Abstract
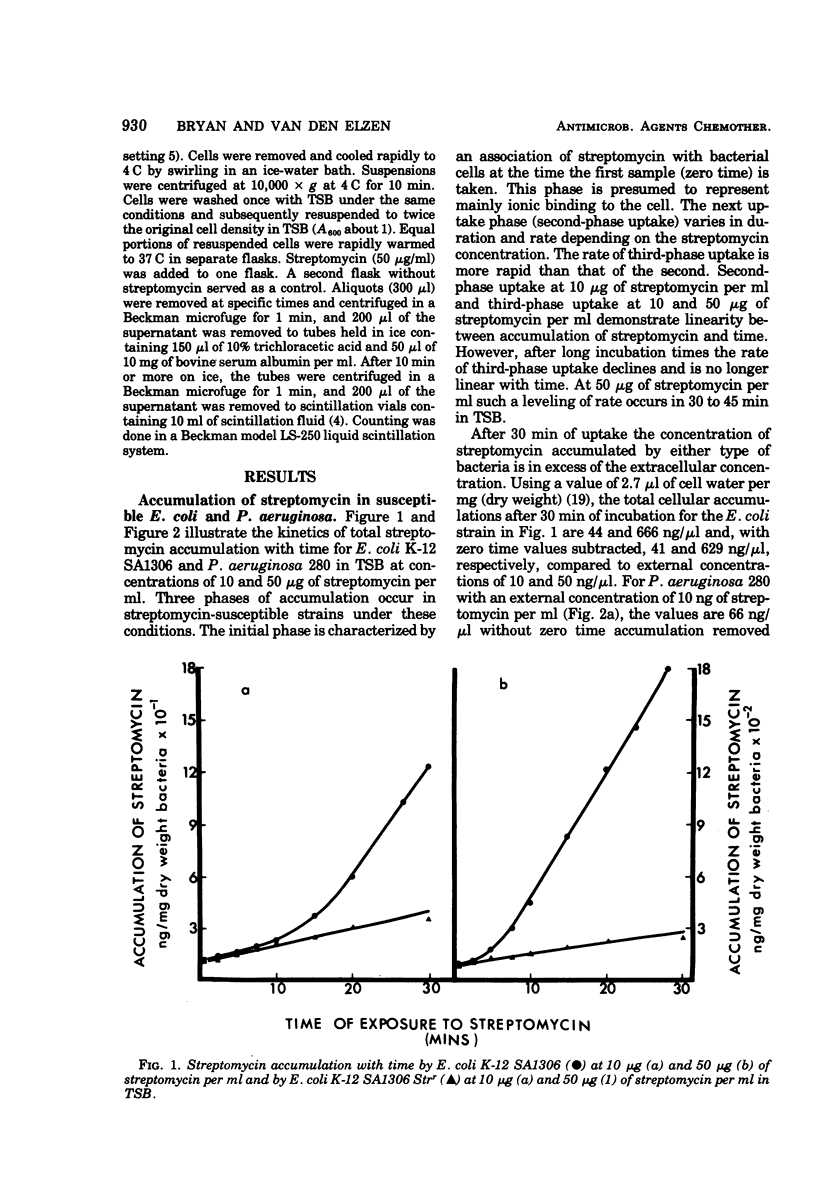
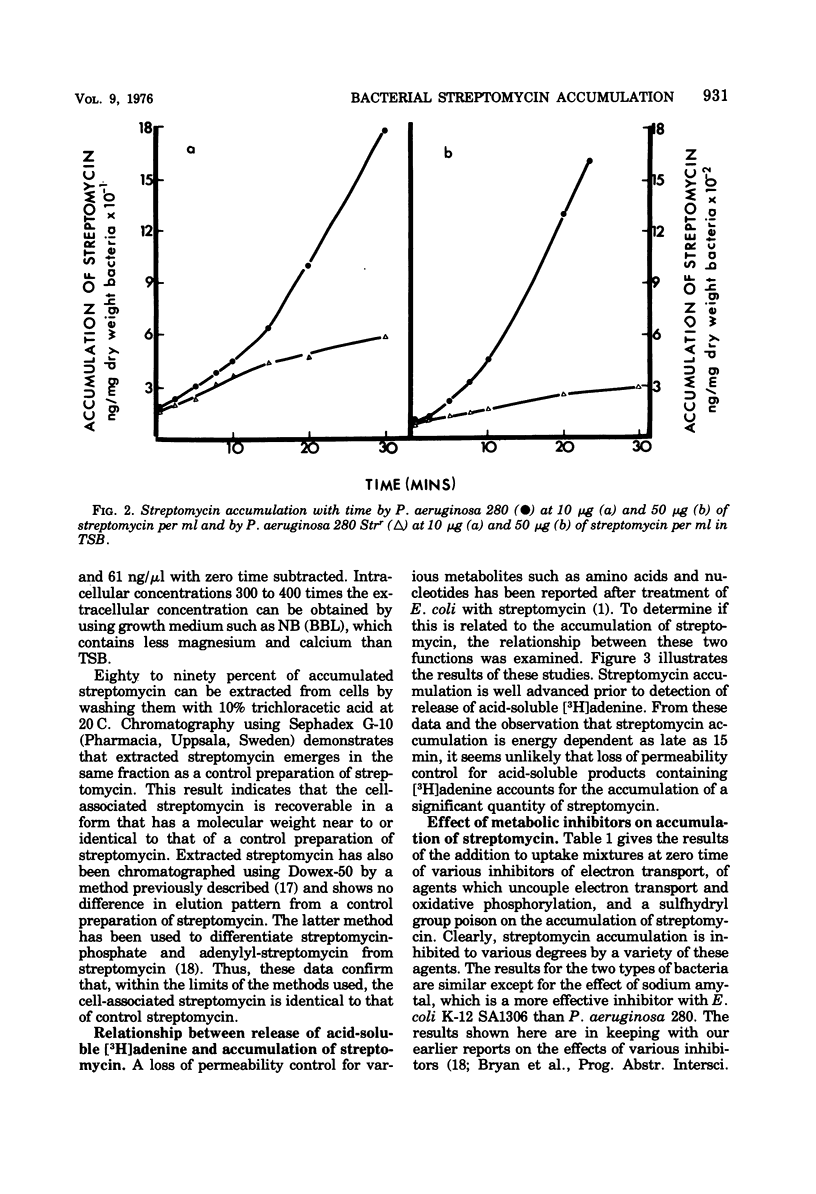
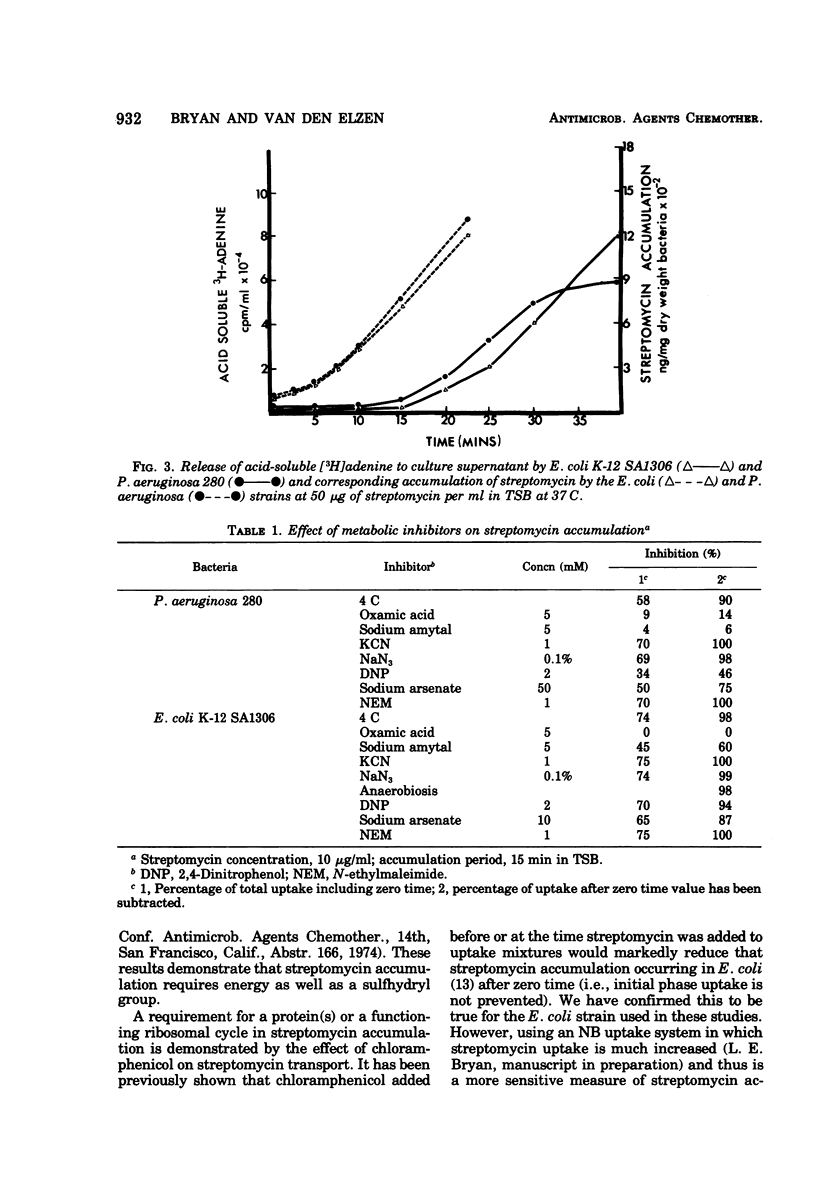
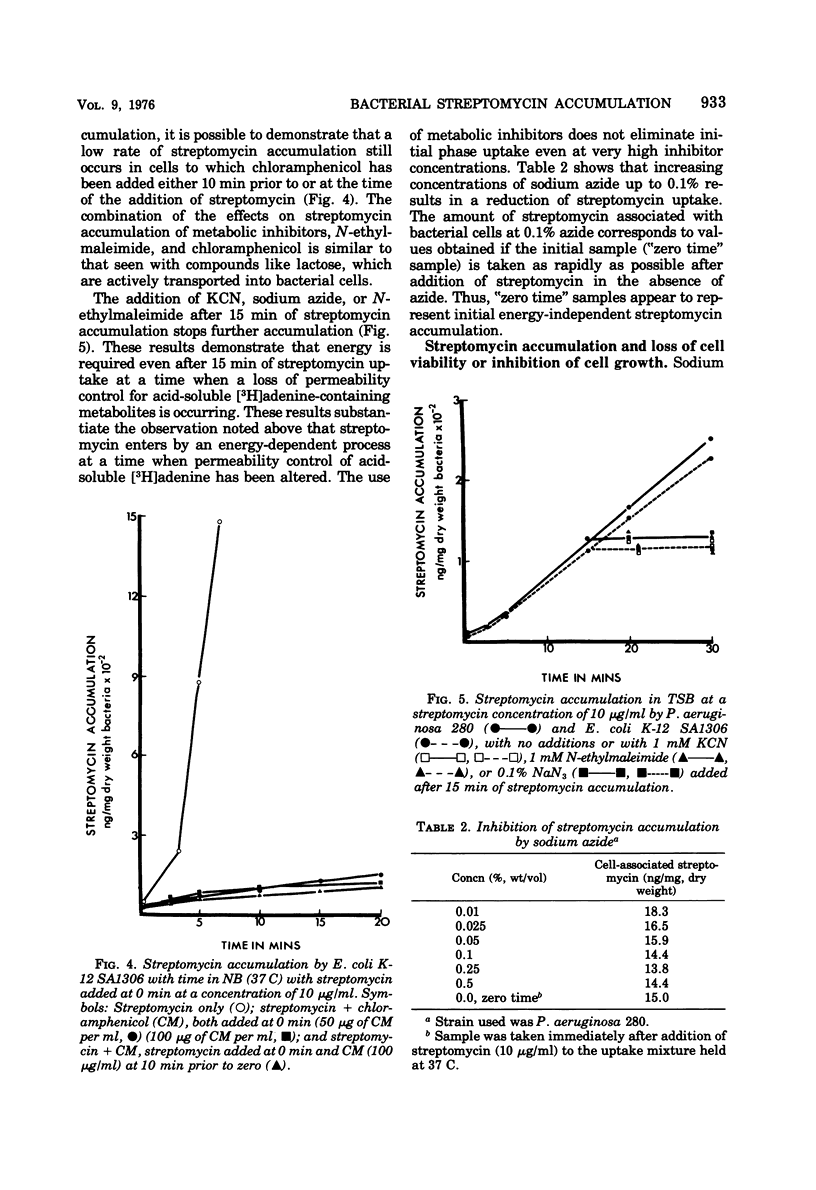
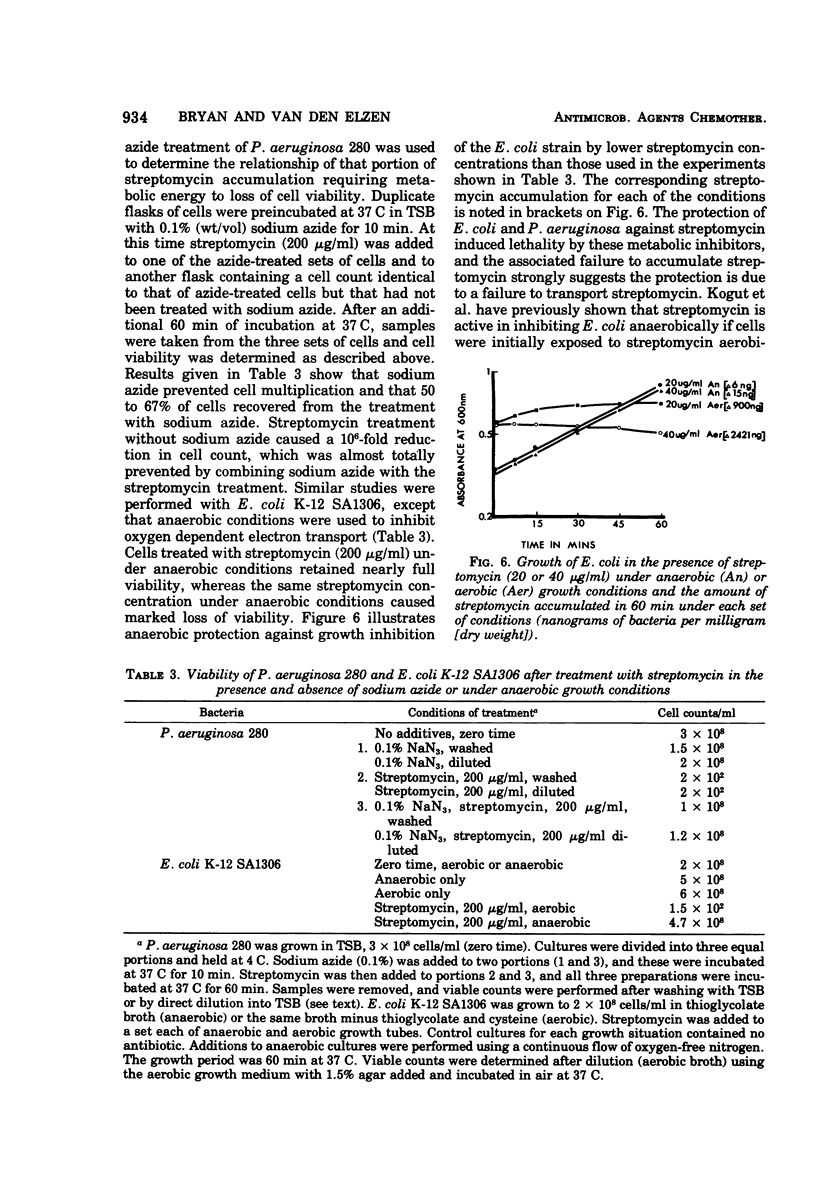
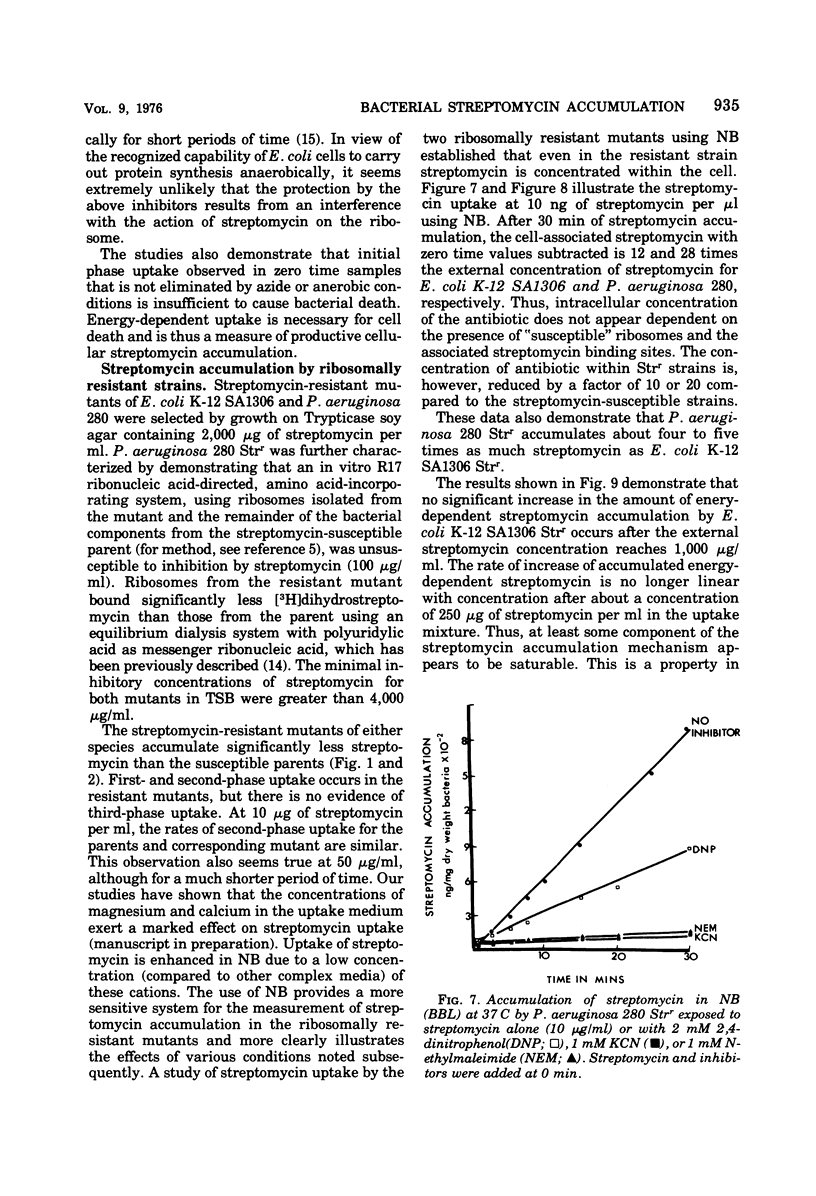
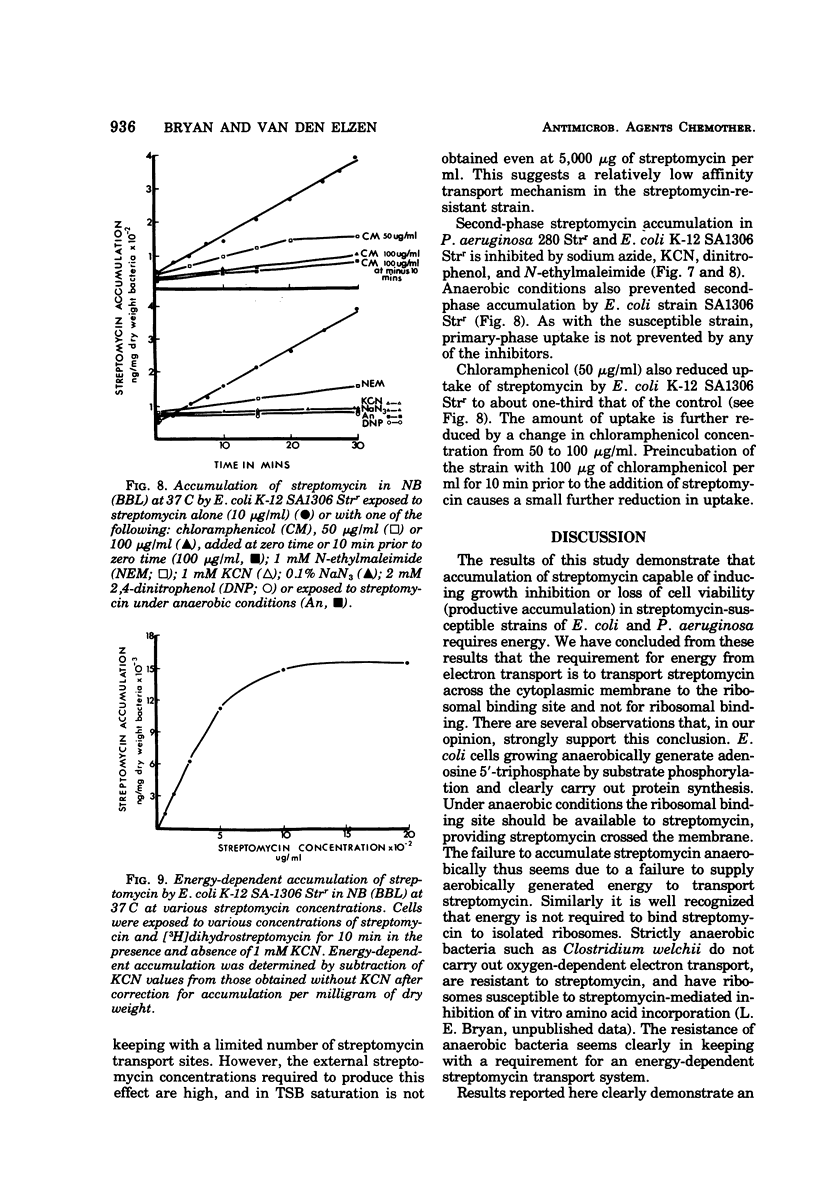
Streptomycin accumulation by susceptible strains of Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa has been shown to be prevented or inhibited by inhibitors of electron transport, sulfhydryl groups and protein synthesis, and agents that uncouple oxidative phosphorylation. Streptomycin is recovered from cells in an unchanged form and is intracellularly concentrated above extracellular concentrations. Accumulation kinetics are multiphasic; an initial phase which cannot be prevented by the above inhibitors is unable to cause inhibition of cell growth or loss of