Abstract
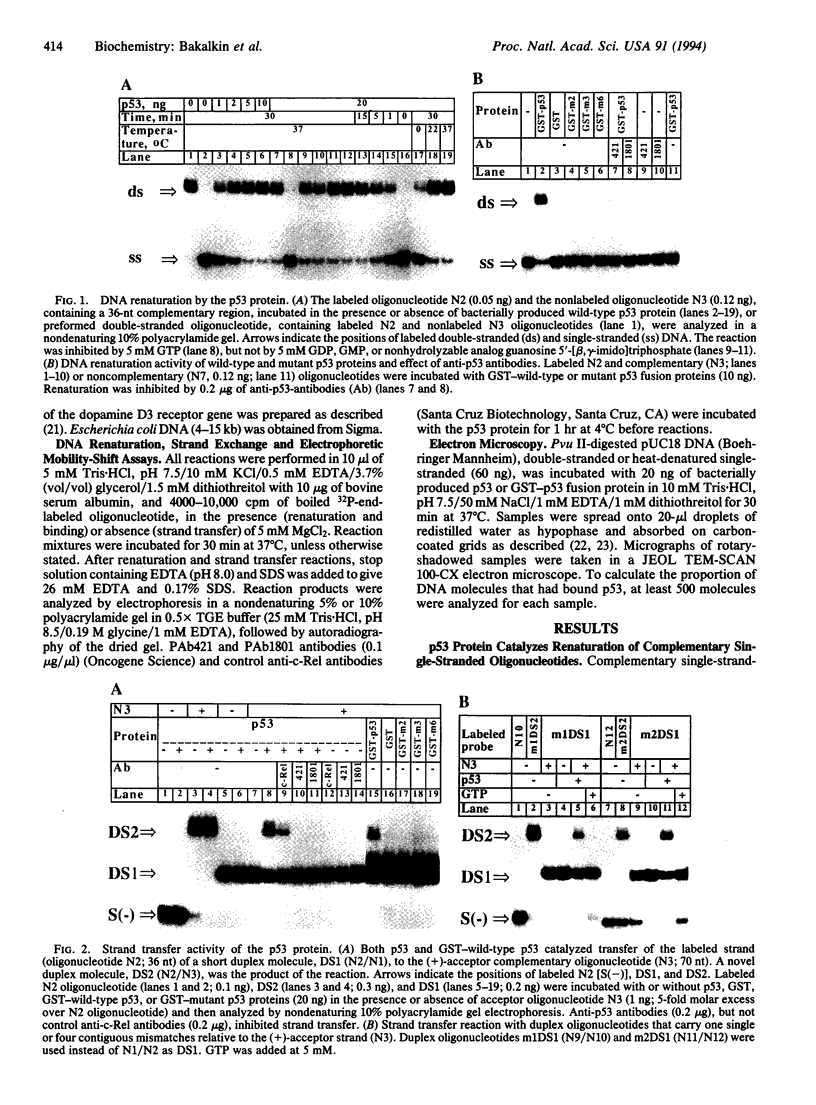
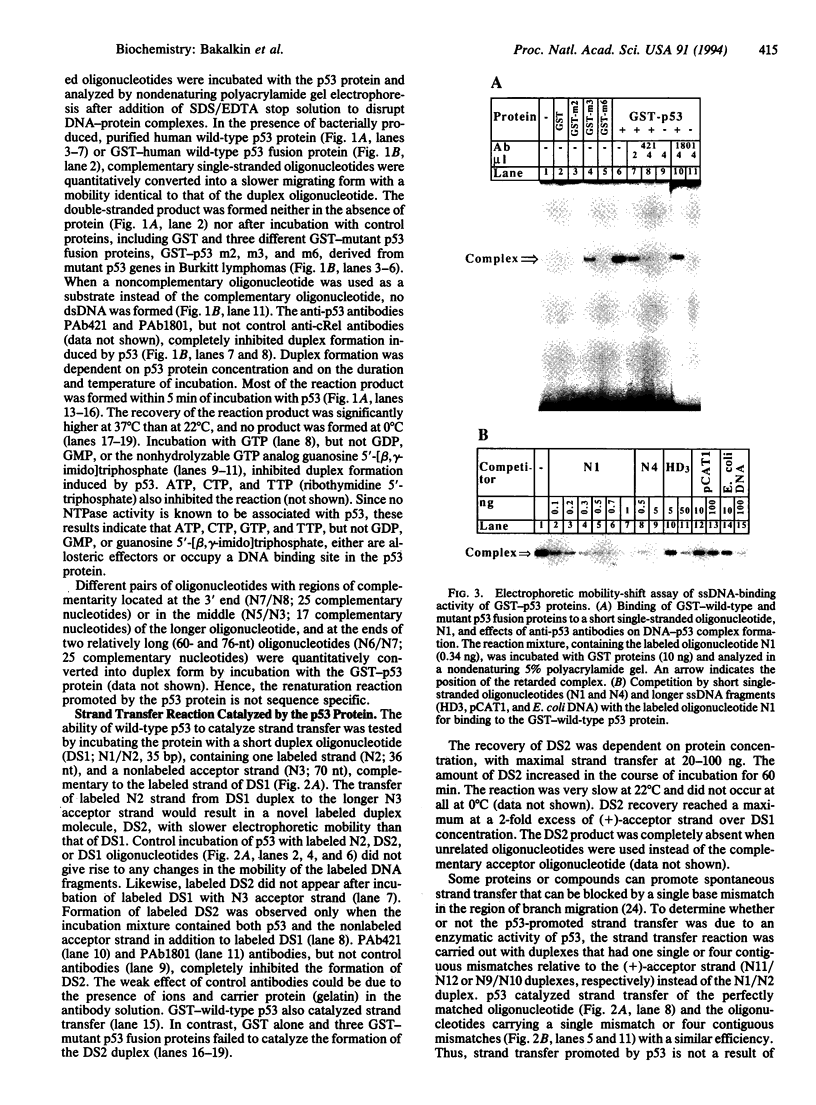
The p53 tumor-suppressor protein has previously been shown to bind double-stranded and single-stranded DNA. We report that the p53 protein can bind single-stranded DNA ends and catalyze DNA renaturation and DNA strand transfer. Both a bacterially expressed wild-type p53 protein and a glutathione S-transferase-wild-type p53 fusion protein catalyzed renaturation of different short (25- to 76-nt) complementary single-stranded DNA fragments and promoted strand transfer between short (36-bp) duplex DNA and complementary single-stranded DNA. Mutant p53 fusion proteins carrying amino acid substitutions Glu-213, Ile-237, or Tyr-238, derived from mutant p53 genes of Burkitt lymphomas, failed to catalyze these reactions. Wild-type p53 had significantly higher binding affinity for short (36- to 76-nt) than for longer (> or = 462-nt) single-stranded DNA fragments in an electrophoretic mobility-shift assay. Moreover, electron microscopy showed that p53 preferentially binds single-stranded DNA ends. Binding of DNA ends to p53 oligomers may allow alignment of complementary strands. These findings suggest that p53 may play a direct role in the repair of DNA breaks, including the joining of complementary single-stranded DNA ends.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bargonetti J., Friedman P. N., Kern S. E., Vogelstein B., Prives C. Wild-type but not mutant p53 immunopurified proteins bind to sequences adjacent to the SV40 origin of replication. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1083–1091. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90560-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bours V., Villalobos J., Burd P. R., Kelly K., Siebenlist U. Cloning of a mitogen-inducible gene encoding a kappa B DNA-binding protein with homology to the rel oncogene and to cell-cycle motifs. Nature. 1990 Nov 1;348(6296):76–80. doi: 10.1038/348076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donehower L. A., Harvey M., Slagle B. L., McArthur M. J., Montgomery C. A., Jr, Butel J. S., Bradley A. Mice deficient for p53 are developmentally normal but susceptible to spontaneous tumours. Nature. 1992 Mar 19;356(6366):215–221. doi: 10.1038/356215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. J., Allan G. J., Shanahan F., Vousden K. H., Crook T. p53 is frequently mutated in Burkitt's lymphoma cell lines. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):2879–2887. