Abstract
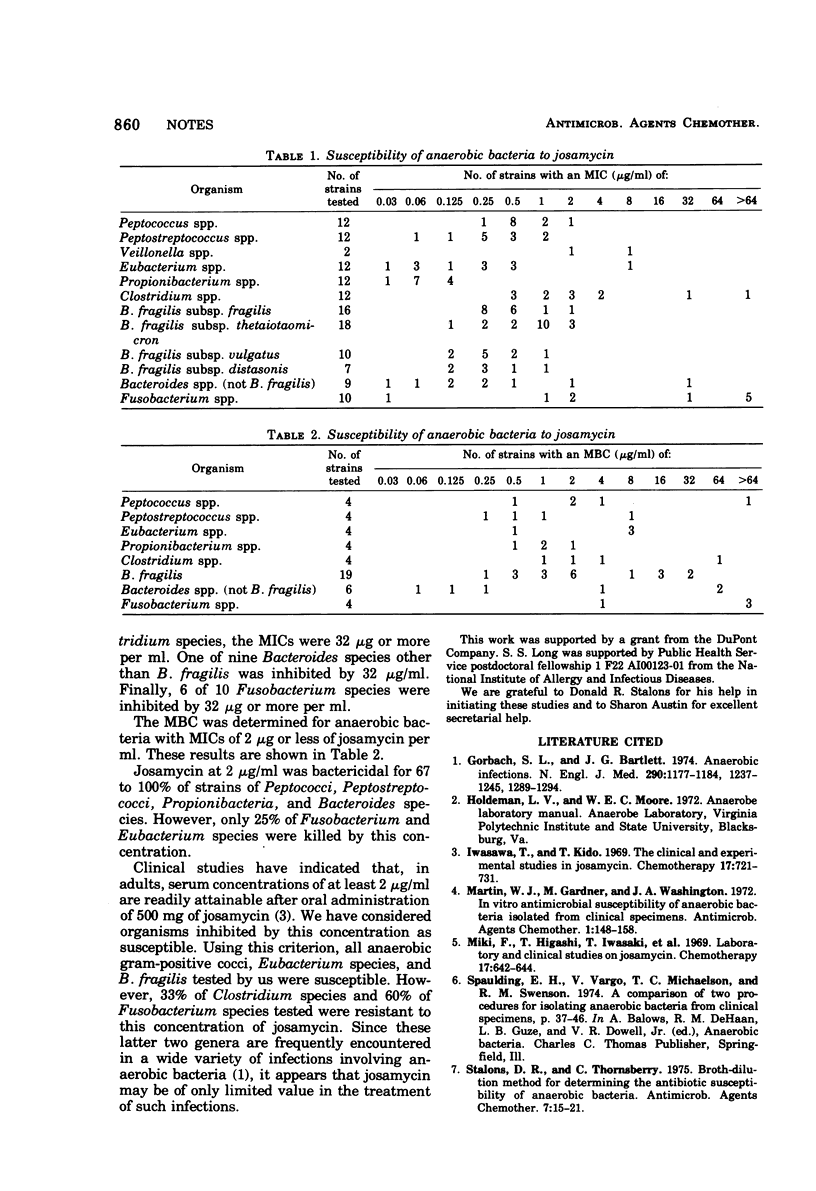
A total of 132 strains of anaerobic bacteria were tested for susceptibility to josamycin, using a broth dilution technique. All strains of Peptococcus species, Peptostreptococcus species, and Bacteroides fragilis were inhibited by 2 μg or less per ml. Seventy percent of these susceptible strains were also killed by 2 μg or less of josamycin per ml. However, 2 of 12 Clostridium species and 6 of 10 Fusobacterium species had minimum inhibitory concentrations of 32 μg or more per ml.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gorbach S. L., Bartlett J. G. Anaerobic infections. 1. N Engl J Med. 1974 May 23;290(21):1177–1184. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197405232902106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W. J., Gardner M., Washington J. A., 2nd In vitro antimicrobial susceptibility of anaerobic bacteria isolated from clinical specimens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Feb;1(2):148–158. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.2.148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalons D. R., Thornsberry C. Broth-dilution method for determining the antibiotic susceptibility of anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Jan;7(1):15–21. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


