Abstract
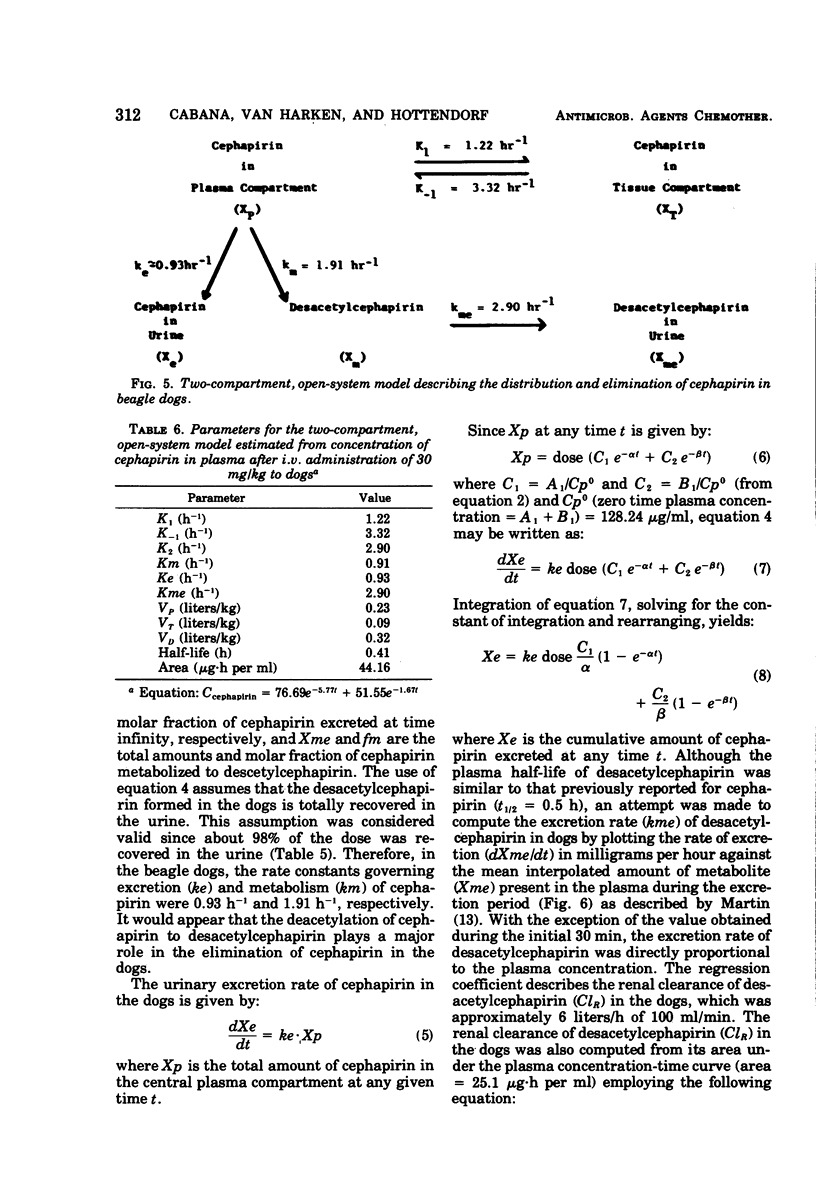
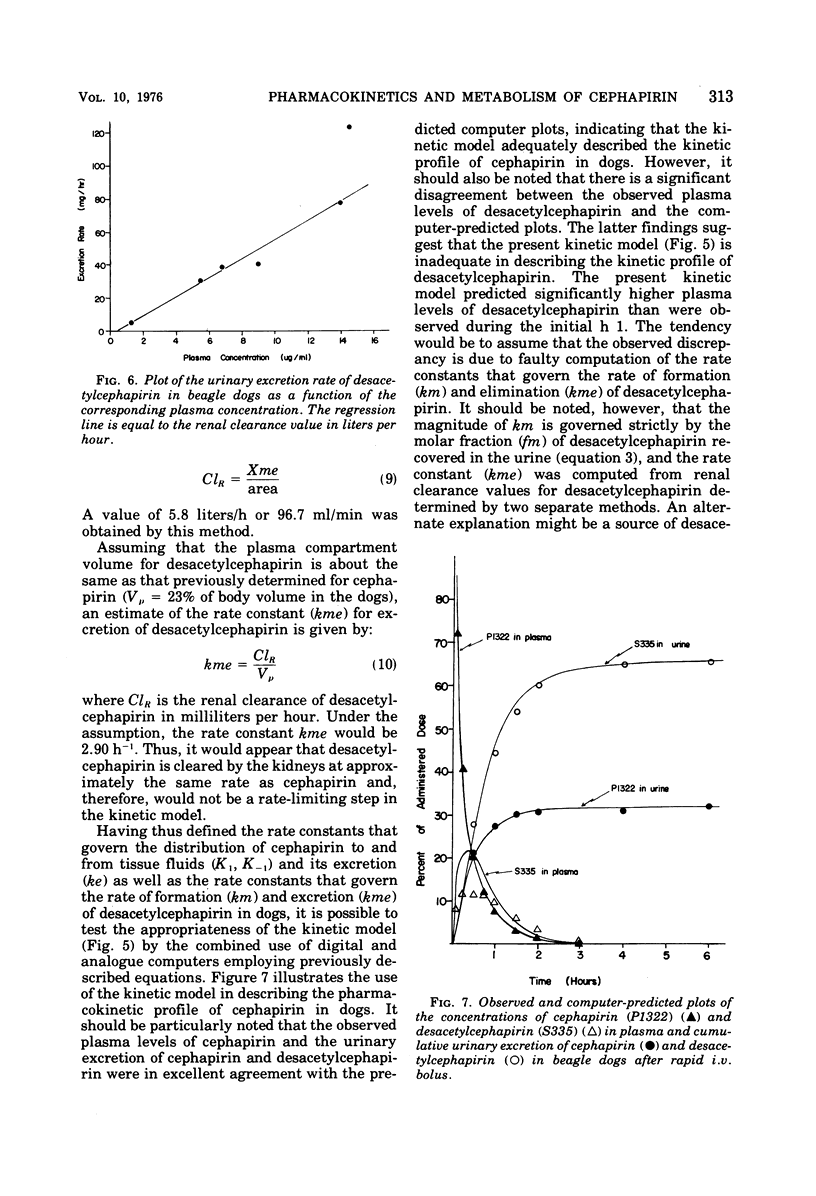
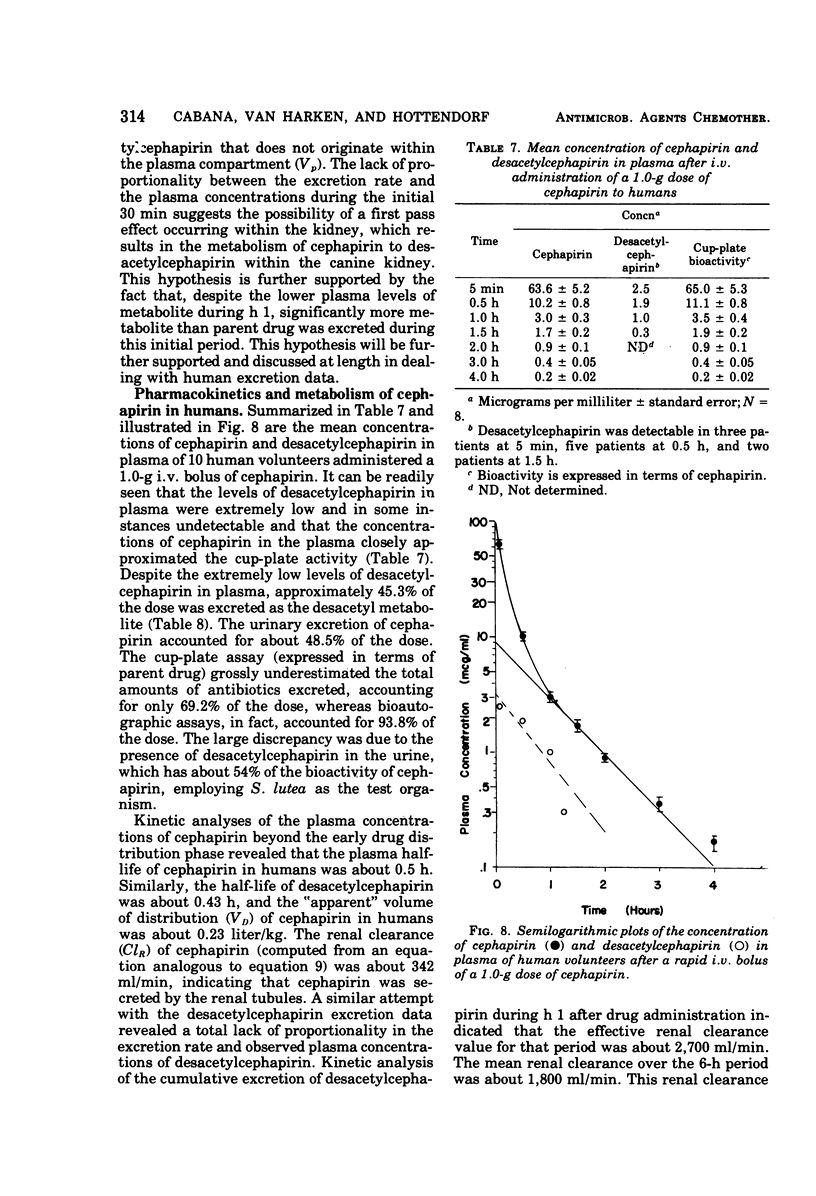
Comparative drug disposition studies in mice, rats, dogs, and humans indicate that cephapirin, a new semisynthetic cephalosporin antibiotic that exhibits broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity, is metabolized to desacetylcephapirin in these species. Pharmacokinetic analyses of the concentrations of cephapirin and desacetylcephapirin in plasma and urine reveal that the rate and extent of deacetylation decreases from rodents to dogs to humans. The kinetic analyses also suggest that the kidney performs a role not only in the excretion but also in the metabolism of cephapirin to desacetylcephapirin.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axelrod J., Meyers B. R., Hirschman S. Z. Cephapirin: pharmacology in normal human volunteers. J Clin Pharmacol New Drugs. 1972 Feb-Mar;12(2):84–88. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1972.tb00150.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodner S. J., Koenig M. G. Clinical and in vitro evaluation of cephapirin: a new parenteral cephalosporin. Am J Med Sci. 1972 Jan;263(1):43–51. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197201000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bran J. L., Levison M. E., Kaye D. Clinical and in vitro evaluation of cephapirin, a new cephalosporin antibiotic. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Jan;1(1):35–40. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.1.35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabana B. E., Van Harken D. R., Hottendorf G. H., Doluisio J. T., Griffen W. O., Jr, Bourne D. W., Dittert L. W. The role of the kidney in the elimination of cephapirin in man. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1975 Dec;3(6):419–438. doi: 10.1007/BF01059474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirshbaum A., Arret B. Outline of details for official microbiological assays of antibiotics. J Pharm Sci. 1967 Apr;56(4):511–515. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600560418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEE C. C., HERR E. B., Jr, ANDERSON R. C. Pharmacological and toxicological studies on cephalotin. Clin Med (Northfield) 1963 Jun;70:1123–1138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loo J. C., Riegelman S. New method for calculating the intrinsic absorption rate of drugs. J Pharm Sci. 1968 Jun;57(6):918–928. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600570602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin B. K. Treatment of data from drug urinary excretion. Nature. 1967 Apr 15;214(5085):247–249. doi: 10.1038/214247a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennick B. R. Renal excretion of drugs: tubular transport and metabolism. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1972;12:141–156. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.12.040172.001041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riegelman S., Loo J. C., Rowland M. Shortcomings in pharmacokinetic analysis by conceiving the body to exhibit properties of a single compartment. J Pharm Sci. 1968 Jan;57(1):117–123. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600570123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riegelman S., Loo J., Rowland M. Concept of a volume of distribution and possible errors in evaluation of this parameter. J Pharm Sci. 1968 Jan;57(1):128–133. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600570125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu T. Serum levels and urinary excretion of parent antibiotics and desacetyl forms after parenteral administration of cephalothin and cephapirin. Jpn J Antibiot. 1975 Aug;28(4):628–633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner J. G., Northam J. I. Estimation of volume of distribution and half-life of a compound after rapid intravenous injection. J Pharm Sci. 1967 Apr;56(4):529–531. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600560424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wan S. H., Riegelman S. Renal contribution to overall metabolism of drugs. I. Conversion of benzoic acid to hippuric acid. J Pharm Sci. 1972 Aug;61(8):1278–1284. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600610822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wan S. H., Riegelman S. Renal contribution to overall metabolism of drugs. II. Biotransformation of salicylic acid to salicyluric acid. J Pharm Sci. 1972 Aug;61(8):1284–1287. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600610823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wan S. H., Von Lehmann B., Riegelman S. Renal contribution to overall metabolism of drugs. 3. Metabolism of p-aminobenzoic acid. J Pharm Sci. 1972 Aug;61(8):1288–1292. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600610824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



