Abstract
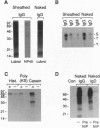
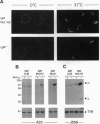
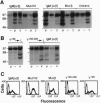
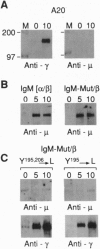
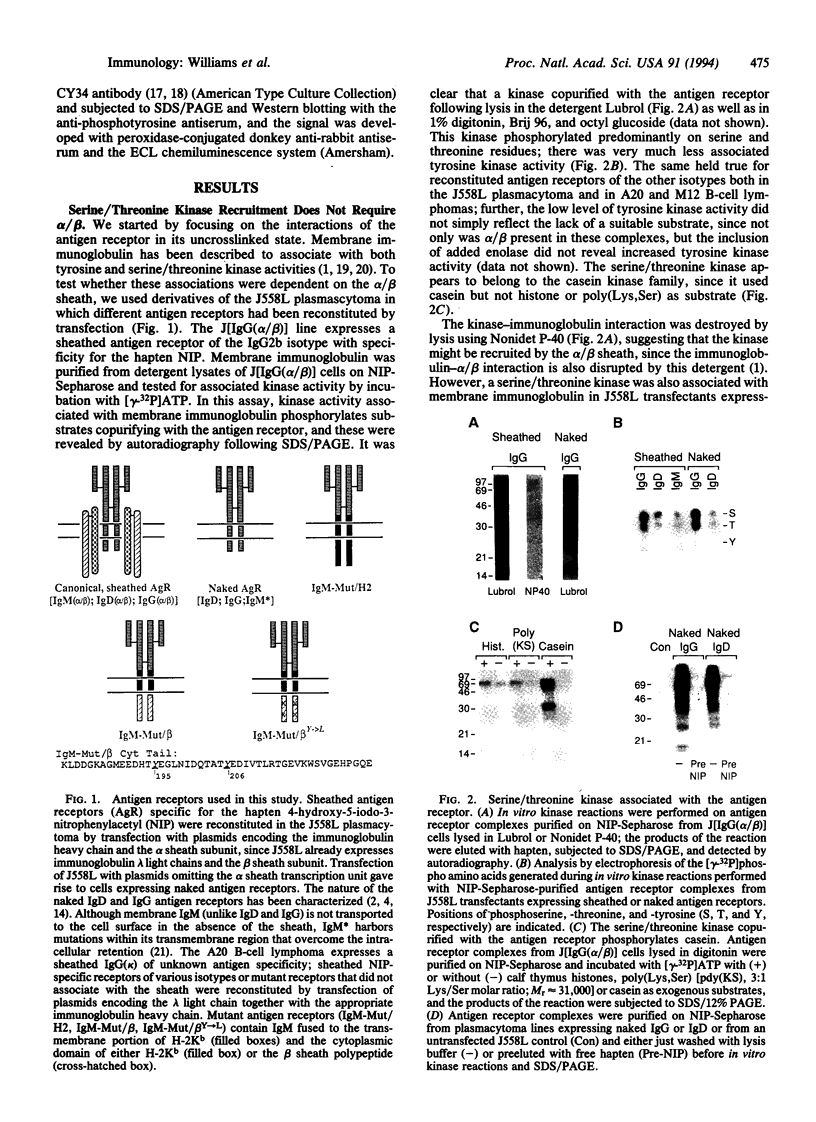
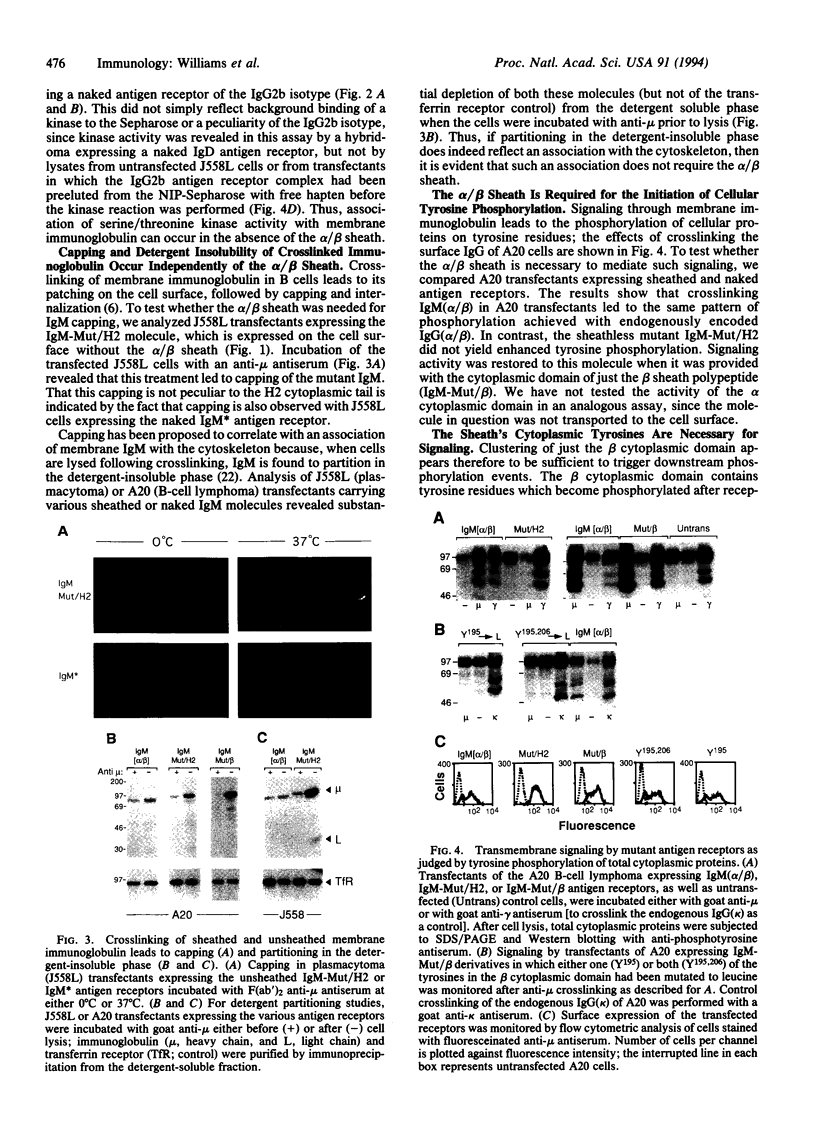
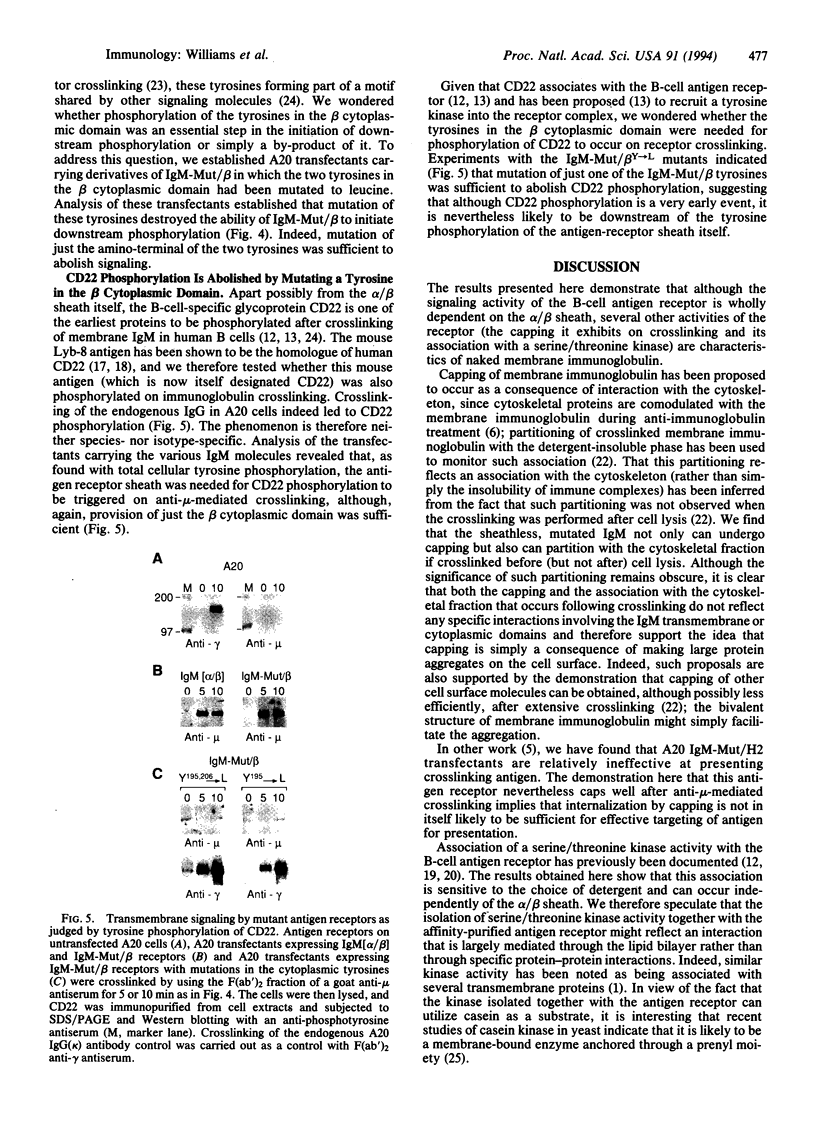
The B-cell antigen receptor is composed of membrane immunoglobulin sheathed by an alpha/beta heterodimer. The complex is noncovalently associated with protein kinase activity, and crosslinking of the receptor leads to capping and transmembrane signaling. Here we show that the sheath is not necessary either for this capping or for the association of membrane immunoglobulin with the detergent-insoluble cytoskeletal fraction that occurs following crosslinking. It is also not required for association of membrane immunoglobulin with a casein-kinase-like serine/threonine kinase. The sheath is essential, however, for transmembrane signaling. Provision of just the cytoplasmic domain of the beta sheath polypeptide to a mutant, unsheathed IgM molecule was sufficient to restore full signaling capability as judged by the phosphorylation of a variety of cellular proteins, including the B-cell-specific transmembrane protein CD22. This signaling was destroyed by mutating one of the tyrosines in the beta cytoplasmic domain. These results not only suggest that receptor signaling is mediated through phosphorylation of the tyrosines in the sheath's cytoplasmic domains but, together with previous work, indicate that different motifs within the sheath mediate presentation and signaling.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bijsterbosch M. K., Meade C. J., Turner G. A., Klaus G. G. B lymphocyte receptors and polyphosphoinositide degradation. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):999–1006. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80080-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., Hochman P. S., Unanue E. R. Ligand-induced association of surface immunoglobulin with the detergent-insoluble cytoskeletal matrix of the B lymphocyte. J Immunol. 1982 Mar;128(3):1198–1204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell M. A., Sefton B. M. Protein tyrosine phosphorylation is induced in murine B lymphocytes in response to stimulation with anti-immunoglobulin. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2125–2131. