Abstract
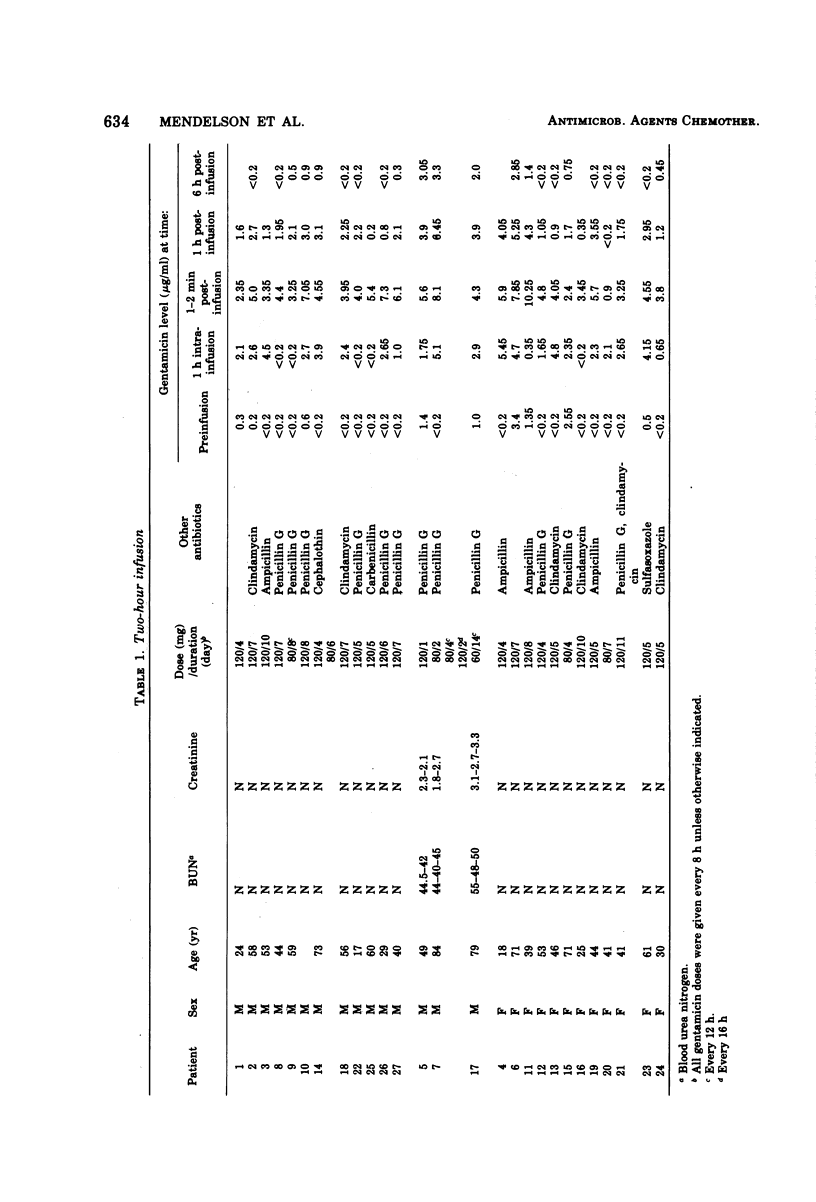
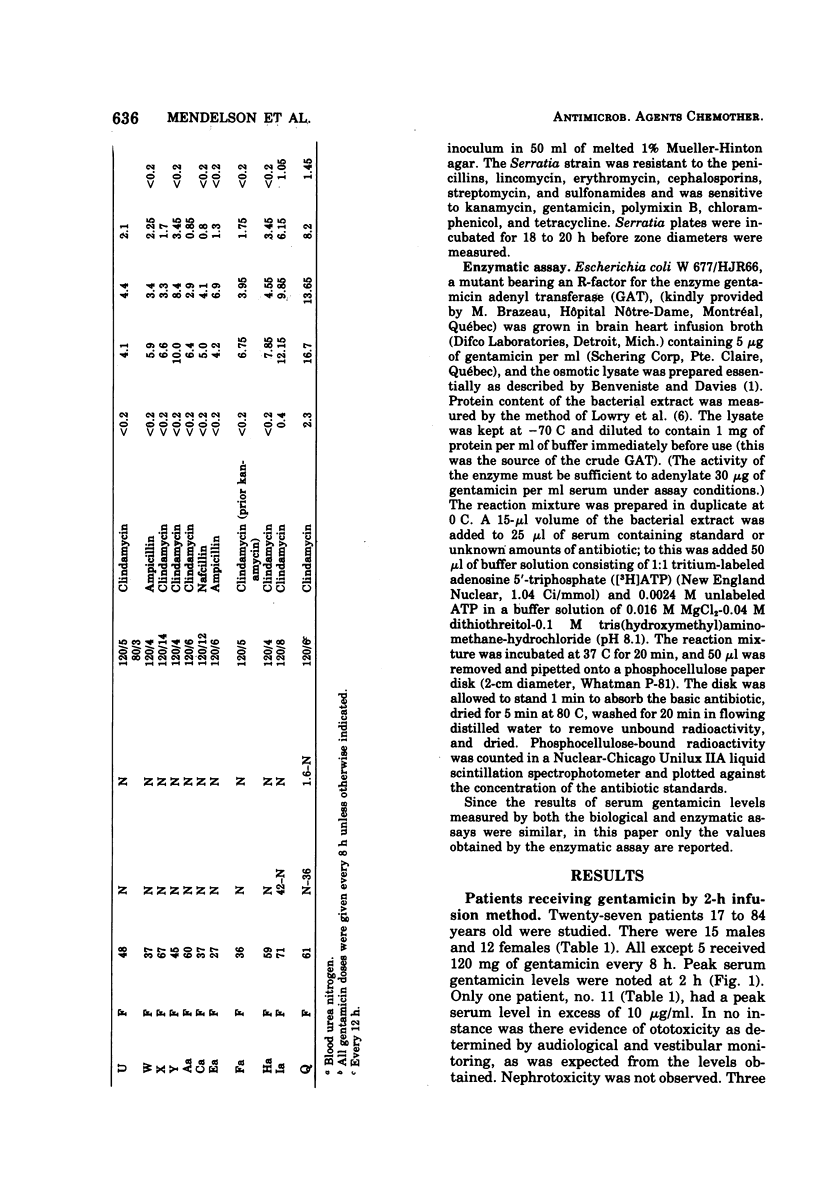
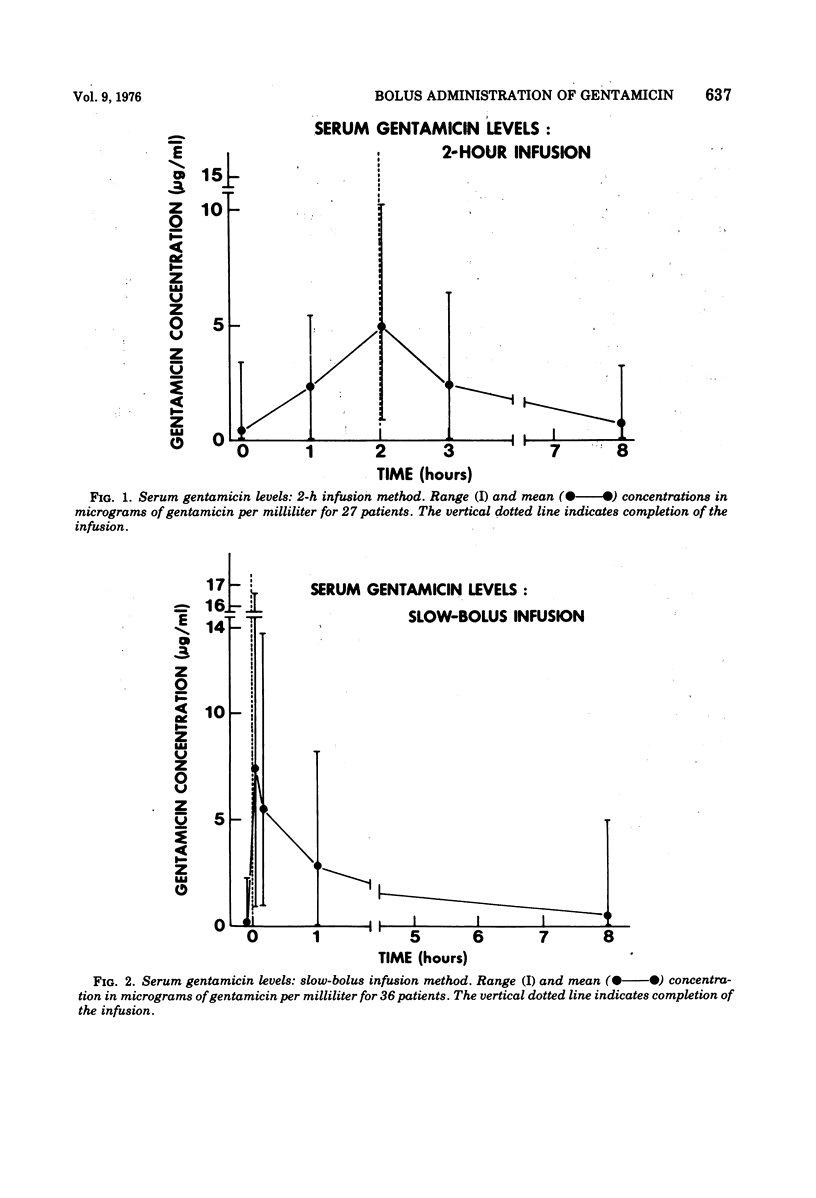
A study was done to assess the safety of gentamicin administration by a bolus method. A total of 63 patients were randomly treated with intravenous gentamicin by bolus administration (3 to 5 min) and by slow infusion (2 h). Serum gentamicin levels were measured. Renal and audiovestibular function were monitored. Pure-tone audiometry was performed at the beginning, on day 3, and at the end of therapy. The study revealed that the bolus administration was safe and nontoxic.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benveniste R., Davies J. R-factor mediated gentamicin resistance: A new enzyme which modifies aminoglycoside antibiotics. FEBS Lett. 1971 May 20;14(5):293–296. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80282-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewitt W. L. Reflections on the clinical pharmacology of gentamicin. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1973;(Suppl):151–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelson J., Portnoy J., Sigman H. Pharmacology of gentamicin in the biliary tract of humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Nov;4(5):538–541. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.5.538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen A. B., Elb S. The use of gentamicin intravenously. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1973;(Suppl):23–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



