to cephaloridine. The results obtained indicate that cefoxitin and cefuroxime both are superior in their antibacterial spectra to the cephalosporins that are now in clinical use.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brumfitt W., Kosmidis J., Hamilton-Miller J. M., Gilchrist J. N. Cefoxitin and cephalothin: antimicrobial activity, human pharmacokinetics, and toxicology. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Sep;6(3):290–299. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.3.290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericsson H. M., Sherris J. C. Antibiotic sensitivity testing. Report of an international collaborative study. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;217(Suppl):1+–1+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moellering R. C., Jr, Dray M., Kunz L. J. Susceptibility of clinical isolates of bacteria to cefoxitin and cephalothin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Sep;6(3):320–323. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.3.320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Sykes R. B., Griffiths A., Thornton J. E. Cefuroxime, a new cephalosporin antibiotic: activity in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Mar;9(3):511–519. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.3.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onishi H. R., Daoust D. R., Zimmerman S. B., Hendlin D., Stapley E. O. Cefoxitin, a semisynthetic cephamycin antibiotic: resistance to beta-lactamase inactivation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Jan;5(1):38–48. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.1.38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan D. M., O'Callaghan C., Muggleton P. W. Cefuroxime, a new cephalosporin antibiotic: activity in vivo. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Mar;9(3):520–525. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.3.520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEWART G. T., HOLT R. J. LABORATORY AND CLINICAL RESULTS WITH CEPHALORIDINE. Lancet. 1964 Dec 19;2(7373):1305–1309. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)91102-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tally F. P., Jacobus N. V., Bartlett J. G., Gorbach S. L. Susceptibility of anaerobes to cefoxitin and other cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Feb;7(2):128–132. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.2.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turck M., Belcher D. W., Ronald A., Smith R. H., Wallace J. F. New cephalosporin antibiotic--cephaloridine. Clinical and laboratory evaluation. Arch Intern Med. 1967 Jan;119(1):50–59. doi: 10.1001/archinte.119.1.50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallick H., Hendlin D. Cefoxitin, a semisynthetic cephamycin antibiotic: susceptibility studies. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Jan;5(1):25–32. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wretland B., Nord C. E., Wadström T. In vitro sensitivity of isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to carbenicillin, gentamicin, tobramycin, and some other antibiotics. Scand J Infect Dis. 1974;6(1):49–52. doi: 10.3109/inf.1974.6.issue-1.09. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



