Abstract
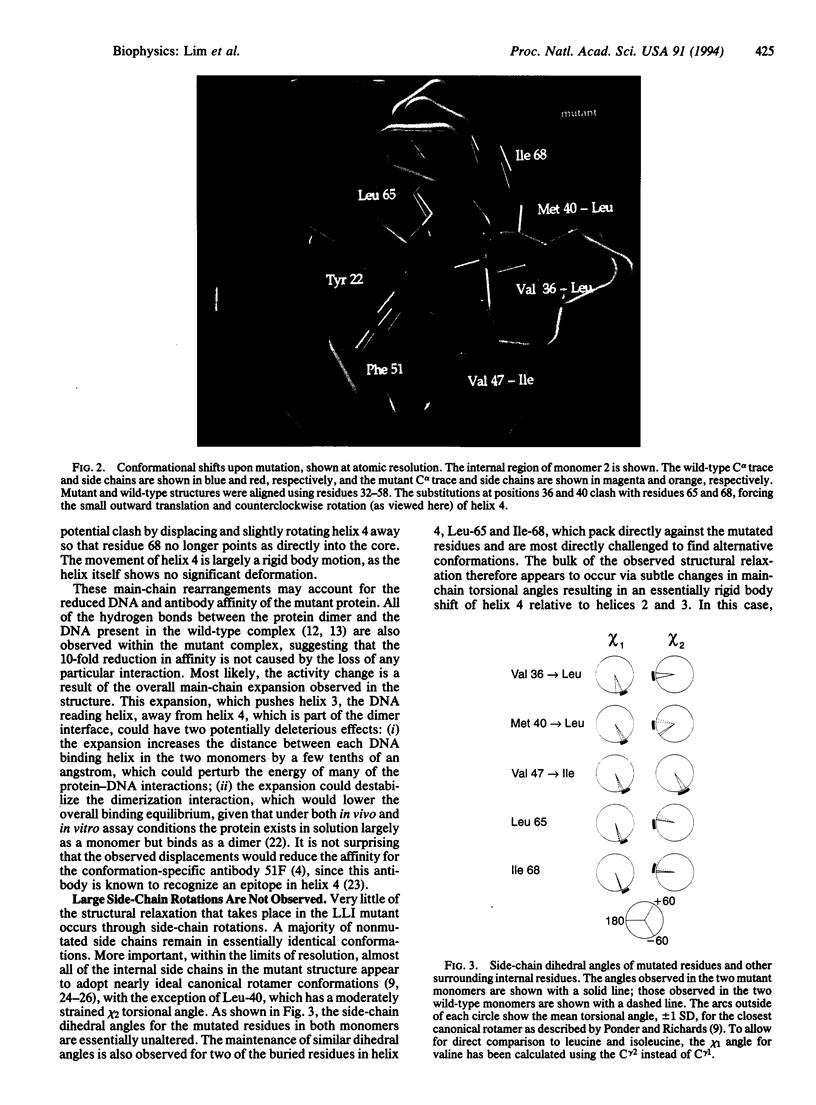
The dense packing observed in protein interiors appears to be crucial for stabilizing the native structure--even subtle internal substitutions are usually destabilizing. Thus, steric complementarity of core residues is thought to be an important criterion for "inverse folding" predictive methods, which judge whether a newly determined sequence is consistent with any known folds. A major problem in the development of useful core packing evaluation algorithms, however, is that there are occasional mutations that are predicted to disrupt native packing but that yield an equally or more stable protein. We have solved the crystal structure of such a variant of lambda repressor, which, despite having three larger core substitutions, is more stable than the wild type. The structure reveals that the protein accommodates the potentially disruptive residues with shifts in its alpha-helical arrangement. The variant is apparently more stable because its packing is improved--the core has a higher packing density and little geometric strain. These rearrangements, however, cause repositioning of functional residues, which result in reduced DNA binding activity. By comparing these results with the predictions of two core packing algorithms, it is clear that the protein possesses a relatively high degree of main-chain flexibility that must be accounted for in order to predict the full spectrum of compatible core sequences. This study also shows how, in protein evolution, a particular set of core residue identities might be selected not because they provide optimal stability but because they provide sufficient stability in addition to the precise structure required for optimal activity.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beamer L. J., Pabo C. O. Refined 1.8 A crystal structure of the lambda repressor-operator complex. J Mol Biol. 1992 Sep 5;227(1):177–196. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90690-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowie J. U., Lüthy R., Eisenberg D. A method to identify protein sequences that fold into a known three-dimensional structure. Science. 1991 Jul 12;253(5016):164–170. doi: 10.1126/science.1853201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breyer R. M., Sauer R. T. Mutational analysis of the fine specificity of binding of monoclonal antibody 51F to lambda repressor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):13355–13360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brünger A. T., Kuriyan J., Karplus M. Crystallographic R factor refinement by molecular dynamics. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):458–460. doi: 10.1126/science.235.4787.458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly M. L. Solvent-accessible surfaces of proteins and nucleic acids. Science. 1983 Aug 19;221(4612):709–713. doi: 10.1126/science.6879170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daopin S., Alber T., Baase W. A., Wozniak J. A., Matthews B. W. Structural and thermodynamic analysis of the packing of two alpha-helices in bacteriophage T4 lysozyme. J Mol Biol. 1991 Sep 20;221(2):647–667. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)80079-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunbrack R. L., Jr, Karplus M. Backbone-dependent rotamer library for proteins. Application to side-chain prediction. J Mol Biol. 1993 Mar 20;230(2):543–574. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg D., McLachlan A. D. Solvation energy in protein folding and binding. Nature. 1986 Jan 16;319(6050):199–203. doi: 10.1038/319199a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson A. E., Baase W. A., Zhang X. J., Heinz D. W., Blaber M., Baldwin E. P., Matthews B. W. Response of a protein structure to cavity-creating mutations and its relation to the hydrophobic effect. Science. 1992 Jan 10;255(5041):178–183. doi: 10.1126/science.1553543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamlin R. Multiwire area X-ray diffractometers. Methods Enzymol. 1985;114:416–452. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)14029-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley J. H., Baase W. A., Matthews B. W. Design and structural analysis of alternative hydrophobic core packing arrangements in bacteriophage T4 lysozyme. J Mol Biol. 1992 Apr 20;224(4):1143–1159. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90475-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan S. R., Pabo C. O. Structure of the lambda complex at 2.5 A resolution: details of the repressor-operator interactions. Science. 1988 Nov 11;242(4880):893–899. doi: 10.1126/science.3187530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpusas M., Baase W. A., Matsumura M., Matthews B. W. Hydrophobic packing in T4 lysozyme probed by cavity-filling mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8237–8241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Kossiakoff A. A. Crystal structures of subtilisin BPN' variants containing disulfide bonds and cavities: concerted structural rearrangements induced by mutagenesis. Proteins. 1990;7(4):343–357. doi: 10.1002/prot.340070406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C., Levitt M. Accurate prediction of the stability and activity effects of site-directed mutagenesis on a protein core. Nature. 1991 Aug 1;352(6334):448–451. doi: 10.1038/352448a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim W. A., Farruggio D. C., Sauer R. T. Structural and energetic consequences of disruptive mutations in a protein core. Biochemistry. 1992 May 5;31(17):4324–4333. doi: 10.1021/bi00132a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim W. A., Sauer R. T. The role of internal packing interactions in determining the structure and stability of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1991 May 20;219(2):359–376. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90570-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor M. J., Islam S. A., Sternberg M. J. Analysis of the relationship between side-chain conformation and secondary structure in globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1987 Nov 20;198(2):295–310. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90314-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McRee D. E., Redford S. M., Getzoff E. D., Lepock J. R., Hallewell R. A., Tainer J. A. Changes in crystallographic structure and thermostability of a Cu,Zn superoxide dismutase mutant resulting from the removal of a buried cysteine. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14234–14241. doi: 10.2210/pdb3sod/pdb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris A. L., MacArthur M. W., Hutchinson E. G., Thornton J. M. Stereochemical quality of protein structure coordinates. Proteins. 1992 Apr;12(4):345–364. doi: 10.1002/prot.340120407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Lewis M. The operator-binding domain of lambda repressor: structure and DNA recognition. Nature. 1982 Jul 29;298(5873):443–447. doi: 10.1038/298443a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponder J. W., Richards F. M. Tertiary templates for proteins. Use of packing criteria in the enumeration of allowed sequences for different structural classes. J Mol Biol. 1987 Feb 20;193(4):775–791. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90358-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards F. M. Areas, volumes, packing and protein structure. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1977;6:151–176. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.06.060177.001055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards F. M. The interpretation of protein structures: total volume, group volume distributions and packing density. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jan 5;82(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90570-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg W. S., Terwilliger T. C. Energetics of repacking a protein interior. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1706–1710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauer R. T., Jordan S. R., Pabo C. O. Lambda repressor: a model system for understanding protein-DNA interactions and protein stability. Adv Protein Chem. 1990;40:1–61. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60286-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varadarajan R., Richards F. M. Crystallographic structures of ribonuclease S variants with nonpolar substitution at position 13: packing and cavities. Biochemistry. 1992 Dec 15;31(49):12315–12327. doi: 10.1021/bi00164a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]