Abstract
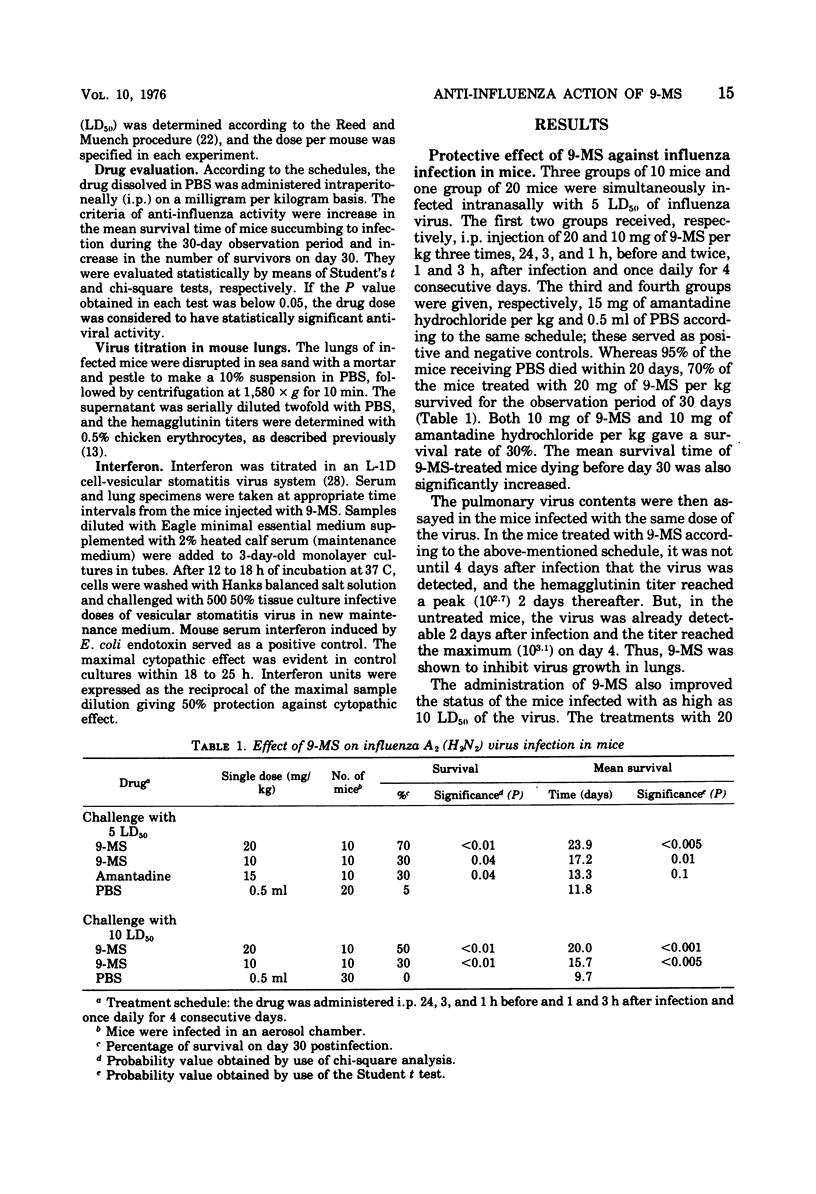
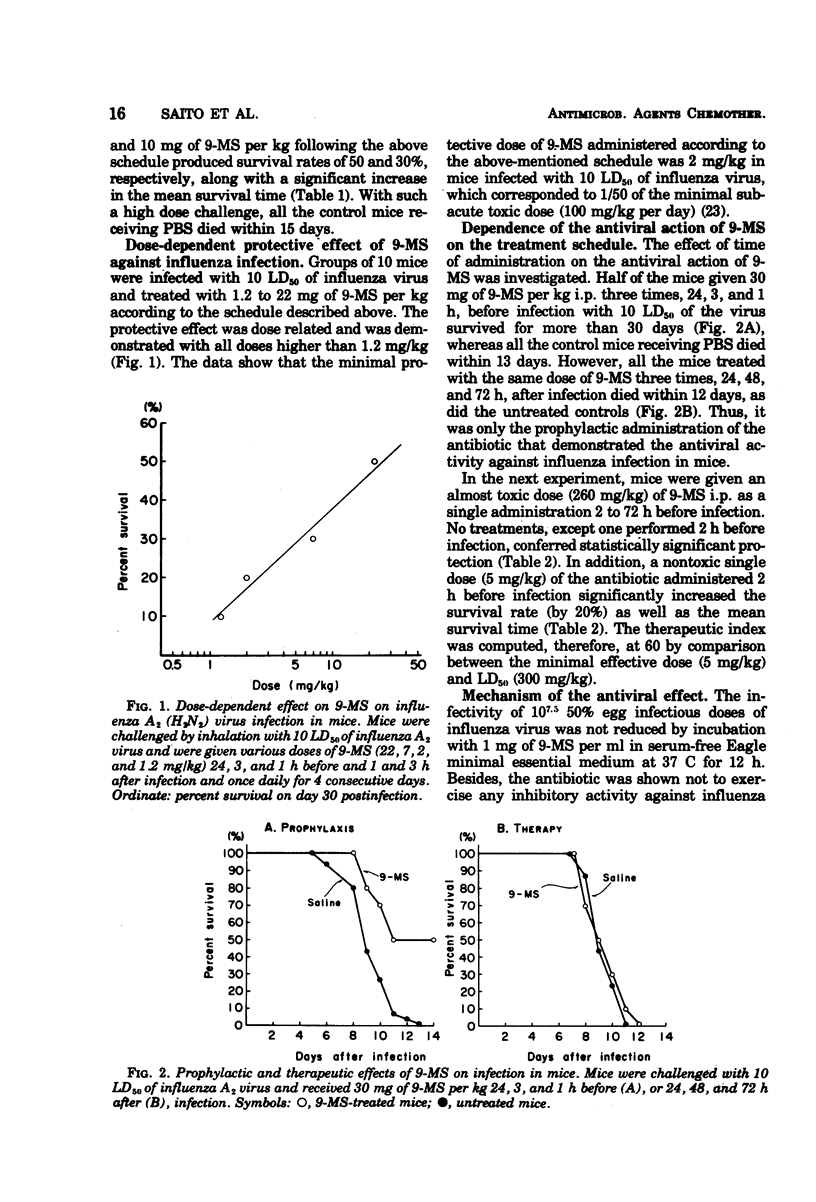
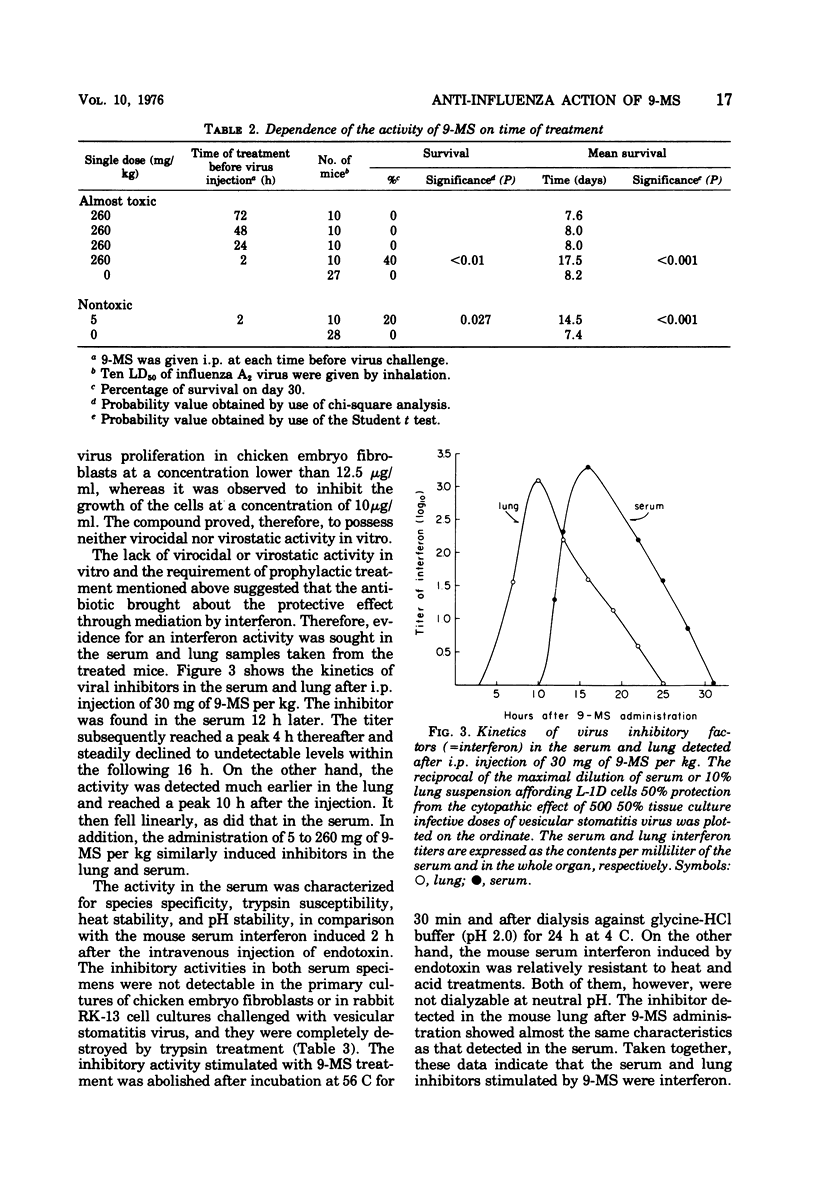
The antiviral effect of 9-methylstreptimidone (9-MS) was examined in mice infected with mouse-adapted influenza A2 (H2N2) virus. Both a single and continuous prophylactic administration of 9-MS protected mice from virus infection, and comparison between the minimal effective and the 50% lethal dose gave a therapeutic index of 60. When the treatment was started after infection, however, no antiviral effect was demonstrated. After a single intraperitoneal administration of 9-MS, a highly potent virus-inhibitory factor was detected in the lungs (10 h later) and the sera (16 h later) of uninfected mice, which was assumed to be an interferon on the basis of the biological characteristics. These results suggest that the protective activity of the antibiotic is due to interferon induction in mice.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Billiau A., Desmyter J., De Somer P. Antiviral activity of chlorite-oxidized oxyamylose, a polyacetal carboxylic acid. J Virol. 1970 Mar;5(3):321–328. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.3.321-328.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black D. R., Eckstein F., DeClercq E., Merigan T. C. Studies on the toxicity and antiviral activity of various polynucleotides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Feb;3(2):198–206. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.2.198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catalano L. W., Jr, Baron S. Protection against herpes virus and encephalomyocarditis virus encephalitis with a double-stranded RNA inducer of interferon. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Feb;133(2):684–687. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claes P., Billiau A., De Clercq E., Desmyter J., Schonne E., Vanderhaeghe H., De Somer P. Polyacetal carboxylic acids: a new group of antiviral polyanions. J Virol. 1970 Mar;5(3):313–320. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.3.313-320.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Clercq E., Merigan T. C. An active interferon inducer obtained from Hemophilus influenzae type B. J Immunol. 1969 Nov;103(5):899–906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Clercq E., Stewart W. E., 2nd, De Somer P. Interferon production linked to toxicity of polyriboinosinic acid-polyribocytidylic acid. Infect Immun. 1972 Sep;6(3):344–347. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.3.344-347.