Abstract
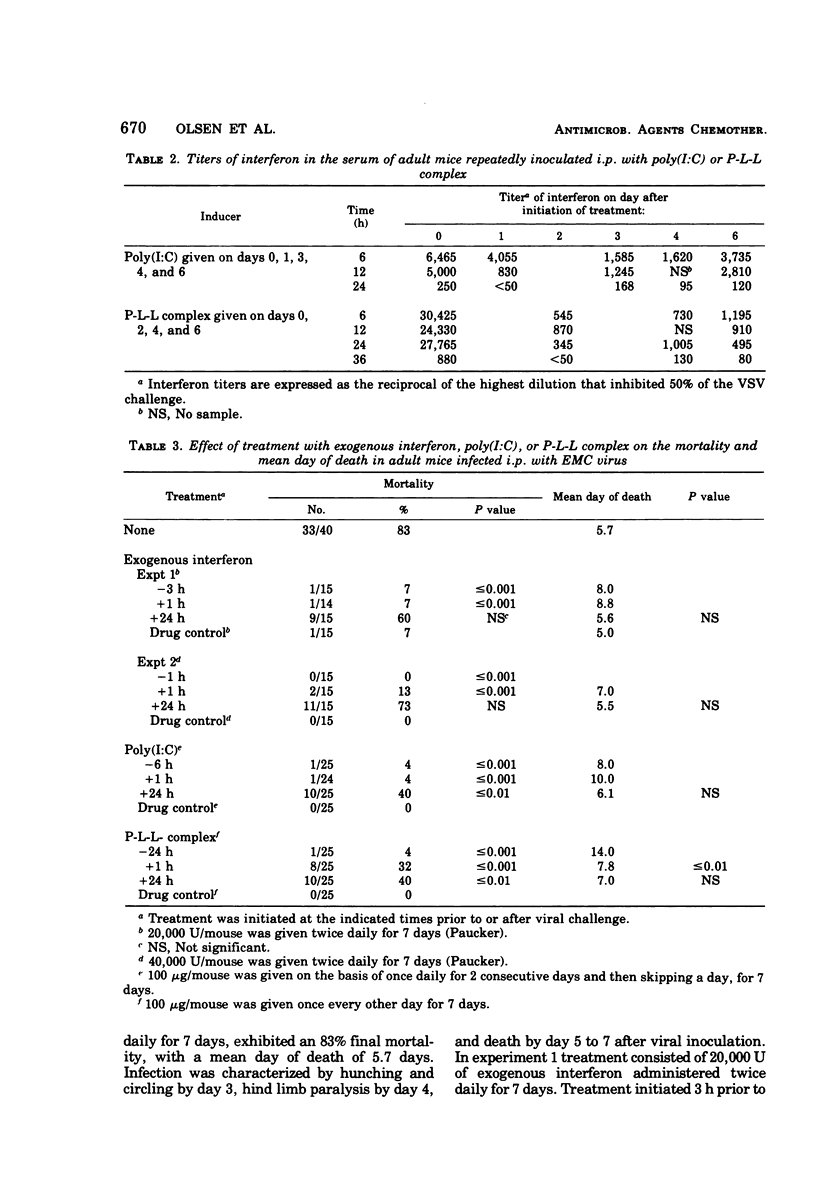
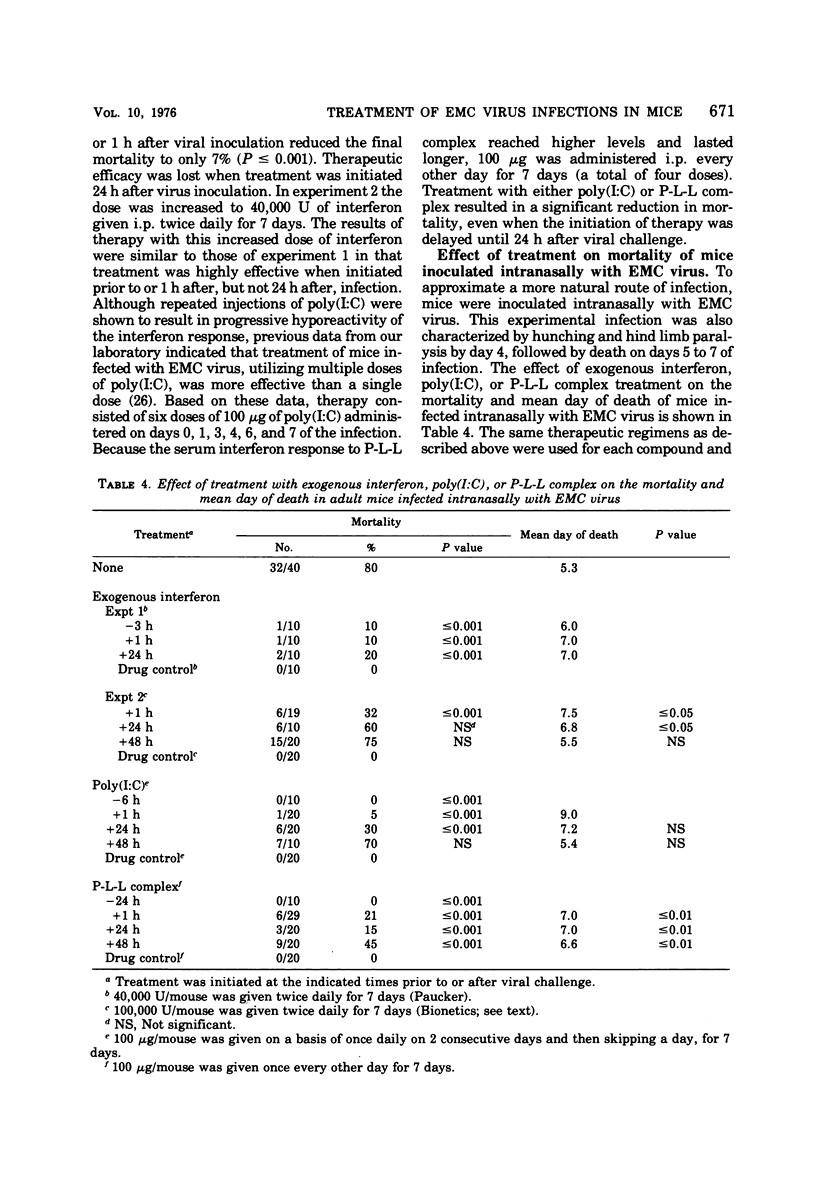
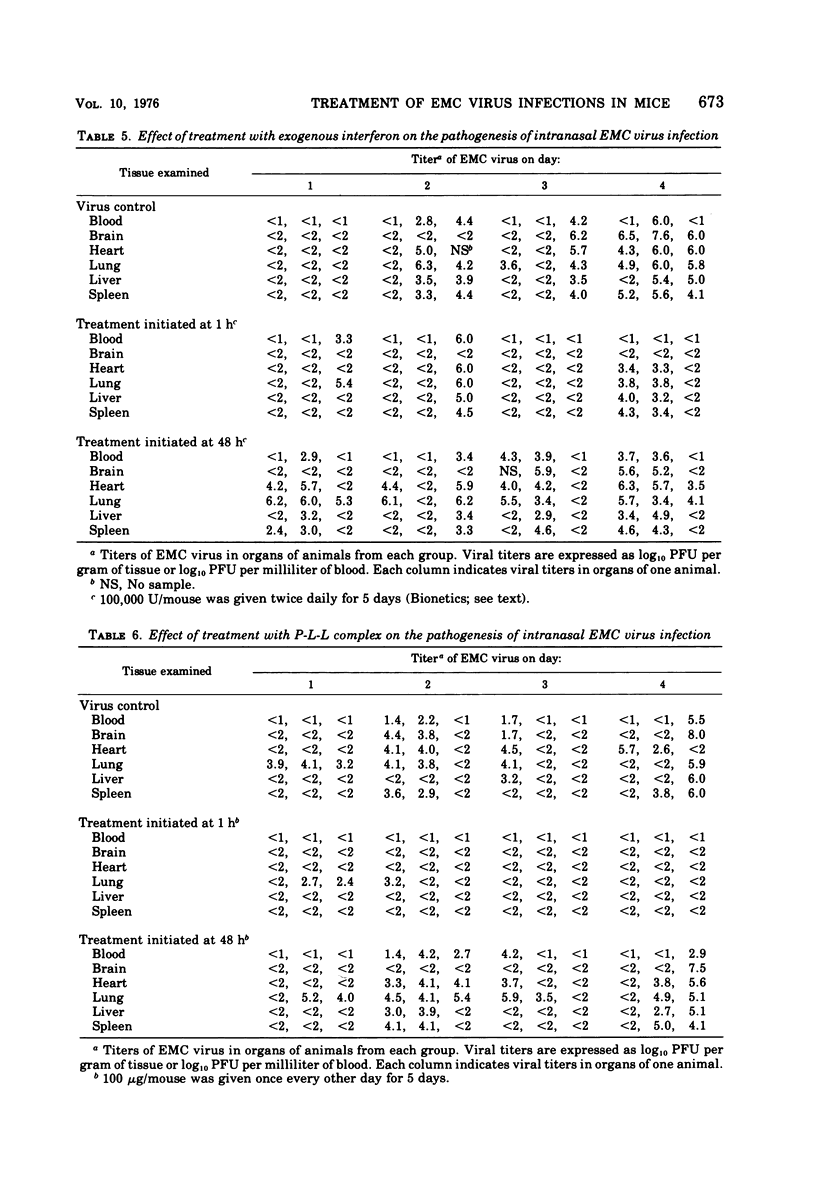
The effect of treatment with exogenous interferon was compared with two interferon inducers, polyinosinic acid-polycytidylic acid [poly(I:C)] and [poly(I:C)]-poly-l-lysine complex (P-L-L complex), in two model encephalomyocarditis virus infections of mice. Although both inducers stimulated the production of interferon, the peak serum levels induced by P-L-L complex were five- to eightfold greater than those induced with poly(I:C). When encephalomyocarditis virus was inoculated by either the intraperitoneal or the intranasal route, interferon and both of the inducers protected mice against mortality and prolonged the mean day of death when the compounds were given prior to or immediately after viral challenge. In general, treatment with interferon was not as successful as treatment with poly(I:C) or P-L-L complex. In these infections, P-L-L complex appeared to be the most effective agent in that successful treatment resulted when drug therapy was initiated as late as 48 h after virus inoculation. An examination of the effect of treatment on the pathogenesis of the infection indicated that protection was associated with the prevention of viremia and subsequent seeding of target organs, particularly the central nervous system.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baron S., Buckler C. E., Friedman R. M., McCloskey R. V. Role of interferon during viremia. II. Protective action of circulating interferon. J Immunol. 1966 Jan;96(1):17–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catalano L. W., Jr, Baron S. Protection against herpes virus and encephalomyocarditis virus encephalitis with a double-stranded RNA inducer of interferon. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Feb;133(2):684–687. