Abstract
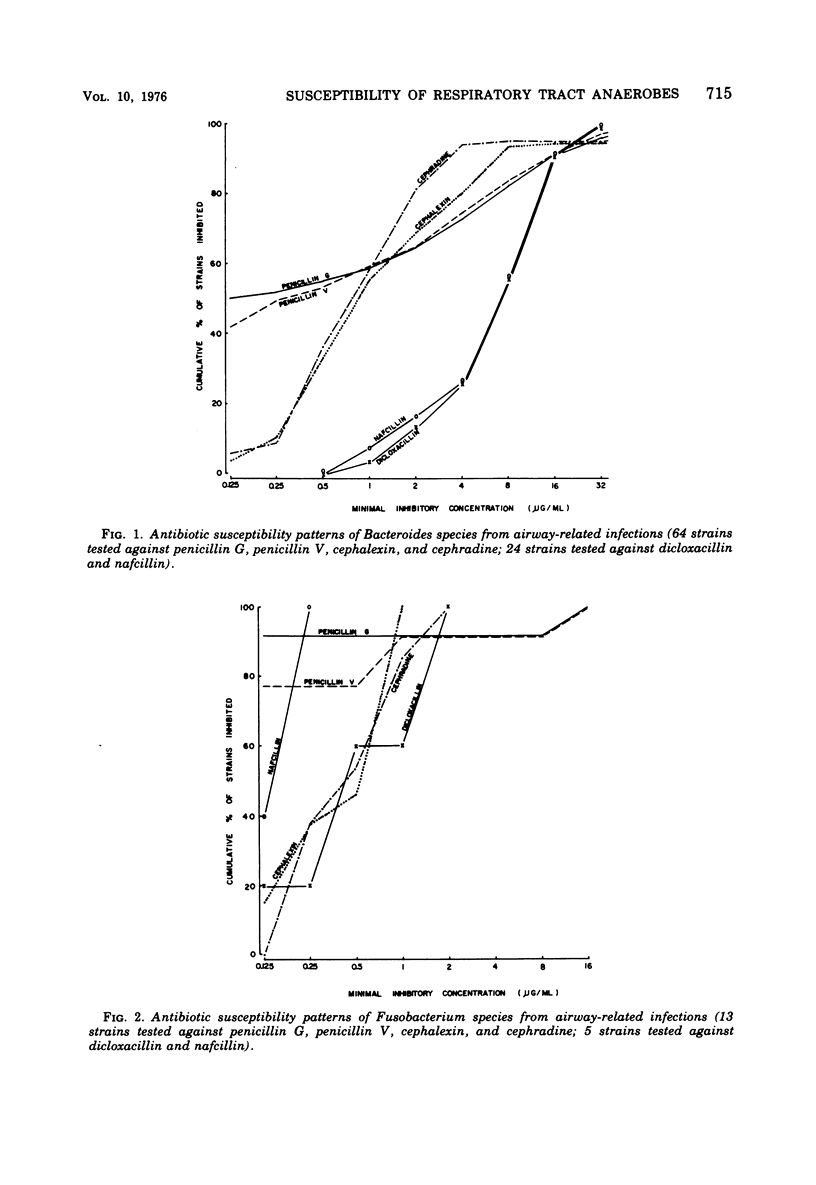