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Somer P., De Clercq E., Billiau A., Schonne E., Claesen M. Antiviral activity of polyacrylic and polymethacrylic acids. II. Mode of action in vivo. J Virol. 1968 Sep;2(9):886–893. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.9.886-893.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field A. K., Tytell A. A., Lampson G. P., Hilleman M. R. Inducers of interferon and host resistance. II. Multistranded synthetic polynucleotide complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Sep;58(3):1004–1010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.3.1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gláz E. T., Szolgay E., Stöger I., Tálas M. Antiviral activity and induction of interferon-like substance by quinacrine and acranil. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 May;3(5):537–541. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.5.537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. A., Baron S., Chanock R. M. The effect of an interferon inducer on influenza virus. Bull World Health Organ. 1969;41(3):689–693. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman W. W., Korst J. J., Niblack J. F., Cronin T. H. N,N-dioctadecyl-N',N'-bis(2-hydroxyethyl) propanediamine: antiviral activity and interferon stimulation in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Apr;3(4):498–502. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.4.498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISHIDA N., KOSAKA Y., SASAKI Y. Studies on experimental influenza in mice. II. Absolute amount of virus introduced into the respiratory tract of mice by standard inhalation procedure. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1959 Dec 25;71:151–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIT S., DUBBS D. R., PIEKARSKI L. J., HSU T. C. DELETION OF THYMIDINE KINASE ACTIVITY FROM L CELLS RESISTANT TO BROMODEOXYURIDINE. Exp Cell Res. 1963 Aug;31:297–312. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(63)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger R. E., Mayer G. D. Tilorone hydrochloride: an orally active antiviral agent. Science. 1970 Sep 18;169(3951):1213–1214. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3951.1213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard B. J., Eccleston E., Jones D. Toxicity of interferon inducers of the double stranded RNA type. Nature. 1969 Dec 6;224(5223):1023–1024. doi: 10.1038/2241023a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer G. D., Krueger R. F. Tilorone hydrochloride: mode of action. Science. 