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07837.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritsche M., Haessler C., Brandner G. Induction of nuclear accumulation of the tumor-suppressor protein p53 by DNA-damaging agents. Oncogene. 1993 Feb;8(2):307–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall P. A., McKee P. H., Menage H. D., Dover R., Lane D. P. High levels of p53 protein in UV-irradiated normal human skin. Oncogene. 1993 Jan;8(1):203–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollstein M., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Harris C. C. p53 mutations in human cancers. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):49–53. doi: 10.1126/science.1905840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikawa S., Takai T., Toyosato M., Takahashi H., Noda M., Kakidani H., Kubo T., Hirose T., Inayama S., Hayashida H. Isolation and structural organization of the human preproenkephalin B gene. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):611–614. doi: 10.1038/306611a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jönsson E., Lannfelt L., Sokoloff P., Schwartz J. C., Sedvall G. Lack of association between schizophrenia and alleles in the dopamine D3 receptor gene. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1993 May;87(5):345–349. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1993.tb03384.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastan M. B., Onyekwere O., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Craig R. W. Participation of p53 protein in the cellular response to DNA damage. Cancer Res. 1991 Dec 1;51(23 Pt 1):6304–6311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastan M. B., Zhan Q., el-Deiry W. S., Carrier F., Jacks T., Walsh W. V., Plunkett B. S., Vogelstein B., Fornace A. J., Jr A mammalian cell cycle checkpoint pathway utilizing p53 and GADD45 is defective in ataxia-telangiectasia. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):587–597. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90593-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern S. E., Kinzler K. W., Baker S. J., Nigro J. M., Rotter V., Levine A. J., Friedman P., Prives C., Vogelstein B. Mutant p53 proteins bind DNA abnormally in vitro. Oncogene. 