Abstract
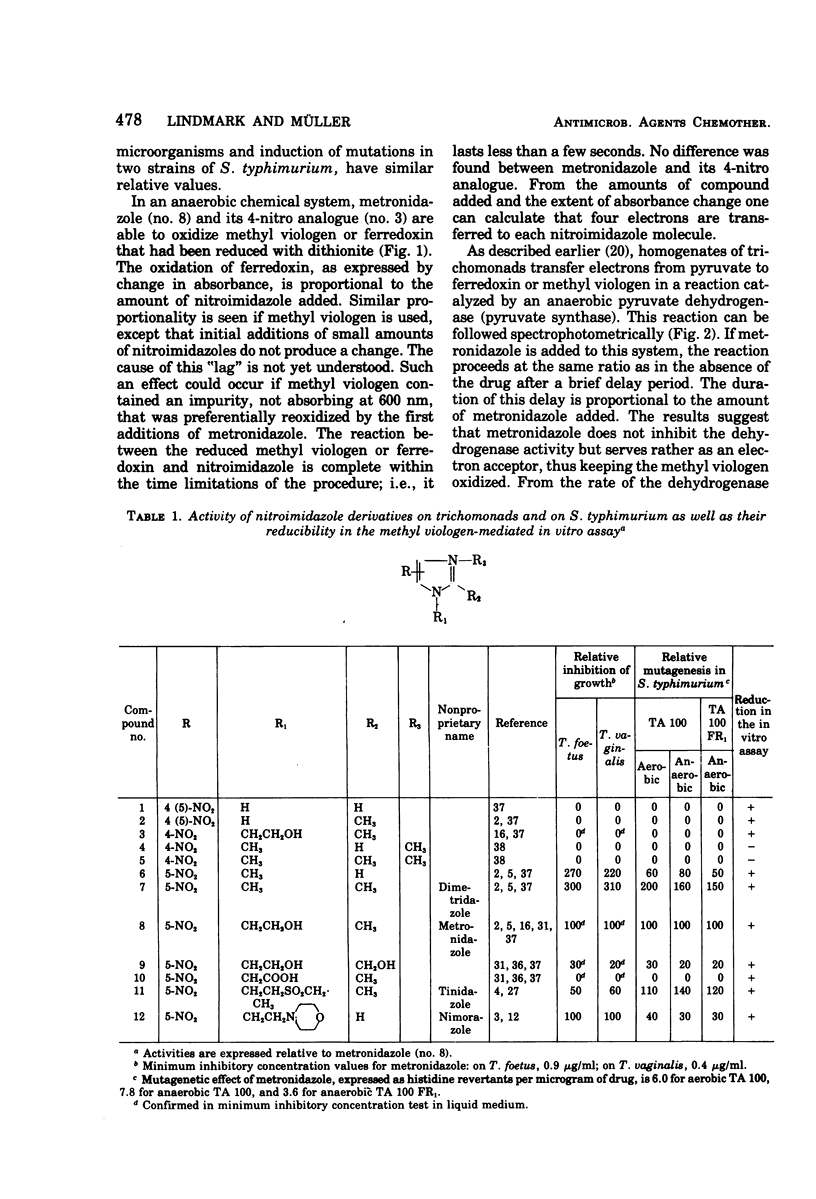
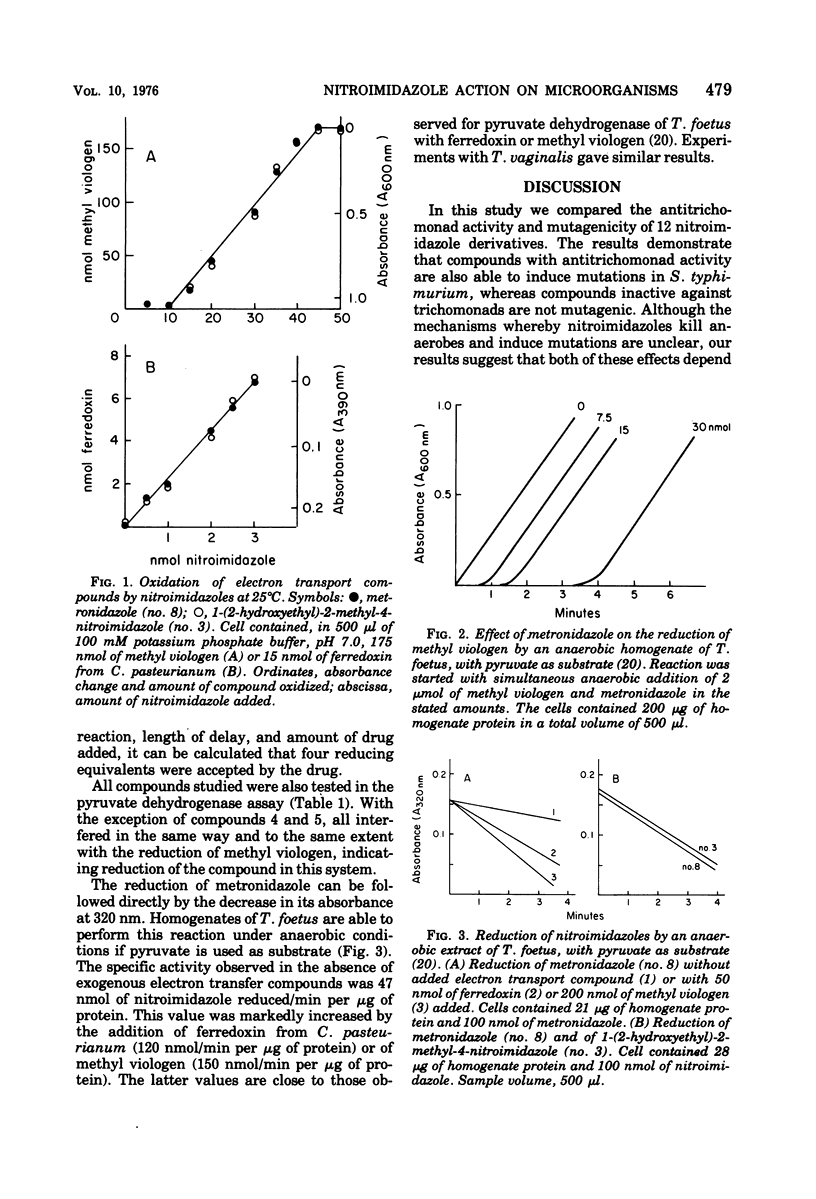
Twelve 4- and 5-nitroimidazole derivatives, including metronidazole and two of its metabolites, tinidazole, dimetridazole, and nimorazole, were tested for antitrichomonad action on Tritrichomonas foetus (KV1) and Trichomonas vaginalis (ATCC 30001) for mutagenicity on a nitroreductase-positive (TA 100) and a nitroreductase-deficient (TA 100-FR1) strain of Salmonella typhimurium, as well as for the reducibility of the nitro group by T. foetus homogenates. Compounds with activity <1% of that of metronidazole are regarded as inactive. All antitrichomonad compounds induce mutations and can be reduced. S. typhimurium TA 100 gave mutations under both aerobiosis and anaerobiosis; TA 100-FR1, however, gave mutations only under anaerobiosis. Certain compounds that are reducible, and the nonreducible derivatives, were inactive. Metronidazole and its inactive 4-nitro analogue were reduced in a four-electron process in ferredoxin- or methyl viologen-mediated reactions with the same velocity. The results underscore the role of the reduction of the nitro group in the antitrichomonad and in the mutagenic activity of nitroimidazoles.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames B. N., Mccann J., Yamasaki E. Methods for detecting carcinogens and mutagens with the Salmonella/mammalian-microsome mutagenicity test. Mutat Res. 1975 Dec;31(6):347–364. doi: 10.1016/0165-1161(75)90046-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler K., Howes H. L., Lynch J. E., Pirie D. K. Nitroimidazole derivatives. Relationship between structure and antitrichomonal activity. J Med Chem. 1967 Sep;10(5):891–897. doi: 10.1021/jm00317a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavier R., Cénac J. Contribution à l'étude des propriétés trichomonacides du nimorazole. Therapeutique. 1972 May-Jun;48(5):391–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosar C., Crisan C., Horclois R., Jacob R. M., Robert J., Tchelitcheff S., Vaupré R. Nitro-imidazoles--Préparation et activité chimiothérapeutique. Arzneimittelforschung. 1966 Jan;16(1):23–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIAMOND L. S. The establishment of various trichomonads of animals and man in axenic cultures. J Parasitol. 1957 Aug;43(4):488–490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eakins M. N., Conroy P. J., Searle A. J., Slater T. F., Willson R. L. Metronidazole (Flagyl), a radiosensitiser of possible clinical use in cancer chemotherapy: some biochemical and pharmacological considerations. Biochem Pharmacol. 1976 May 15;25(10):1151–1156. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(76)90362-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards D. I., Dye M., Carne H. The selective toxicity of antimicrobial nitroheterocyclic drugs. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 May;76(1):135–145. doi: 10.1099/00221287-76-1-135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Füzi M., Csukás Z. Das antibakterielle Wirkungsspektrum des Metronidazols. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1970;213(2):258–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giraldi P. N., Mariotti V., Nannini G., Tosolini G. P., Dradi E., Logemann W., De Carneri I., Monti G. Studies on antiprotozoans. II. Synthesis and biological activity of some N-alkylamino-nitroimidazoles. Arzneimittelforschung. 1970 Jan;20(1):52–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunberg E., Titsworth E. H. Chemotherapeutic properties of heterocyclic compounds: monocyclic compounds with five-membered rings. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1973;27:317–346. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.27.100173.001533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ings R. M., McFadzean J. A., Ormerod W. E. The mode of action of metronidazole in Trichomonas vaginalis and other micro-organisms. Biochem Pharmacol. 1974 May 1;23(9):1421–1429. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(74)90362-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancini G. C., Arioli V., Lazzari E., Bellani P. Synthesis and relationship between structure and activity of 2-nitroimidazole derivatives. J Med Chem. 1969 Sep;12(5):775–780. doi: 10.1021/jm00305a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legator M. S., Connor T. H., Stoeckel M. Detection of mutagenic activity of metronidazole and niridazole in body fluids of humans and mice. Science. 1975 Jun 13;188(4193):1118–1119. doi: 10.1126/science.766186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legator M. S., Connor T., Stoeckel M. The detection of mutagenic substances in the urine and blood of man. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Dec 31;269:16–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1976.tb35133.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCalla D. R., Reuvers A., Kaiser C. Mode of action of nitrofurazone. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1126–1134. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1126-1134.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCalla D. R., Voutsinos D. On the mutagenicity of nitrofurans. Mutat Res. 1974 Feb;26(1):3–16. doi: 10.1016/s0027-5107(74)80065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCann J., Choi E., Yamasaki E., Ames B. N. Detection of carcinogens as mutagens in the Salmonella/microsome test: assay of 300 chemicals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):5135–5139. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.5135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCann J., Spingarn N. E., Kobori J., Ames B. N. Detection of carcinogens as mutagens: bacterial tester strains with R factor plasmids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):979–983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M., Lindmark D. G. Uptake of metronidazole and its effect on viability in trichomonads and Entamoeba invadens under anaerobic and aerobic conditions. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Apr;9(4):696–700. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.4.696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien R. W., Morris J. G. Effect of metronidazole on hydrogen production by Clostridium acetobutylicum. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;84(3):225–233. doi: 10.1007/BF00425200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph E. D., Kirby W. M. Bioassay of metronidazole with either anaerobic or aerobic incubation. J Infect Dis. 1975 Nov;132(5):587–591. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.5.587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenkranz H. S., Speck W. T. Mutagenicity of metronidazole: activation by mammalian liver microsomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Sep 16;66(2):520–525. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90541-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAMUELS R., STOUDER D. J. Disc testing of drugs against plated Trichomonas vaginalis. J Protozool. 1962 Aug;9:249–254. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1962.tb02613.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck W. T., Stein A. B., Rosenkranz H. S. Mutagenicity of metronidazole: presence of several active metabolites in human urine. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1976 Feb;56(2):283–284. doi: 10.1093/jnci/56.2.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stambaugh J. E., Feo L. G., Manthei R. W. The isolation and identification of the urinary oxidative metabolites of metronidazole in man. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1968 Jun;161(2):373–381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stambaugh J. E., Manthei R. W. The characterization of substituted nitroimidazoles on paper and thin layer chromatography by colorimetric reactions. J Chromatogr. 1967 Nov;31(1):128–136. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)86034-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urtasun R. C., Sturmwind J., Rabin H., Band P. R., Chapman J. D. Letter: "High-dose" metronidazole: a preliminary pharmacological study prior to its investigational use in clinical radiotherapy trials. Br J Radiol. 1974 May;47(557):297–299. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-47-557-297-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vetter H., Jr, Knappe J. Flavodoxin and ferredoxin of Escherichia coli. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1971 Mar;352(3):433–446. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1971.352.1.433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voogd C. E., Van der Stel J. J., Jacobs J. J. The mutagenic action of nitroimidazoles. I. Metronidazole, nimorazole, dimetridazole and ronidazole. Mutat Res. 1974 Dec;26(6):483–490. doi: 10.1016/s0027-5107(74)80049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