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07381.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Auger K. R., Carpenter C., Duckworth B., Graziani A., Kapeller R., Soltoff S. Oncogenes and signal transduction. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):281–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90639-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter R. H., Park D. J., Rhee S. G., Fearon D. T. Tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C induced by membrane immunoglobulin in B lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2745–2749. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. R., Campbell K. S., Kazlauskas A., Johnson S. A., Hertz M., Potter T. A., Pleiman C., Cambier J. C. The B cell antigen receptor complex: association of Ig-alpha and Ig-beta with distinct cytoplasmic effectors. Science. 1992 Oct 2;258(5079):123–126. doi: 10.1126/science.1439759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold M. R., Law D. A., DeFranco A. L. Stimulation of protein tyrosine phosphorylation by the B-lymphocyte antigen receptor. Nature. 1990 Jun 28;345(6278):810–813. doi: 10.1038/345810a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold M. R., Matsuuchi L., Kelly R. B., DeFranco A. L. Tyrosine phosphorylation of components of the B-cell antigen receptors following receptor crosslinking. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3436–3440. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane P. J., McConnell F. M., Schieven G. L., Clark E. A., Ledbetter J. A. The role of class II molecules in human B cell activation. Association with phosphatidyl inositol turnover, protein tyrosine phosphorylation, and proliferation. J Immunol. 1990 May 15;144(10):3684–3692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law C. L., Torres R. M., Sundberg H. A., Parkhouse R. M., Brannan C. I., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A., Clark E. A. Organization of the murine Cd22 locus. Mapping to chromosome 7 and characterization of two alleles. J Immunol. 1993 Jul 1;151(1):175–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law D. A., Gold M. R., DeFranco A. L. Examination of B lymphoid cell lines for membrane immunoglobulin-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation and src-family tyrosine kinase mRNA expression. Mol Immunol. 1992 Jul-Aug;29(7-8):917–926. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(92)90130-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leprince C., Draves K. E., Geahlen R. L., Ledbetter J. A., Clark E. A. CD22 associates with the human surface IgM-B-cell antigen receptor complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3236–3240. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leprince C., Draves K. E., Ledbetter J. A., Torres R. M., Clark E. A. Characterization of molecular components associated with surface immunoglobulin M in human B lymphocytes: presence of tyrosine and serine/threonine protein kinases. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Aug;22(8):2093–2099. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuberger M. S., Patel K. J., Dariavach P., Nelms K., Peaker C. J., Williams G. T. The mouse B-cell antigen receptor: definition and assembly of the core receptor of the five immunoglobulin isotypes. Immunol Rev. 1993 Apr;132:147–161. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1993.tb00841.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel K. J., Neuberger M. S. Antigen presentation by the B cell antigen receptor is driven by the alpha/beta sheath and occurs independently of its cytoplasmic tyrosines. Cell. 1993 Sep 10;74(5):939–946. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90473-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesando J. M., Bouchard L. S., McMaster B. E. CD19 is functionally and physically associated with surface immunoglobulin. J Exp Med. 1989 Dec 1;170(6):2159–2164. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.6.2159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieker T., Penninger J., Hala K., Cooper M. D., Wick G. In situ analyses of in ovo graft-vs.-host reaction induced by thymic nurse cell lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Apr;23(4):904–910. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiner G. F., Unanue E. R. Membrane and cytoplasmic changes in B lymphocytes induced by ligand-surface immunoglobulin interaction. Adv Immunol. 1976;24:37–165. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60329-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulte R. J., Campbell M. A., Fischer W. H., Sefton B. M. Tyrosine phosphorylation of CD22 during B cell activation. Science. 