Abstract
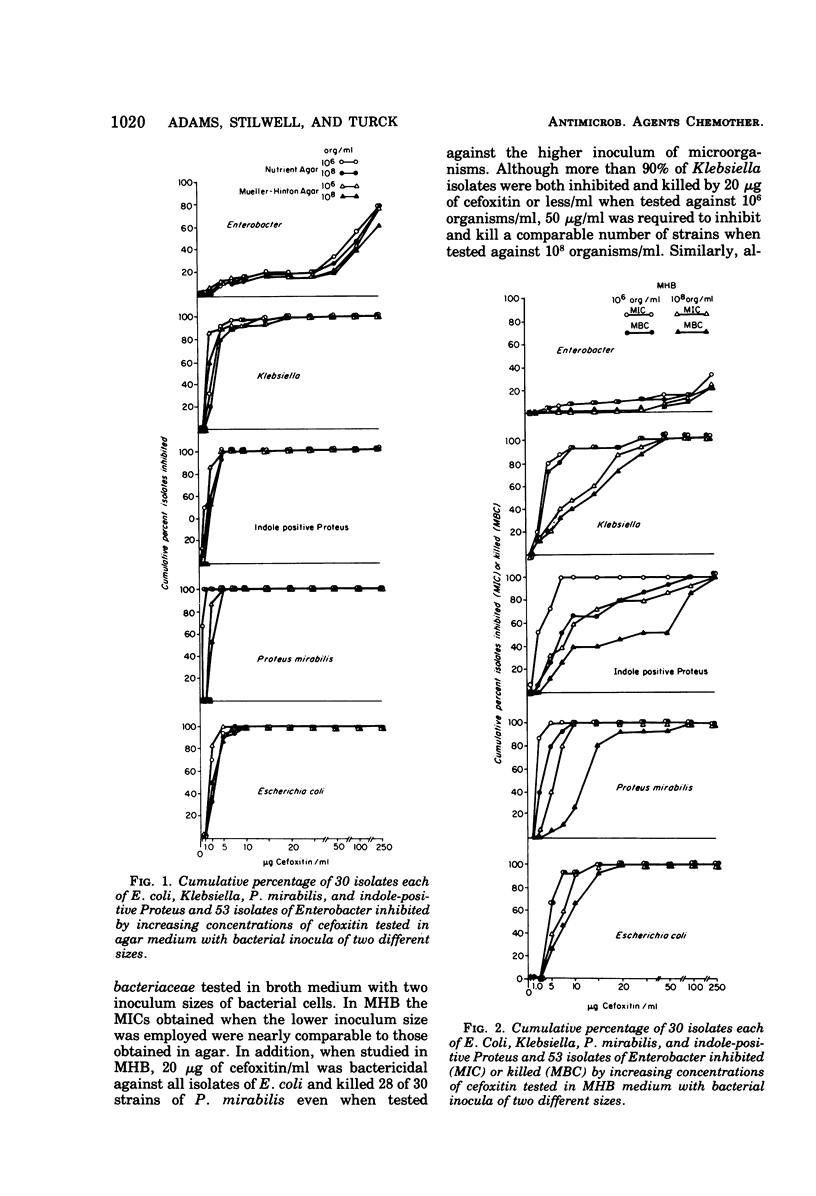
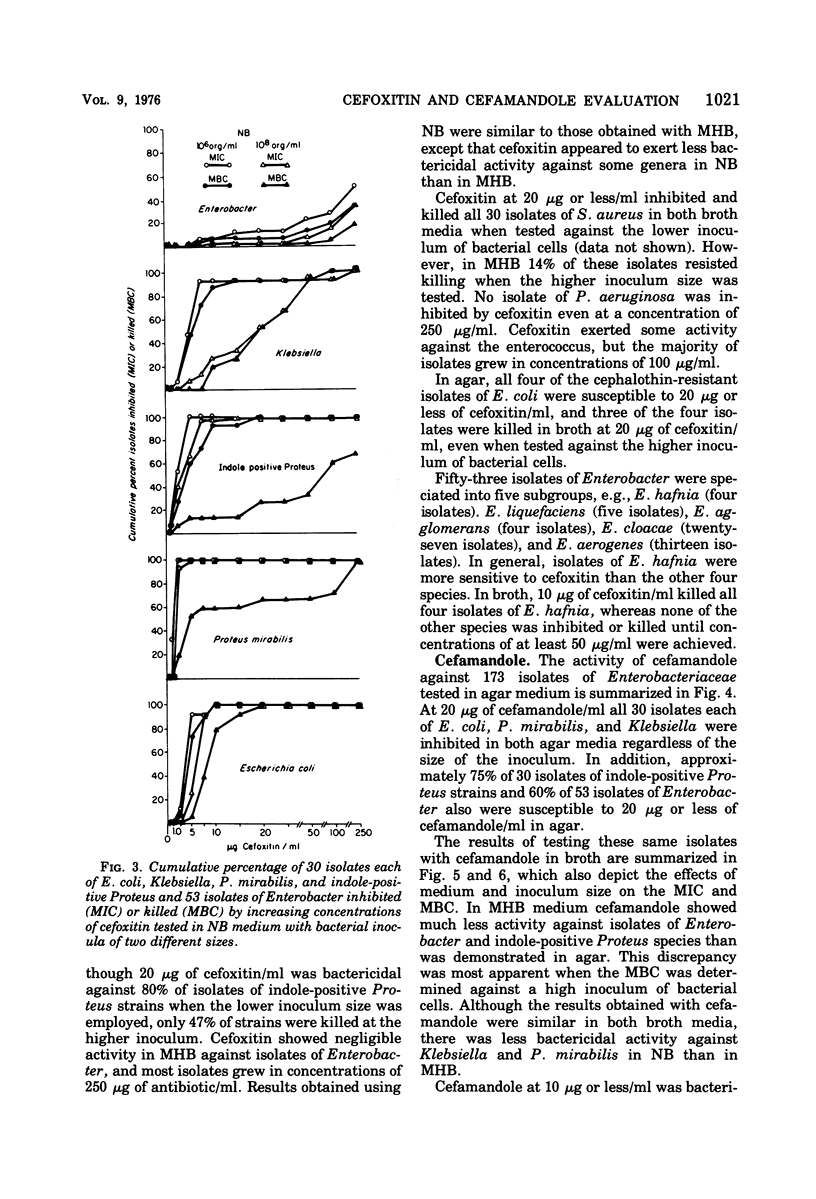
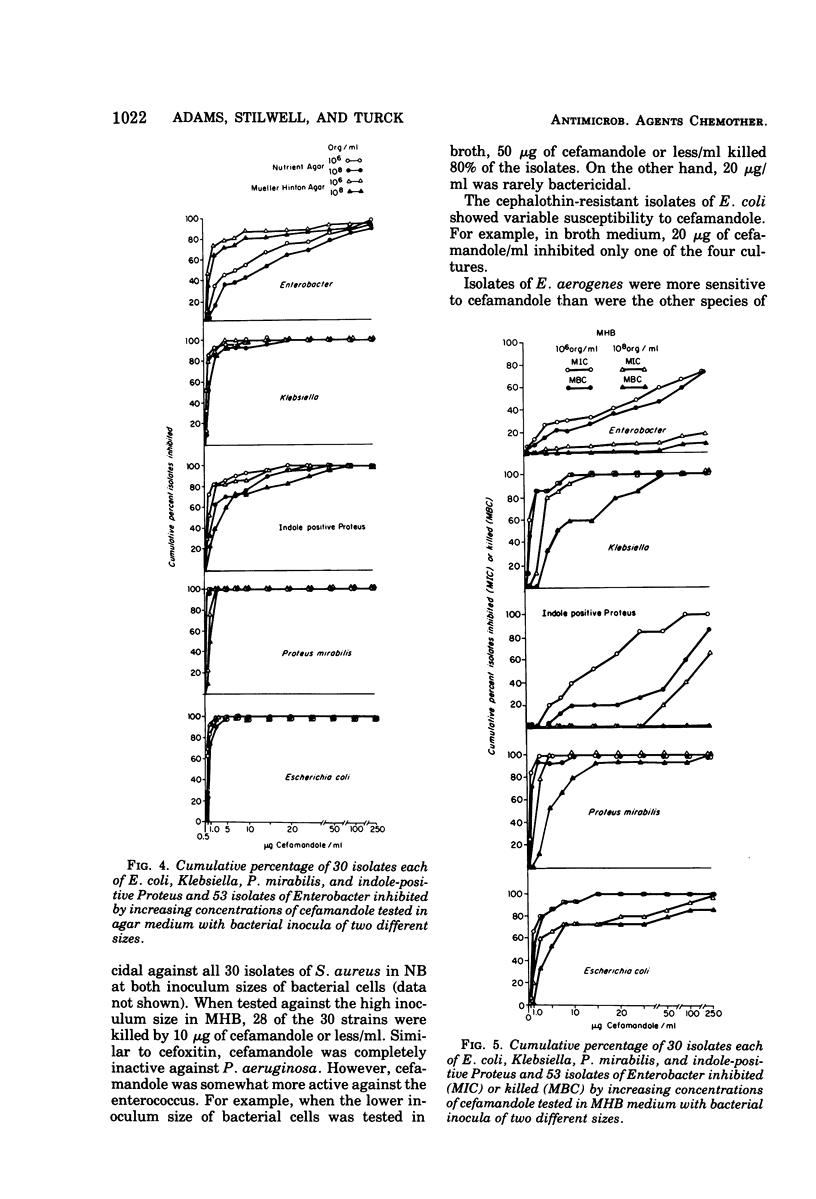
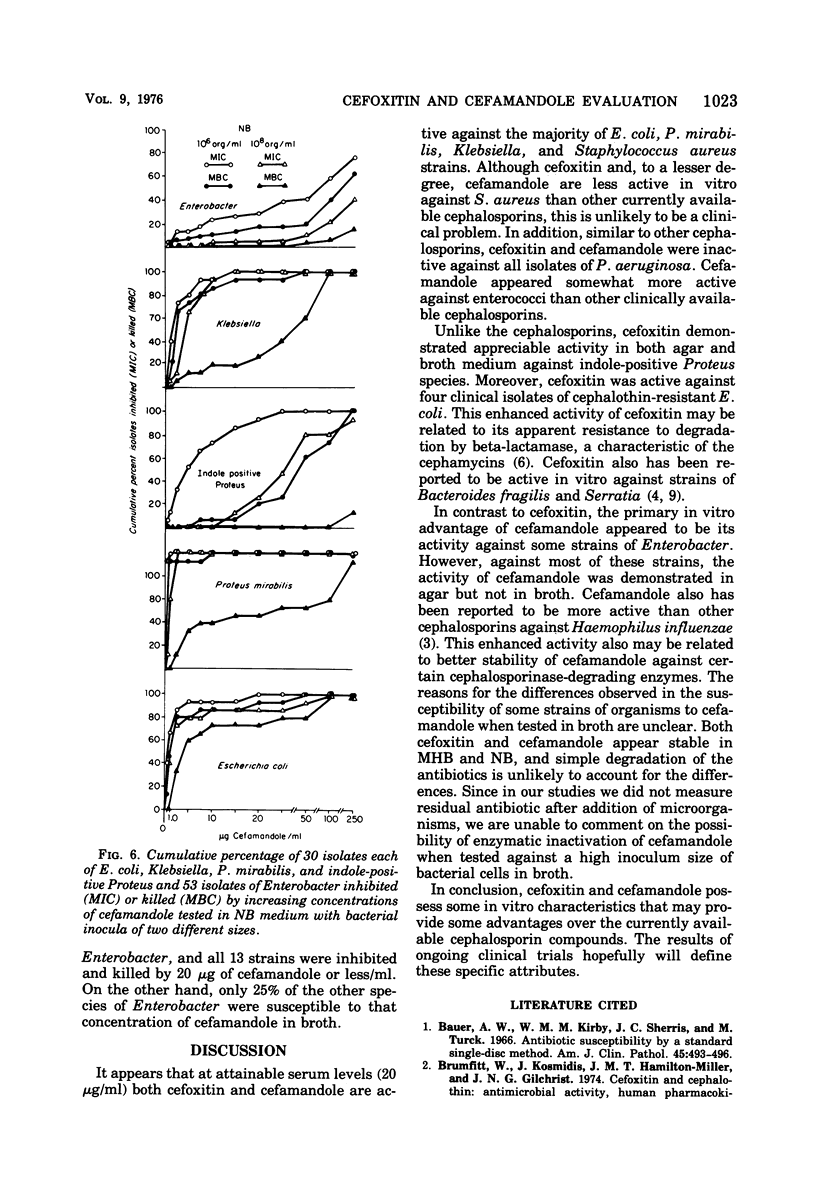
Cefoxitin and cefamandole were evaluated in vitro against 263 organisms. Studies were performed in Mueller-Hinton and nutrient broth and agar employing inoculum sizes of 106 and 108 organisms per ml. At obtainable serum levels both antibiotics were bactericidal for nearly all strains of Escherichia coli, Klebsiella, Proteus mirabilis, and Staphylococcus aureus but were inactive against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and enterococcus. In agar, cefamandole appeared to be active against most strains of Enterobacter and indole-positive Proteus, whereas cefoxitin was active against indole-positive Proteus but not Enterobacter. Moreover, in broth medium most strains of Enterobacter were not readily inhibited by either antibiotic and only 40 and 73% of indole-positive Proteus were inhibited by 10 μg of cefamandole per ml in