Abstract
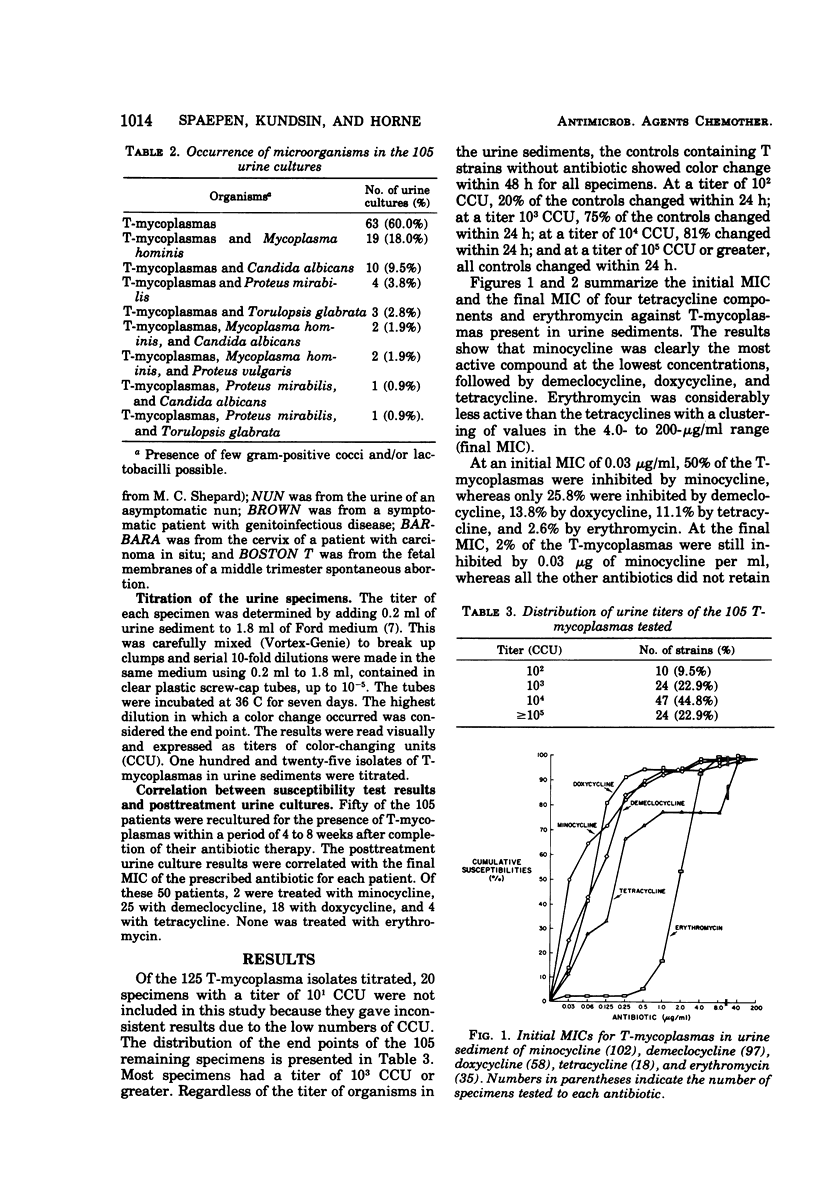
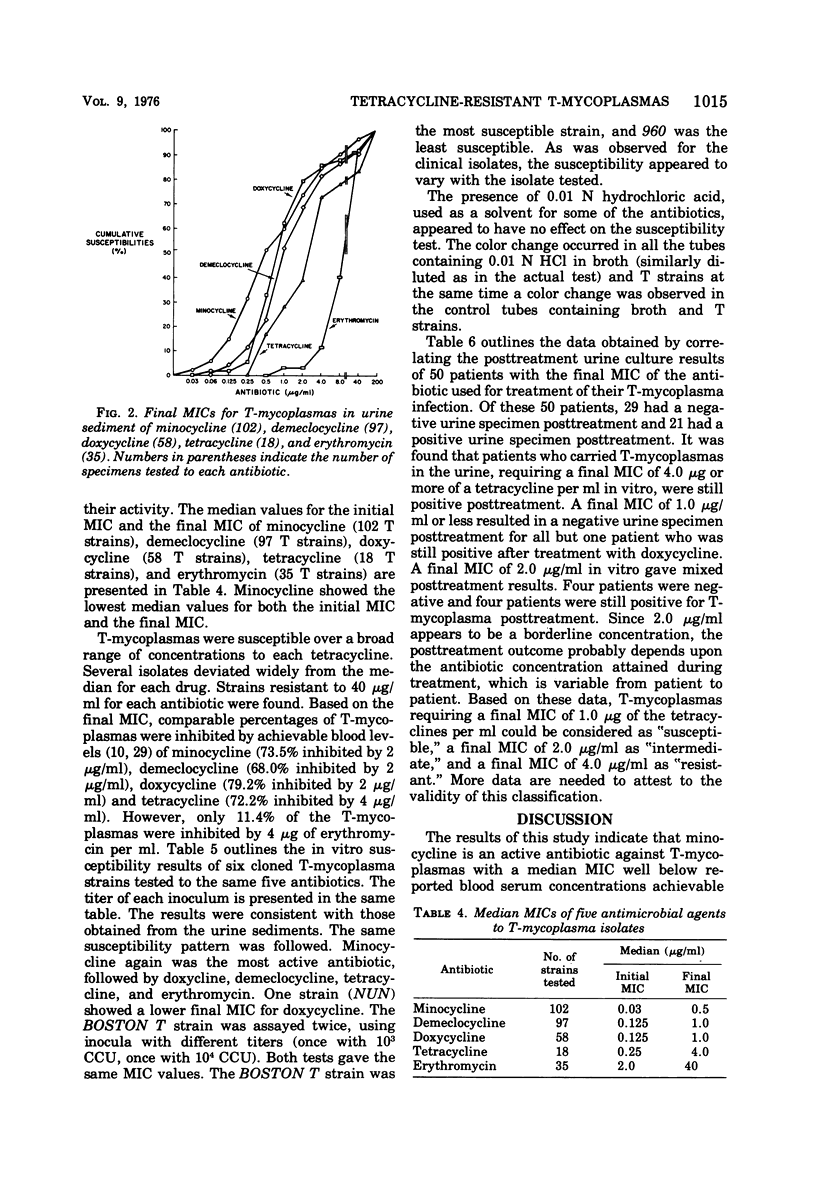
The susceptibilities of T-mycoplasmas (Ureaplasma urealyticum) to minocycline, demeclocycline, doxycycline, tetracycline, and erythromycin were determined by a direct tube dilution test. T-mycoplasma-positive urine sediments of 105 patients with a history of reproductive failure were used as inocula. Minocycline was found to be the most active of the group of antibiotics commonly used to eradicate T-mycoplasma infection. Based on the median initial minimum inhibitory concentration, minocycline was the lowest with 0.03 μg/ml, followed by demeclocycline and doxycycline with 0.125 μg/ml, tetracycline with 0.25 μg/ml, and erythromycin with 2.0 μg/ml. Six T-mycoplasma isolates which had been cloned three times were also tested for susceptibility to the same five antibiotics. The same susceptibility pattern was found. Strains resistant to high concentrations of all antibiotics occurred. Strong positive correlation was seen in 21 patients between in vitro highly resistant strains and positive posttreatment cultures. These results indicate that empirical treatment of genital mycoplasma infections is not justified. Cultures should be taken pretreatment, susceptibility testing performed prior to treatment, and follow-up cultures done posttreatment.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Addey J. P., Taylor-Robinson D., Dimic M. Viability of mycoplasmas after storage in frozen or lyophilised states. J Med Microbiol. 1970 Feb;3(1):137–145. doi: 10.1099/00222615-3-1-137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett A. H., Kundsin R. B., Shapiro S. R. T-strain mycoplasmas, the etiologic agent of non-specific urethritis: a venereal disease. J Urol. 1973 Mar;109(3):427–429. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)60442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun P., Klein J. O., Kass E. H. Susceptibility of genital mycoplasmas to antimicrobial agents. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Jan;19(1):62–70. doi: 10.1128/am.19.1.62-70.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabricant J., Freundt E. A. Importance of extension and standardization of laboratory tests for the identification and classification of mycoplasma. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):50–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27643.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford D. K., Smith J. R. Non-specific urethritis associated with a tetracycline-resistant T-mycoplasma. Br J Vener Dis. 1974 Oct;50(5):373–374. doi: 10.1136/sti.50.5.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraterrigo C. C., Perlman D. Tetracycline inhibition of Mycoplasma ribosomal protein synthesis. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1971 Mar;24(3):185–188. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.24.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnarpe H., Friberg J. Mycoplasma and human reproductive failure. II. Concentrations of doxycycline in serum and seminal fluid and the effect on the growth of T-Mycoplasmas. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1972 Dec 1;114(7):963–966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnarpe H., Friberg J. T-mycoplasmas as a possible cause for reproductive failure. Nature. 