Abstract
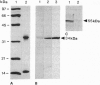
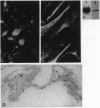
We have cloned a protein from bovine brain, brain-derived voltage-dependent anion channel 1 (BR1-VDAC), that is identical to a recently sequenced plasmalemmal-bound porin from human lymphocytes. mRNA hybridization indicates that BR1-VDAC is widely distributed throughout nervous and nonnervous tissues. In situ localization substantiated that the BR1-VDAC is associated with the plasmalemma of astrocytes. A monoclonal antibody that recognizes the N terminus of the BR1-VDAC protein completely blocks an astrocytic high-conductance anion channel that has electrophysiological similarities with the mitochondrial VDAC. Since the high-conductance anion channel in astrocytes has been shown to respond to hypoosmotic solutions, its molecular identification provides the basis for a better understanding of volume regulation in brain tissue.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AUTILIO L. A., NORTON W. T., TERRY R. D. THE PREPARATION AND SOME PROPERTIES OF PURIFIED MYELIN FROM THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. J Neurochem. 1964 Jan;11:17–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1964.tb06719.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babel D., Walter G., Götz H., Thinnes F. P., Jürgens L., König U., Hilschmann N. Studies on human porin. VI. Production and characterization of eight monoclonal mouse antibodies against the human VDAC "Porin 31HL" and their application for histotopological studies in human skeletal muscle. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1991 Dec;372(12):1027–1034. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1991.372.2.1027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R., Brdiczka D. The cation-selective substate of the mitochondrial outer membrane pore: single-channel conductance and influence on intermembrane and peripheral kinases. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1992 Feb;24(1):33–39. doi: 10.1007/BF00769528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blachly-Dyson E., Zambronicz E. B., Yu W. H., Adams V., McCabe E. R., Adelman J., Colombini M., Forte M. Cloning and functional expression in yeast of two human isoforms of the outer mitochondrial membrane channel, the voltage-dependent anion channel. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 25;268(3):1835–1841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatz A. L., Magleby K. L. Single voltage-dependent chloride-selective channels of large conductance in cultured rat muscle. Biophys J. 1983 Aug;43(2):237–241. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84344-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bureau M. H., Khrestchatisky M., Heeren M. A., Zambrowicz E. B., Kim H., Grisar T. M., Colombini M., Tobin A. J., Olsen R. W. Isolation and cloning of a voltage-dependent anion channel-like Mr 36,000 polypeptide from mammalian brain. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8679–8684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole T., Awni L. A., Nyakatura E., Götz H., Walter G., Thinnes F. P., Hilschmann N. Studies on human porin. VIII. Expression of "Porin 31HL" channels in the plasmalemma of the acute-lymphoblastic-leukemia cell line KM3 as revealed by light- and electron-microscopy. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1992 Sep;373(9):891–896. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1992.373.2.891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colombini M. A candidate for the permeability pathway of the outer mitochondrial membrane. Nature. 1979 Jun 14;279(5714):643–645. doi: 10.1038/279643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Pinto V., Prezioso G., Thinnes F., Link T. A., Palmieri F. Peptide-specific antibodies and proteases as probes of the transmembrane topology of the bovine heart mitochondrial porin. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 22;30(42):10191–10200. doi: 10.1021/bi00106a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalonen T., Johansson S., Holopainen I., Oja S. S., Arhem P. A high-conductance multi-state anion channel in cultured rat astrocytes. Acta Physiol Scand. 1989 Aug;136(4):611–612. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1989.tb08709.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimelberg H. K., Anderson E., Kettenmann H. Swelling-induced changes in electrophysiological properties of cultured astrocytes and oligodendrocytes. II. Whole-cell currents. Brain Res. 1990 Oct 8;529(1-2):262–268. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90836-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb H. A., Brown C. D., Murer H. Identification of a voltage-dependent anion channel in the apical membrane of a Cl(-)-secretory epithelium (MDCK). Pflugers Arch. 1985 Mar;403(3):262–265. doi: 10.1007/BF00583597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König U., Götz H., Walter G., Babel D., Hohmeier H. E., Thinnes F. P., Hilschmann N. Zur Kenntnis der Porine des Menschen. V. Die Plasmalemmständigkeit von "Porin 31HL" ist keine Folge einer Zell-Transformation. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1991 Aug;372(8):565–572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrero Hector, Orkand Paula M., Kettenmann Helmut, Orkand Richard K. Single Channel Recording from Glial Cells on the Untreated Surface of the Frog Optic Nerve. Eur J Neurosci. 1991;3(8):813–819. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1991.tb01677.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy S., Pearce B. Functional receptors for neurotransmitters on astroglial cells. Neuroscience. 1987 Aug;22(2):381–394. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90342-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak L., Ascher P., Berwald-Netter Y. Ionic channels in mouse astrocytes in culture. J Neurosci. 1987 Jan;7(1):101–109. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-01-00101.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schein S. J., Colombini M., Finkelstein A. Reconstitution in planar lipid bilayers of a voltage-dependent anion-selective channel obtained from paramecium mitochondria. J Membr Biol. 1976 Dec 28;30(2):99–120. doi: 10.1007/BF01869662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarze W., Kolb H. A. Voltage-dependent kinetics of an anionic channel of large unit conductance in macrophages and myotube membranes. Pflugers Arch. 1984 Nov;402(3):281–291. doi: 10.1007/BF00585511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnhof U. Single voltage-dependent K+ and Cl- channels in cultured rat astrocytes. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1987 May;65(5):1043–1050. doi: 10.1139/y87-165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thinnes F. P., Götz H., Kayser H., Benz R., Schmidt W. E., Kratzin H. D., Hilschmann N. Zur Kenntnis der Porine des Menschen. I. Reinigung eines Porins aus menschlichen B-Lymphozyten (Porin 31HL) und sein topochemischer Nachweis auf dem Plasmalemm der Herkunftszelle. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1989 Dec;370(12):1253–1264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thinnes F. P., Schmid A., Benz R., Hilschmann N. Studies on human porin. III. Does the voltage-dependent anion channel "Porin 31HL" form part of the chloride channel complex, which is observed in different cells and thought to be affected in cystic fibrosis? Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1990 Nov;371(11):1047–1050. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1990.371.2.1047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usowicz M. M., Gallo V., Cull-Candy S. G. Multiple conductance channels in type-2 cerebellar astrocytes activated by excitatory amino acids. Nature. 1989 Jun 1;339(6223):380–383. doi: 10.1038/339380a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]