1992 Nov 6;258(5084):1001–1004. doi: 10.1126/science.1279802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symington F. W., Subbarao B., Mosier D. E., Sprent J. Lyb-8.2: A new B cell antigen defined and characterized with a monoclonal antibody. Immunogenetics. 1982;16(5):381–391. doi: 10.1007/BF00372098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Noesel C. J., Borst J., De Vries E. F., Van Lier R. A. Identification of two distinct phosphoproteins as components of the human B cell antigen receptor complex. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Dec;20(12):2789–2793. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830201238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkitaraman A. R., Williams G. T., Dariavach P., Neuberger M. S. The B-cell antigen receptor of the five immunoglobulin classes. Nature. 1991 Aug 29;352(6338):777–781. doi: 10.1038/352777a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang P. C., Vancura A., Mitcheson T. G., Kuret J. Two genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae encode a membrane-bound form of casein kinase-1. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Mar;3(3):275–286. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.3.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. T cell antigen receptor signal transduction: a tale of tails and cytoplasmic protein-tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1993 Apr 23;73(2):209–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90221-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wienands J., Reth M. Glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol linkage as a mechanism for cell-surface expression of immunoglobulin D. Nature. 1992 Mar 19;356(6366):246–248. doi: 10.1038/356246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams G. T., Dariavach P., Venkitaraman A. R., Gilmore D. J., Neuberger M. S. Membrane immunoglobulin without sheath or anchor. Mol Immunol. 1993 Nov;30(16):1427–1432. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(93)90104-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams G. T., Venkitaraman A. R., Gilmore D. J., Neuberger M. S. The sequence of the mu transmembrane segment determines the tissue specificity of the transport of immunoglobulin M to the cell surface. J Exp Med. 1990 Mar 1;171(3):947–952. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.3.947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]