1973 Mar 9;242(5393):120–121. doi: 10.1038/242120a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnarpe H. Spectinomycin and doxycycline in treatment of acute venereal disease: their influence on genital mycoplasmas and on the serum bactericidal effect. Microbios. 1974 May;10(40):247–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horne H. W., Hertig A. T., Kundsin R. B., Kosasa T. S. Sub-clinical endometrial inflammation and T-mycoplasma: a possible cause of human reproductive failure. Int J Fertil. 1973;18(4):226–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horne H. W., Jr, Kundsin R. B., Kosasa T. S. The role of mycoplasma infection in human reproductive failure. Fertil Steril. 1974 Apr;25(4):380–389. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(16)40340-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELTON W. H. STORAGE OF MYCOPLASMA STRAINS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Mar;87:588–592. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.3.588-592.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kundsin R. B., Driscoll S. G., Ming P. L. Strain of mycoplasma associated with human reproductive failure. Science. 1967 Sep 29;157(3796):1573–1574. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3796.1573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kundsin R. B., Driscoll S. G. The role of mycoplasmas in human reproductive failure. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1970 Oct 30;174(2):794–797. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1970.tb45596.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman M. C. Proceedings: Preservation of Mycoplasmatales and L-phase variants in the American type culture collection by freezing and freeze-drying. Cryobiology. 1973 Nov;10(5):400–402. doi: 10.1016/0011-2240(73)90065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raccach M., Rottem S., Razin S. Survival of frozen mycoplasmas. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Aug;30(2):167–171. doi: 10.1128/am.30.2.167-171.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S. The cell membrane of mycoplasma. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):115–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27651.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. L., Perlman D. Antibiotic resustance mechanisms in Mycoplasma species. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1971 Sep;24(9):575–582. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.24.575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard M. C. Cultivation and properties of T-strains of mycoplasma associated with nongonococcal urethritis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):505–514. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27695.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard M. C. Nongonococcal urethritis associated with human strains of "T" mycoplasmas. JAMA. 1970 Feb 23;211(8):1335–1340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steigbigel N. H., Reed C. W., Finland M. Absorption and excretion of five tetracycline analogues in normal young men. Am J Med Sci. 1968 May;255:296–312. doi: 10.1097/00000441-196805000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson D. Mycoplasmas of various hosts and their antibiotic sensitivities. Postgrad Med J. 1967 Mar;43(Suppl):100–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