cell viability. Prevention of further phases of uptake does prevent these events. Inhibitor-susceptible accumulation is time dependent and begins almost immediately upon exposure of cells to streptomycin. Streptomycin accumulation remains energy dependent even when cells are losing acid-soluble [3H]adenine, presumably through loss of permeability control. These results demonstrate that streptomycin accumulation necessary for inhibition of cell growth or cell death requires energy and is not a process of diffusion or secondary to membrane leakage. Streptomycin accumulation in ribosomally resistant mutants of E. coli and P. aeruginosa is similar in that both energy-independent and energy-dependent accumulation can be demonstrated. The total energy-dependent accumulation is, however, significantly lower than that in streptomycin-susceptible cells due to the absence of an additional energy-dependent phase of accumulation, which seems dependent on ribosomal binding of streptomycin. Ribosomally resistant strains can be shown to concentrate streptomycin accumulated by the energy-dependent process above the external concentration in nutrient broth but not in Trypticase soy broth. The energy-dependent accumulation can be saturated in the Strr strain of E. coli in nutrient broth, implying limited accumulation sites.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANAND N., DAVIS B. D., ARMITAGE A. K. Uptake of streptomycin by Escherichia coli. Nature. 1960 Jan 2;185:23–24. doi: 10.1038/185023a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANAND N., DAVIS B. D. Damage by streptomycin to the cell membrane of Escherichia coli. Nature. 