Abstract
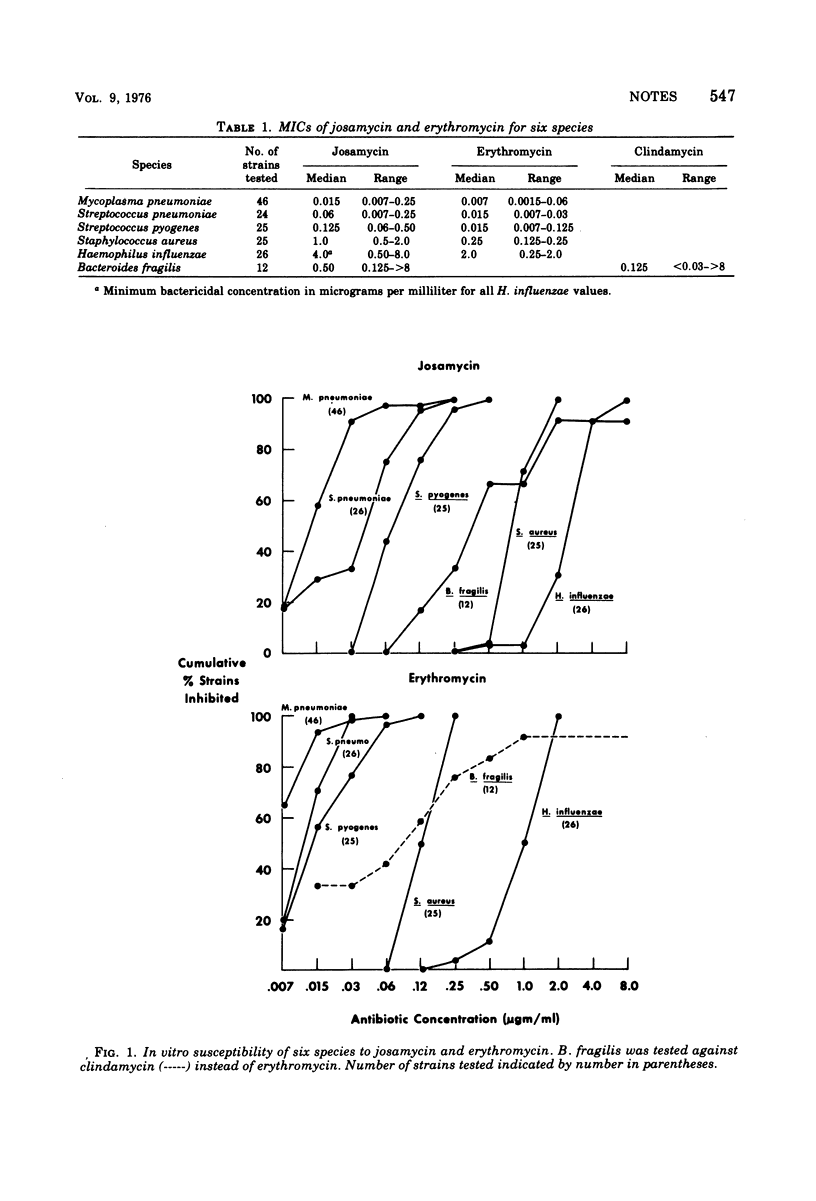
The in vitro activity of josamycin and erythromycin against five bacterial species was compared. In general, erythromycin was slightly more active by weight than josamycin, although both agents had a similar range of activity.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- MacLowry J. D., Jaqua M. J., Selepak S. T. Detailed methodology and implementation of a semiautomated serial dilution microtechnique for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Jul;20(1):46–53. doi: 10.1128/am.20.1.46-53.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