Mueller-Hinton and nutrient broth, respectively. However, in both broth media, 10 μg of cefoxitin per ml continued to be inhibitory and bactericidal for most isolates of indole-positive Proteus. Cefoxitin also was bactericidal against four cephalothin-resistant strains of E. coli. These data suggest that cefoxitin broadens the spectrum of existing cephalosporins by enhancing the activity against indole-positive Proteus species as well as some other Enterobacteriaceae. On the other hand, with the exception of strains of Enterobacter aerogenes, the apparent increased in vitro activity of cefamandole was demonstrated in agar and not in broth.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eykyn S., Jenkins C., King A., Phillips I. Antibacterial activity of cefamandole, a new cephalosporin antibiotic, compared with that of cephaloridine, cephalothin, and cephalexin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Jun;3(6):657–661. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.6.657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C. Cefamandole, a cephalosporin antibiotic with an unusually wide spectrum of activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Aug;6(2):177–182. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.2.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C. Cefoxitin, a semisynthetic cephamycin antibiotic: antibacterial spectrum and resistance to hydrolysis by gram-negative beta-lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Aug;6(2):170–176. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.2.170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onishi H. R., Daoust D. R., Zimmerman S. B., Hendlin D., Stapley E. O. Cefoxitin, a semisynthetic cephamycin antibiotic: resistance to beta-lactamase inactivation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Jan;5(1):38–48. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.1.38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reller L. B., Karney W. W., Beaty H. N., Holmes K. K., Turck M. Evaluation of cefazolin, a new cephalosporin antibiotic. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Apr;3(4):488–497. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.4.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TURCK M., ANDERSON K. N., SMITH R. H., WALLACE J. F., PETERSDORF R. G. LABORATORY AND CLINICAL EVALUATION OF A NEW ANTIBIOTIC--CEPHALOTHIN. Ann Intern Med. 1965 Aug;63:199–211. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-63-2-199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tally F. P., Jacobus N. V., Bartlett J. G., Gorbach S. L. Susceptibility of anaerobes to cefoxitin and other cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Feb;7(2):128–132. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.2.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallick H., Hendlin D. Cefoxitin, a semisynthetic cephamycin antibiotic: susceptibility studies. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Jan;5(1):25–32. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