1960 Jan 2;185:22–23. doi: 10.1038/185022a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andry K., Bockrath R. C. Dihydrostreptomycin accumulation in E. coli. Nature. 1974 Oct 11;251(5475):534–536. doi: 10.1038/251534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan L. E., Van Den Elzen H. M. Gentamicin accumulation by sensitive strains of Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1975 Sep;28(9):696–703. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.28.696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan L. E., Van Den Elzen H. M., Tseng J. T. Transferable drug resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Jan;1(1):22–29. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.1.22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang F. N., Flaks J. G. Binding of dihydrostreptomycin to Escherichia coli ribosomes: characteristics and equilibrium of the reaction. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Oct;2(4):294–307. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.4.294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBIN D. T., HANCOCK R., DAVIS B. D. THE SEQUENCE OF SOME EFFECTS OF STREPTOMYCIN IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Aug 13;74:476–489. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91390-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANCOCK R. Uptake of 14C-streptomycin by Bacillus megaterium. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Jul;28:503–516. doi: 10.1099/00221287-28-3-503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANCOCK R. Uptake of 14C-streptomycin by some microorganisms and its relation to their streptomycin sensitivity. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Jul;28:493–501. doi: 10.1099/00221287-28-3-493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HURWITZ C., ROSANO C. L. Accumulation of label from C14-streptomycin by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1962 Jun;83:1193–1201. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.6.1193-1201.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOGUT M., LIGHTBROWN J. W., ISAACSON P. STREPTOMYCIN ACTION AND ANAEROBIOSIS. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 May;39:155–164. doi: 10.1099/00221287-39-2-155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaji H., Tanaka Y. Binding of dihydrostreptomycin to ribosomal subunits. J Mol Biol. 1968 Mar 14;32(2):221–230. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PLOTZ P. H., DUBIN D. T., DAVIS B. D. Influence of salts on the uptake of streptomycin by Escherichia coli. Nature. 1961 Sep 23;191:1324–1325. doi: 10.1038/1911324a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseng J. T., Bryan L. E., Van den Elzen H. M. Mechanisms and spectrum of streptomycin resistance in a natural population of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Sep;2(3):136–141. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.3.136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H., Wilson T. H. The role of energy coupling in the transport of beta-galactosides by Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1966 May 25;241(10):2200–2211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann R. A., Moellering R. C., Jr, Weinberg A. N. Mechanism of resistance to antibiotic synergism in enterococci. J Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;105(3):873–879. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.3.873-879.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