1991 Jan;6(1):131–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern S. E., Kinzler K. W., Bruskin A., Jarosz D., Friedman P., Prives C., Vogelstein B. Identification of p53 as a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1708–1711. doi: 10.1126/science.2047879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern S. E., Pietenpol J. A., Thiagalingam S., Seymour A., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Oncogenic forms of p53 inhibit p53-regulated gene expression. Science. 1992 May 8;256(5058):827–830. doi: 10.1126/science.1589764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P. Cancer. p53, guardian of the genome. Nature. 1992 Jul 2;358(6381):15–16. doi: 10.1038/358015a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberosler P., Hloch P., Ramsperger U., Stahl H. p53-catalyzed annealing of complementary single-stranded nucleic acids. EMBO J. 1993 Jun;12(6):2389–2396. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05893.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oren M. p53: the ultimate tumor suppressor gene? FASEB J. 1992 Oct;6(13):3169–3176. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.13.1397838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panyutin I. G., Hsieh P. Formation of a single base mismatch impedes spontaneous DNA branch migration. J Mol Biol. 1993 Mar 20;230(2):413–424. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ragimov N., Krauskopf A., Navot N., Rotter V., Oren M., Aloni Y. Wild-type but not mutant p53 can repress transcription initiation in vitro by interfering with the binding of basal transcription factors to the TATA motif. Oncogene. 1993 May;8(5):1183–1193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto E., Usheva A., Zambetti G. P., Momand J., Horikoshi N., Weinmann R., Levine A. J., Shenk T. Wild-type p53 binds to the TATA-binding protein and represses transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):12028–12032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.12028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmeyer K., Deppert W. DNA binding properties of murine p53. Oncogene. 1988 Nov;3(5):501–507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szekely L., Selivanova G., Magnusson K. P., Klein G., Wiman K. G. EBNA-5, an Epstein-Barr virus-encoded nuclear antigen, binds to the retinoblastoma and p53 proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5455–5459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Kern S. E., Pietenpol J. A., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Definition of a consensus binding site for p53. Nat Genet. 1992 Apr;1(1):45–49. doi: 10.1038/ng0492-45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]