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catalano L. W., Jr, London W. T., Rice J. M., Sever J. L. Prophylactic and therapeutic use of poly(I)-poly(C) (poly-D-lysine) against herpesvirus encephalitis in mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 May;140(1):66–71. doi: 10.3181/00379727-140-36396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Clercq E., De Somer P. Comparative study of the efficacy of different forms of interferon therapy in the treatment of mice challenged intranassaly with vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Oct;138(1):301–307. doi: 10.3181/00379727-138-35884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emödi G., O'Reilly R., Müller A., Everson L. K., Binswanger U., Just M. Effect of human exogenous leukocyte interferon in cytomegalovirus infections. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jun;133 (Suppl):A199–A204. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.supplement_2.a199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINTER N. B. PROTECTION OF MICE BY INTERFERON AGAINST SYSTEMIC VIRUS INFECTIONS. Br Med J. 1964 Oct 17;2(5415):981–985. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5415.981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finter N. B. Exogenous interferon in animals and its clinical implications. Arch Intern Med. 1970 Jul;126(1):147–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finter N. B. Interferon as an antiviral agent in vivo: quantitative and temporal aspects of the protection of mice against Semliki Forest virus. Br J Exp Pathol. 1966 Aug;47(4):361–371. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerone P. J., Hill D. A., Appell L. H., Baron S. Inhibition of respiratory virus infections of mice with aerosols of synthetic double-stranded ribonucleic Acid. Infect Immun. 1971 Feb;3(2):323–327. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.2.323-327.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I., Bourali C., Thomas M. T., Falcoff E. Effect of repeated inoculation of interferon preparations on infection of mice with encephalomyocarditis virus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Feb;127(2):491–496. doi: 10.3181/00379727-127-32723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I., Fontaine-Brouty-Boyé D., Bourali