1970 Sep 18;169(3951):1214–1215. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3951.1214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaren C., Potter C. W. The relationship between interferon and virus virulence in influenza virus infections of the mouse. J Med Microbiol. 1973 Feb;6(1):21–32. doi: 10.1099/00222615-6-1-21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy B. R., Baron S., Chalhub E. G., Uhlendorf C. P., Chanock R. M. Temperature-sensitive mutants of influenza virus. IV. Induction of interferon in the nasopharynx by wild-type and a temperature-sensitive recombinant virus. J Infect Dis. 1973 Oct;128(4):488–493. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.4.488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemes M. M., Tytell A. A., Lampson G. P., Field A. K., Hilleman M. R. Inducers of interferon and host resistance. VI. Antiviral efficacy of poly I:C in animal models. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Nov;132(2):776–783. doi: 10.3181/00379727-132-34308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito N., Kitame F., Kikuchi M., Ishida N. Studies on a new antiviral antibiotic, 9-methylstreptimidone. I. Physicochemical and biological properties. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1974 Mar;27(3):206–214. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.27.206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siminoff P., Bernard A. M., Hursky V. S., Price K. E. BL-20803, a new, low-molecular-weight interferon inducer. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Jun;3(6):742–743. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.6.742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki F., Oya J., Ishida N. Effect of antilymphocyte serum on influenza virus infection in mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 May;146(1):78–84. doi: 10.3181/00379727-146-38047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki F., Suganuma T., Ishida N. Letter: Interferon induction by an antitumor antibiotic, lymphomycin. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1974 May;27(5):346–348. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.27.346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngner J. S., Stinebring W. R., Taube S. E. Influence of inhibitors of protein synthesis on interferon formation in mice. Virology. 1965 Dec;27(4):541–550. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90179-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


