Abstract
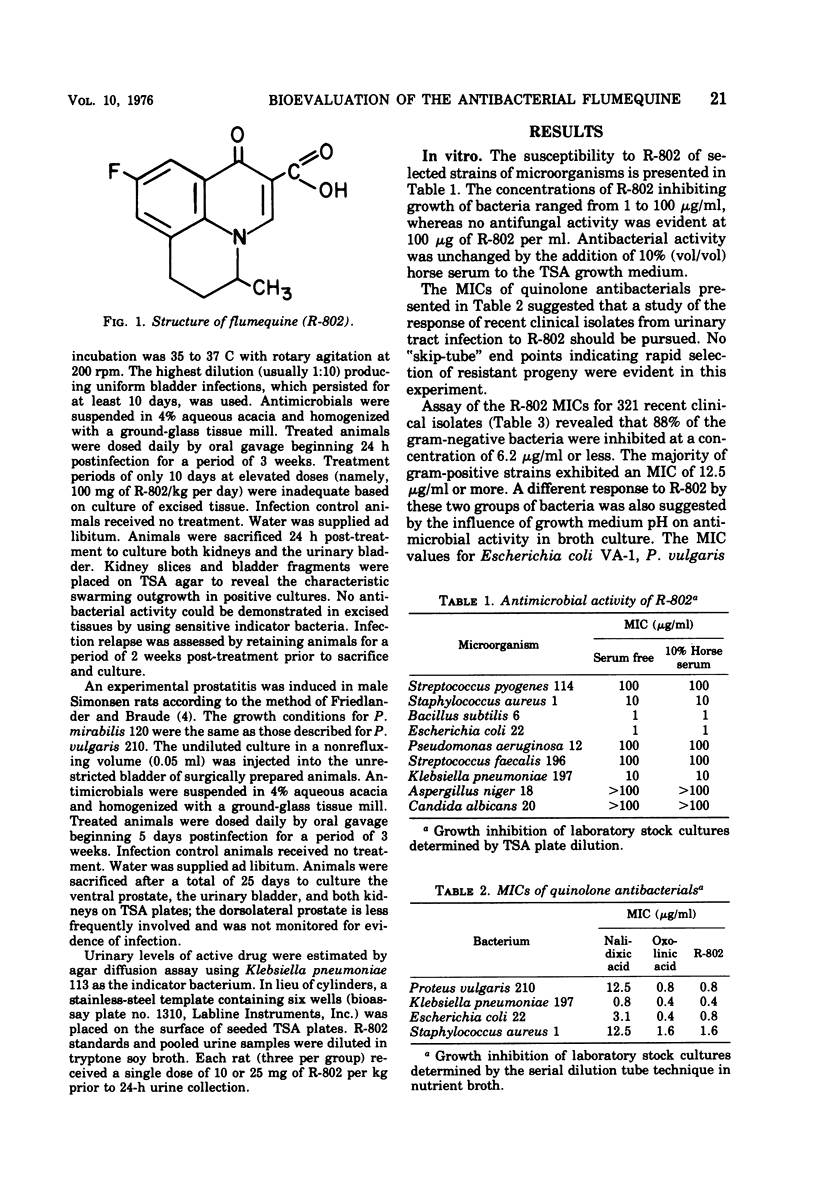
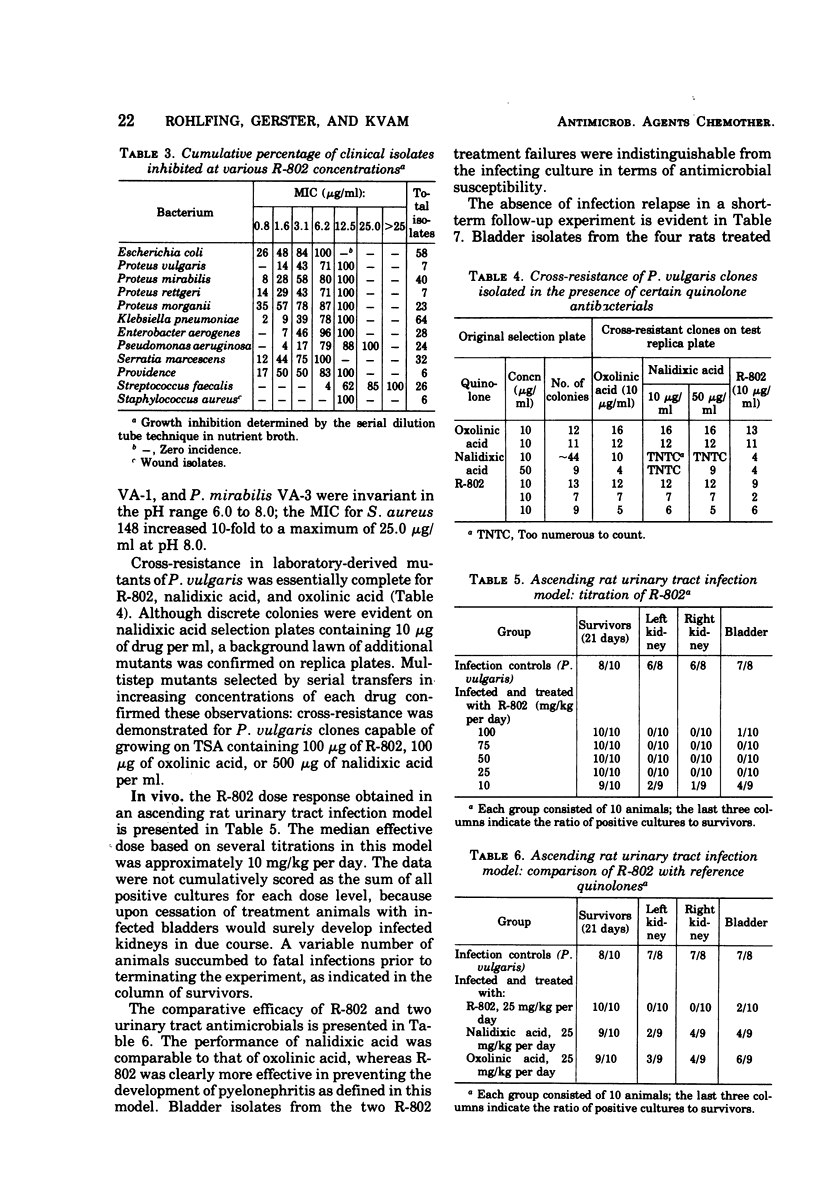
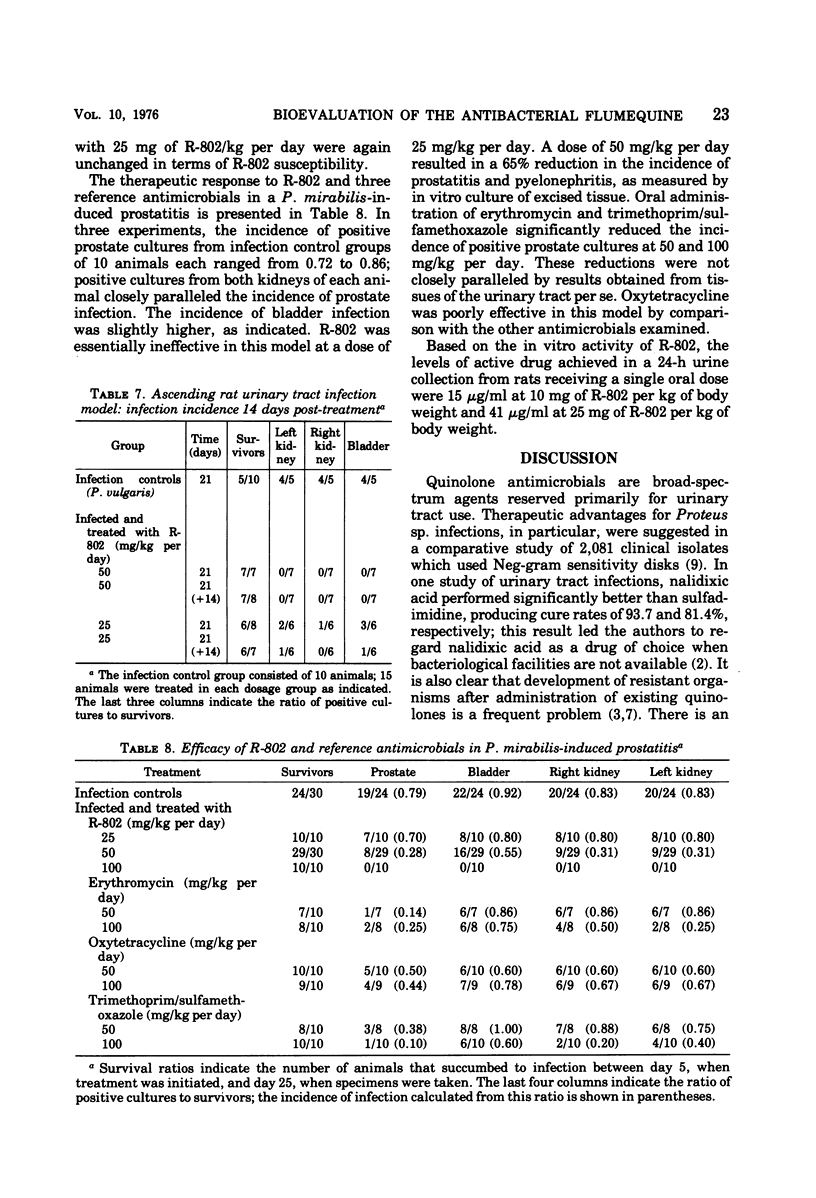
The antimicrobial activity of flumequine (R-802) was characterized by in vitro and in vivo procedures. Assay of the minimal inhibitory concentrations for 321 recent clinical isolates revealed that 88% of the gram-negative bacteria were inhibited by an R-802 concentration of 6.2 μg/ml or less. Cross-resistance in laboratory-derived mutants of Proteus vulgaris was essentially complete for R-802, nalidixic acid, and oxolinic acid, although quantitative differences were evident. R-802 was more effective than either of these quinolone antibacterials in preventing the development of experimental murine pyelonephritis (P. vulgaris). R-802 and trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (1:5) were equally effective in resolving a P. mirabilis-induced prostatitis of rats.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown P. C., Donaghy M. C., Dootson P. H., Titcombe D. H., MacLaren D. M. Sulphadimidine and nalidixic acid therapy in urinary-tract infections in general practice. Practitioner. 1971 Dec;207(242):819–826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark H., Brown N. K., Wallace J. F., Turck M. Emergence of resistant organisms as a function of dose in oxolinic acid therapy. Am J Med Sci. 1971 Mar;261(3):145–148. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197103000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsen P. O., Rhodes P. R. Oxolinic acid, a new chemotherapeutic agent in the treatment of urinary tract infection. J Urol. 1971 Jun;105(6):870–872. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)61650-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamey T. A. Observations on the clinical use of nalidixic acid. Postgrad Med J. 1971 Sep;47(Suppl):21–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



