Abstract
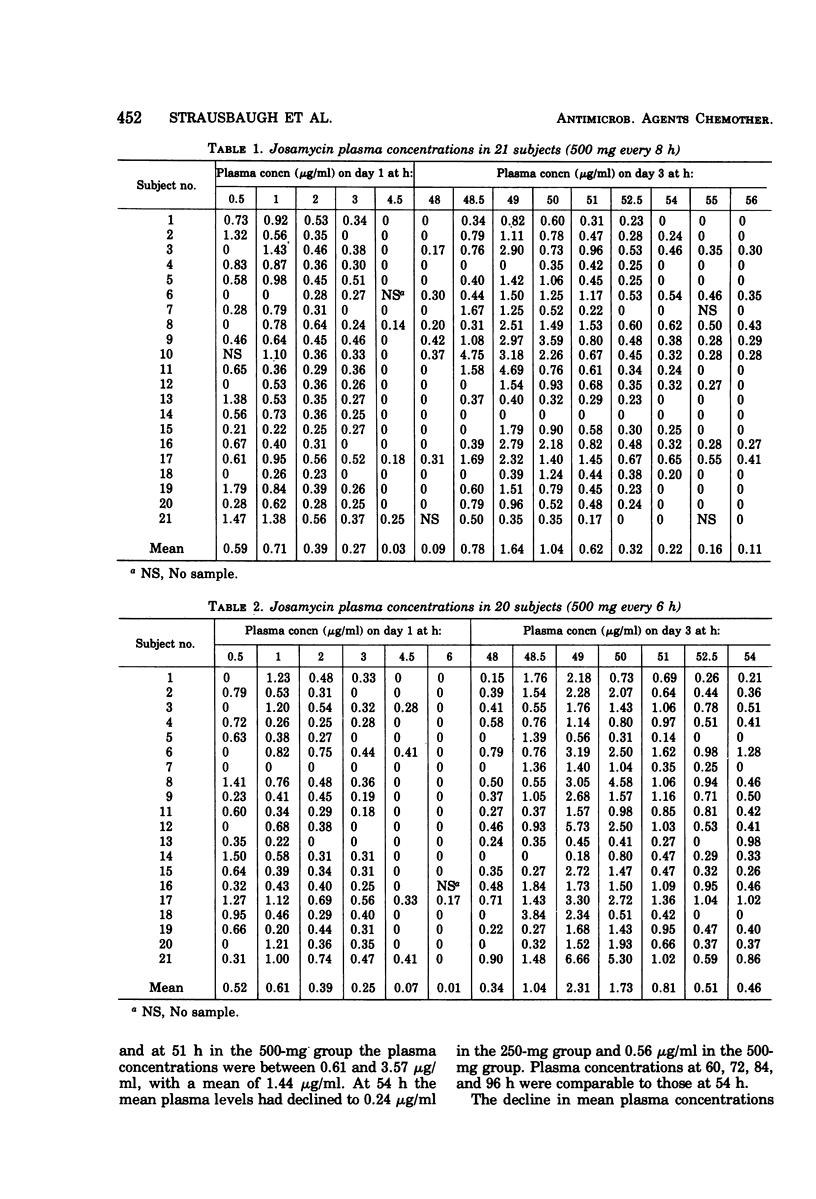
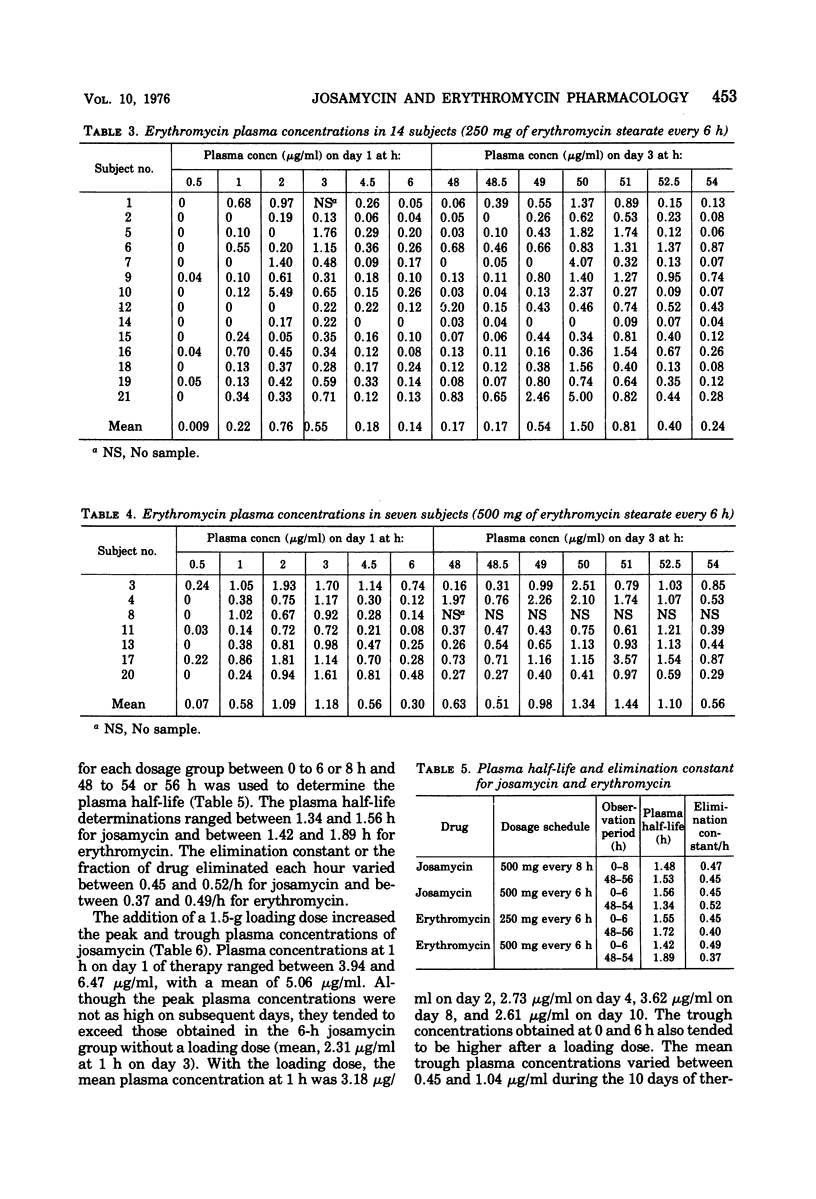
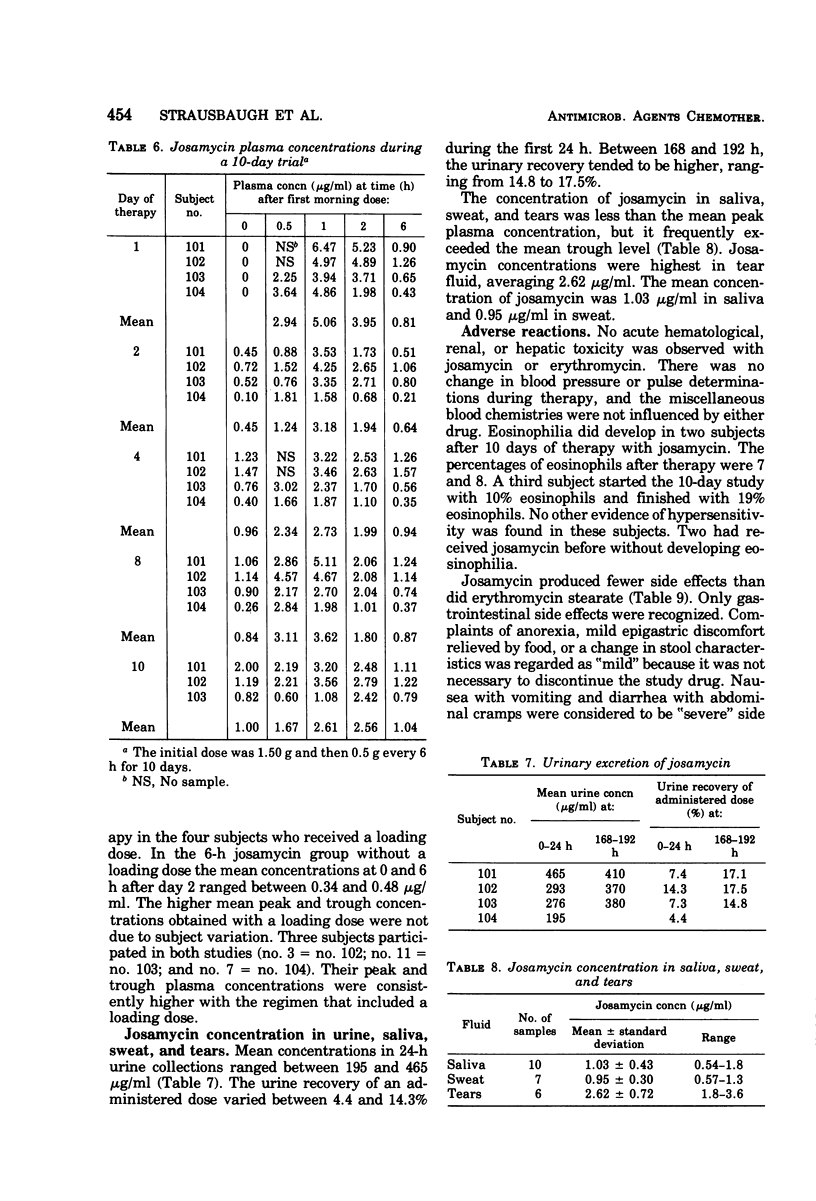
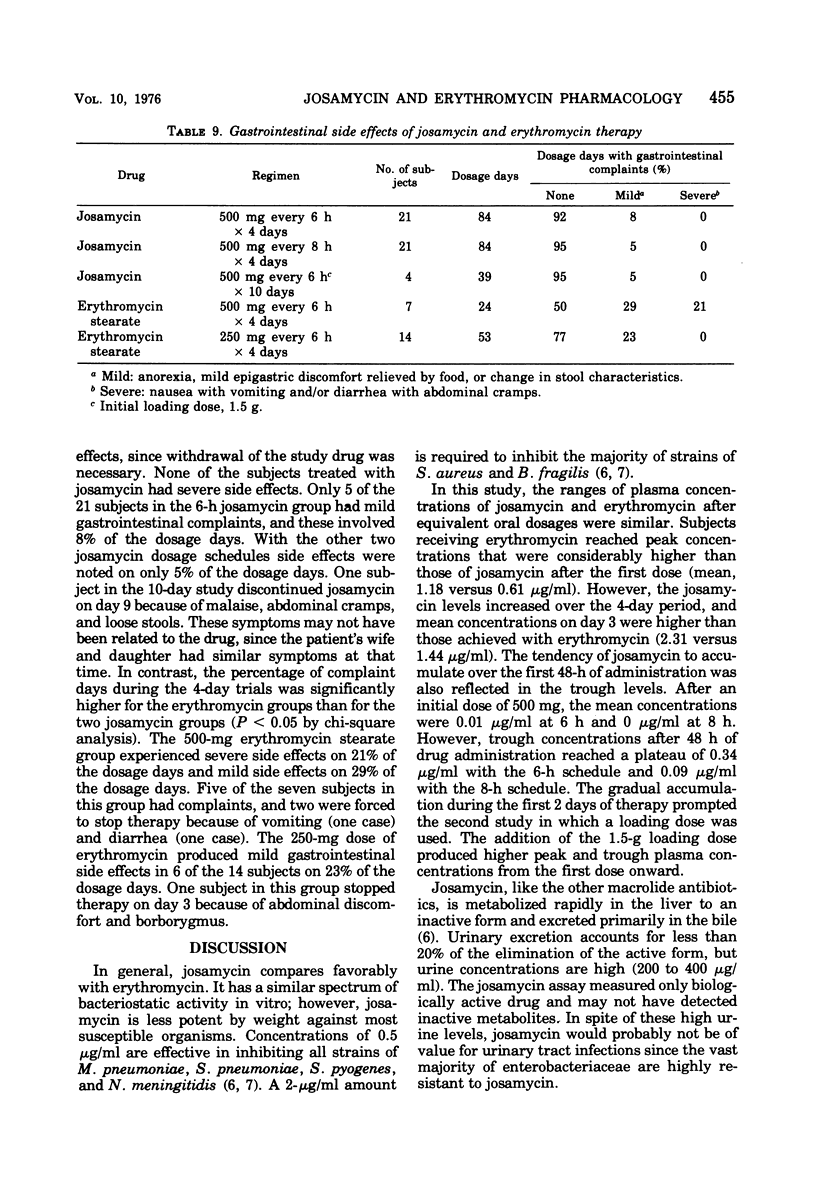
Two macrolide antibiotics, josamycin and erythromycin stearate, were administered orally to healthy, adult male volunteers for a comparative study of their pharmacological properties. In comparable doses, josamycin and erythromycin produced similar plasma concentrations, with similar half-lives and elimination constants. An initial loading dose of 1.5 g of josamycin produced greater peak concentrations of antibiotic throughout a 10-day period with a regimen of every 6 h. In addition, josamycin tended to reach higher peak and trough concentrations after regimens of every 6 or 8 h were maintained for 2 days. Josamycin penetrated into saliva, sweat, and tears, and it was better tolerated in fasting subjects than was erythromycin stearate.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BILLOW B. W., THOMPSON E. A., STERN A., FLORIO A. A CLINICAL STUDY OF ERYTHROMYCIN: A COMPARATIVE EVALUATION OF SEVERAL SALTS. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 1964 May;6:381–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devine L. F., Knowles R. C., Pierce W. E., Peckinpaugh R. O., Hagerman C. R., Lytle R. I. Proposed model for screening antimicrobial agents for potential use in eliminating meningococci from the nasopharynx of healthy carriers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1968;8:307–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeprich P. D. Prediction of antimeningococcic chemoprophylactic efficacy. J Infect Dis. 1971 Feb;123(2):125–133. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.2.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strausbaugh L. J., Dilworth J. A., Gwaltney J. M., Jr, Sande M. A. In vitro susceptibility studies with josamycin and erythromycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Mar;9(3):546–548. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.3.546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



