Abstract
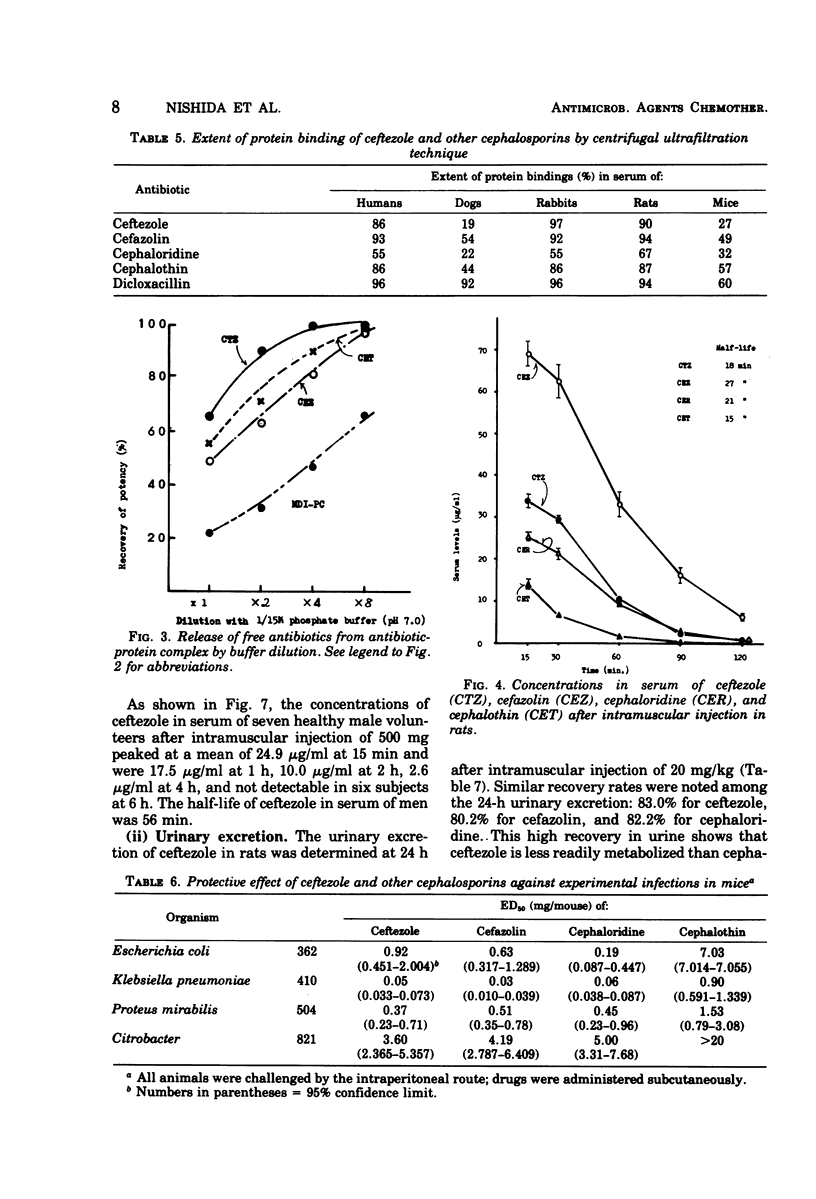
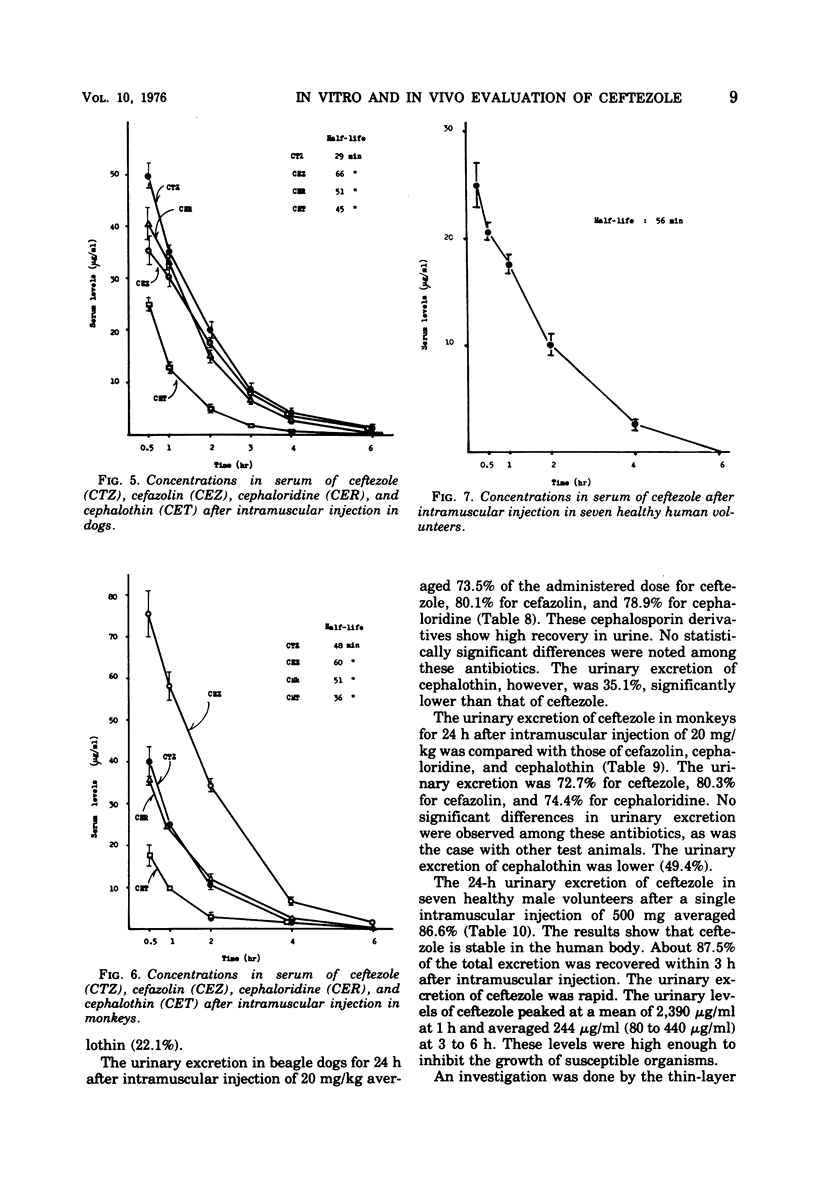
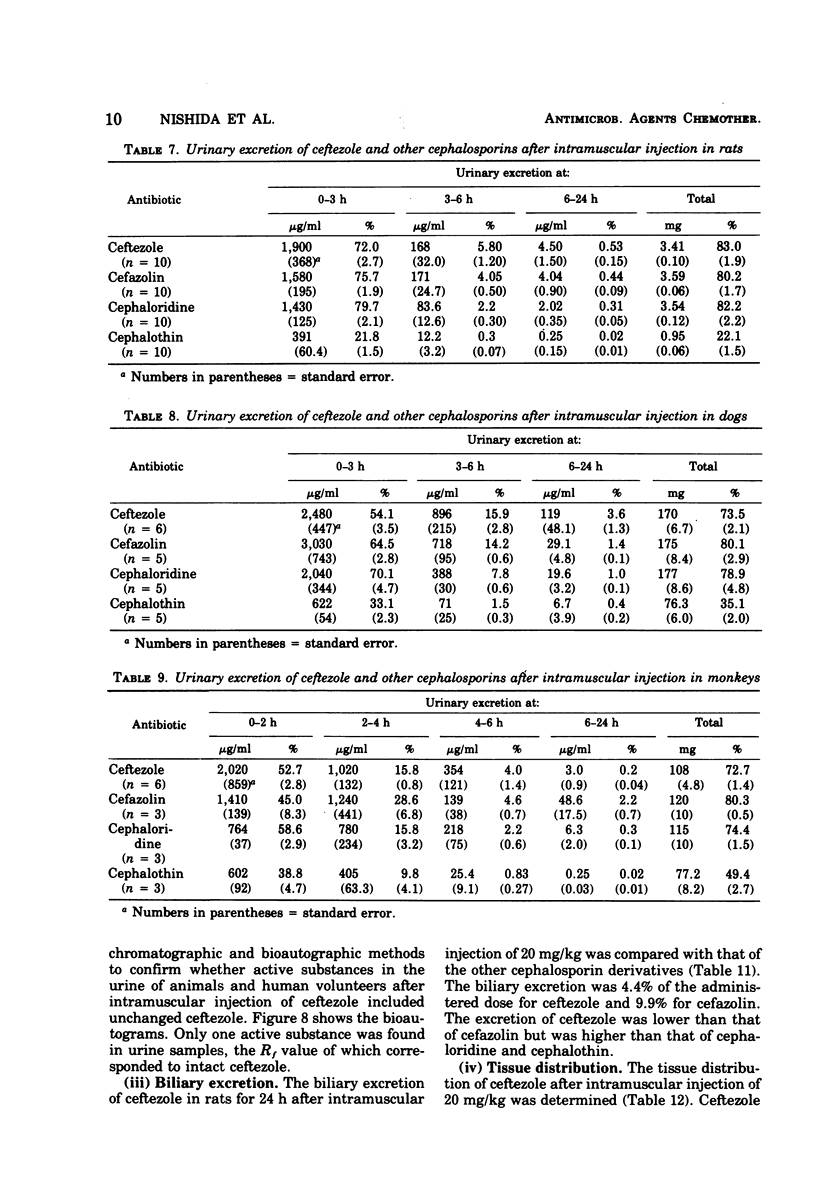
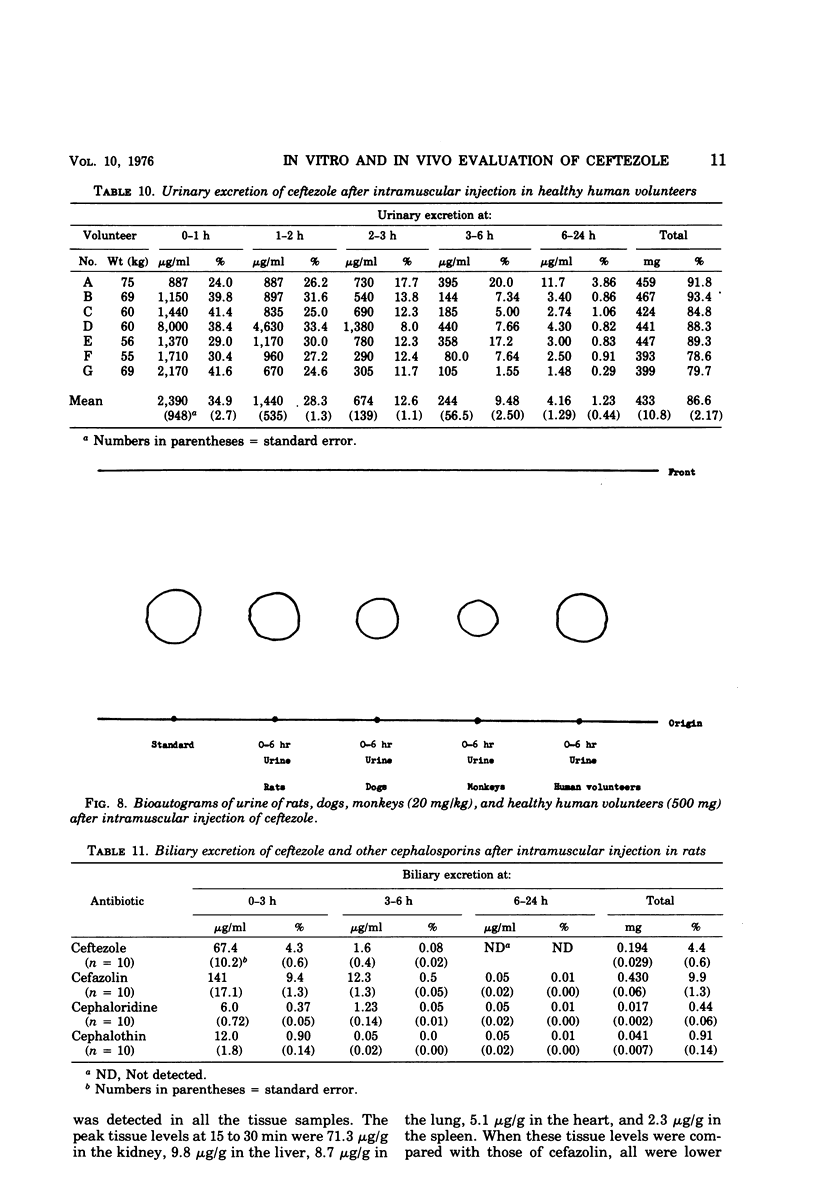
Ceftezole, a new cephalosporin derivative, was compared with cefazolin, cephaloridine, and cephalothin. Data obtained indicate that it is a broad-spectrum antibiotic, with almost identical antimicrobial activity against pathogenic organisms isolated from patients. The therapeutic effect of ceftezole on experimental infections in mice was similar to that of cefazolin and was superior to that of cephalothin. The binding of ceftezole to serum proteins was somewhat less than that of cefazolin. The concentrations of ceftezole in the sera of test animals and human volunteers were determined after intramuscular injection of 20 mg/kg and after a single dose of 500 mg, respectively. The concentration of ceftezole in the serum of volunteers peaked at 24.9 μg/ml 15 min after injection and remained effective (about 2.6 μg/ml) at 4 h. The half-life in serum under the same conditions was 56 min, i.e., about one-half that of cefazolin. The 24-h urinary recovery rate was 87.5%. Most of the administered ceftezole was excreted unchanged mainly through the urinary tract. The biliary excretion rate in SD strain rats after intramuscular injection of 20 mg/kg was about 4.4%. As compared with commercially available cephalosporins, ceftezole was second only to cefazolin in biliary excretion rate. Various tissue levels of ceftezole in animals were higher than cephalothin but, with the exception of renal levels in the early stage after administration, were lower than cefazolin.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Shimizu T. Studies on protein binding of cefazolin and other antibiotics. Jpn J Antibiot. 1974 Jun;27(3):296–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