C., Thomas M. T. A comparison of the efficacy of endogenous, exogenous, and combined endogenous-exogenous interferon in the treatment of mice infected with encephalomyocarditis virus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Jan;130(1):236–242. doi: 10.3181/00379727-130-33529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORSTMANN D. M. ENTEROVIRUS INFECTIONS: ETIOLOGIC, EPIDEMIOLOGIC AND CLINICAL ASPECTS. Calif Med. 1965 Jul;103:1–8. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilleman M. R. Double-stranded RNAs (poly I:C) in the prevention of viral infections. Arch Intern Med. 1970 Jul;126(1):109–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilleman M. R. Prospects for the use of double-stranded ribonucleic acid (poly I:C) inducers in man. J Infect Dis. 1970 Feb;121(2):196–211. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.2.196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones B. R., Coster D. J., Falcon M. G., Cantell K. Clinical trials of topical interferon therapy of ulcerative viral keratitis. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jun;133 (Suppl):A169–A172. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.supplement_2.a169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIBRICK S. CURRENT STATUS OF COXSACKIE AND ECHO VIRUSES IN HUMAN DISEASE. Prog Med Virol. 1964;6:27–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman H. E., Meyer R. F., Laibson P. R., Waltman S. R., Nesburn A. B., Shuster J. J. Human leukocyte interferon for the prevention of recurrences of herpetic keratitis. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jun;133 (Suppl):A165–A168. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.supplement_2.a165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern E. R., Overall J. C., Jr, Glasgow L. A. Herpesvirus hominis infection in newborn mice: treatment with interferon inducer polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Jun;7(6):793–800. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.6.793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy H. B., Baer G., Baron S., Buckler C. E., Gibbs C. J., Iadarola M. J., London W. T., Rice J. A modified polyriboinosinic-polyribocytidylic acid complex that induces interferon in primates. J Infect Dis. 1975 Oct;132(4):434–439. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.4.434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean D. M. Coxsackieviruses and echoviruses. Am J Med Sci. 1966 Mar;251(3):351–368. doi: 10.1097/00000441-196603000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordlund J. J., Wolff S. M., Levy H. B. Inhibition of biologic activity of poly I: poly C by human plasma. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Feb;133(2):439–444. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringfellow D. A., Overall J. C., Jr, Glasgow L. A. Interferon inducers in therapy of infection with encephalomyocarditis virus in mice. I. Effect of single doses of polyriboinosinic-polyribocytidylic acid and tilorone hydrochloride on viral pathogenesis. J Infect Dis. 1974 Nov;130(5):470–480. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.5.470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringfellow D. A., Overall J. C., Jr, Glasgow L. A. Interferon inducers in therapy of infection with encephalomyocarditis virus in mice. II. Effect of multiple doses of polyriboinosinic-polyribocytidylic acid on viral pathogenesis. J Infect Dis. 1974 Nov;130(5):481–488. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.5.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundmacher R., Neumann-Haefelin D., Manthey K. F., Müller O. Interferon in treatment of dendritic keratitis in humans: a preliminary report. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jun;133 (Suppl):A160–A164. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.supplement_2.a160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worthington M., Baron S. Late therapy with an interferon stimulator in an arbovirus encephalitis in mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Jan;136(1):323–327. doi: 10.3181/00379727-136-35257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