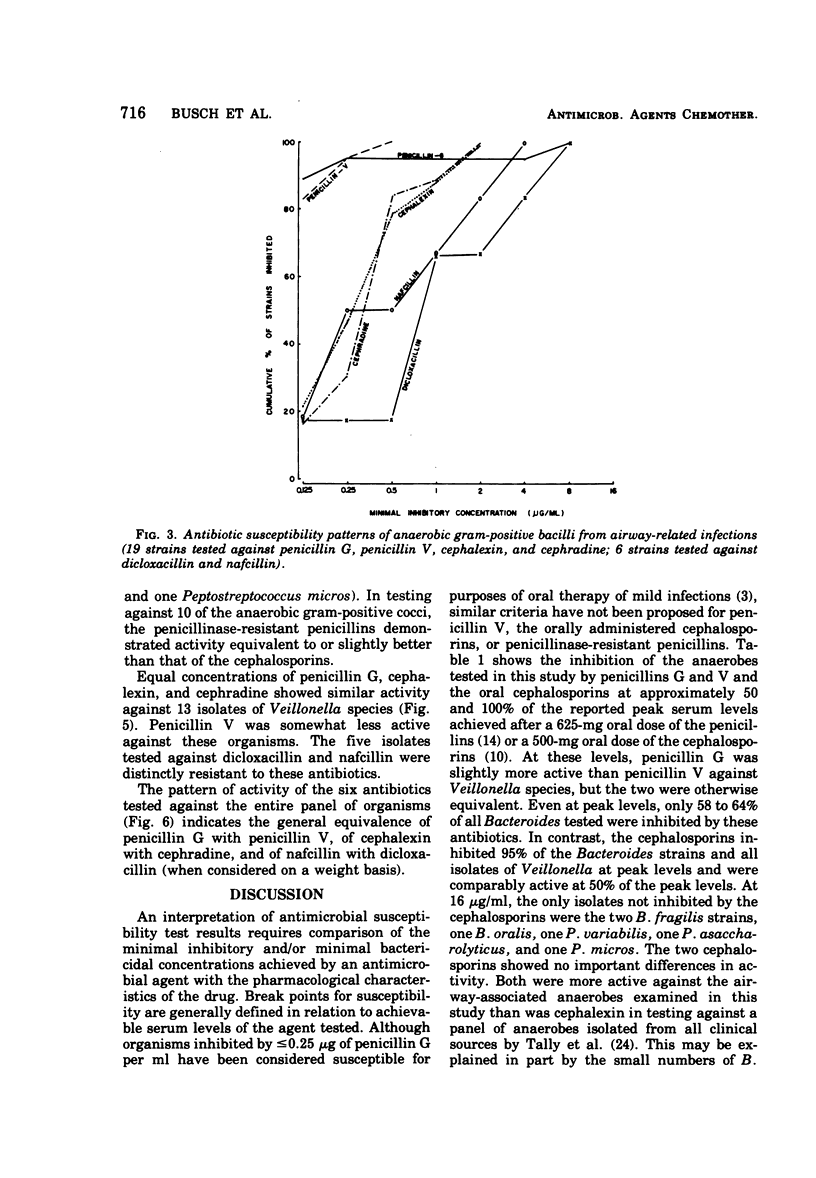
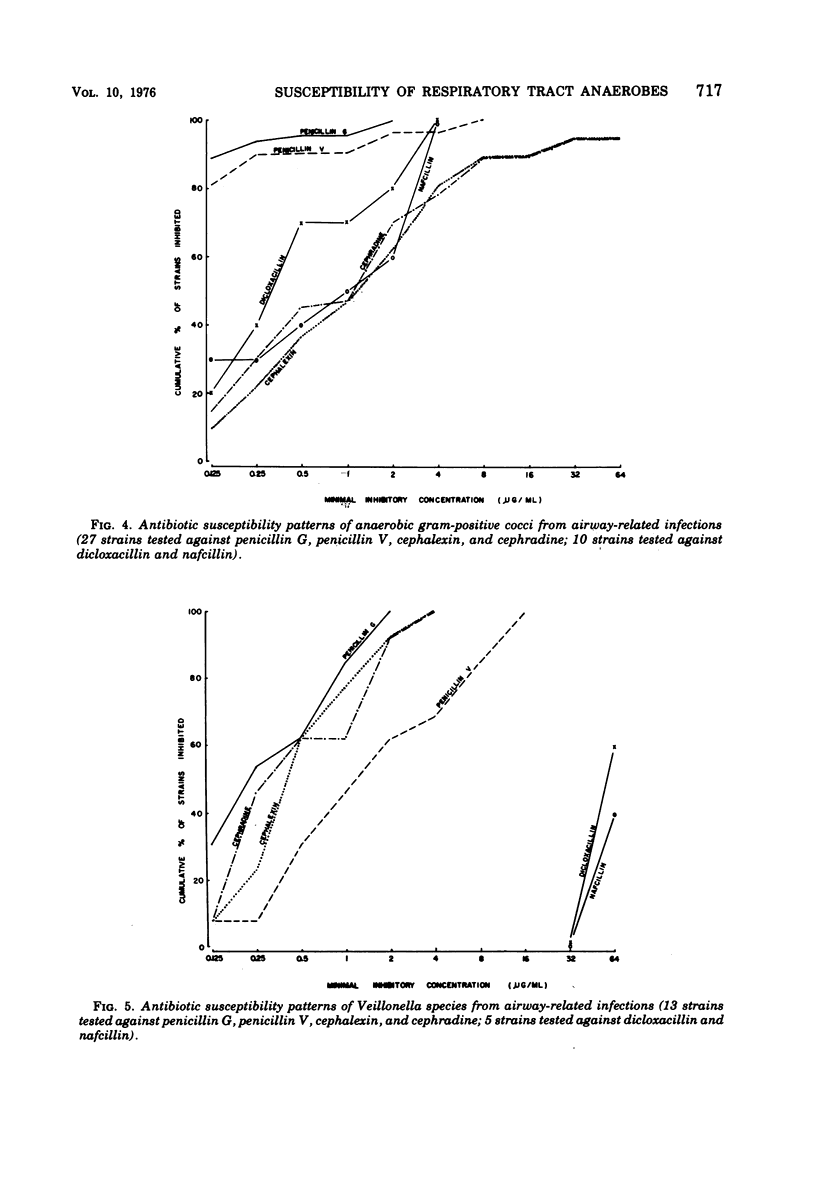
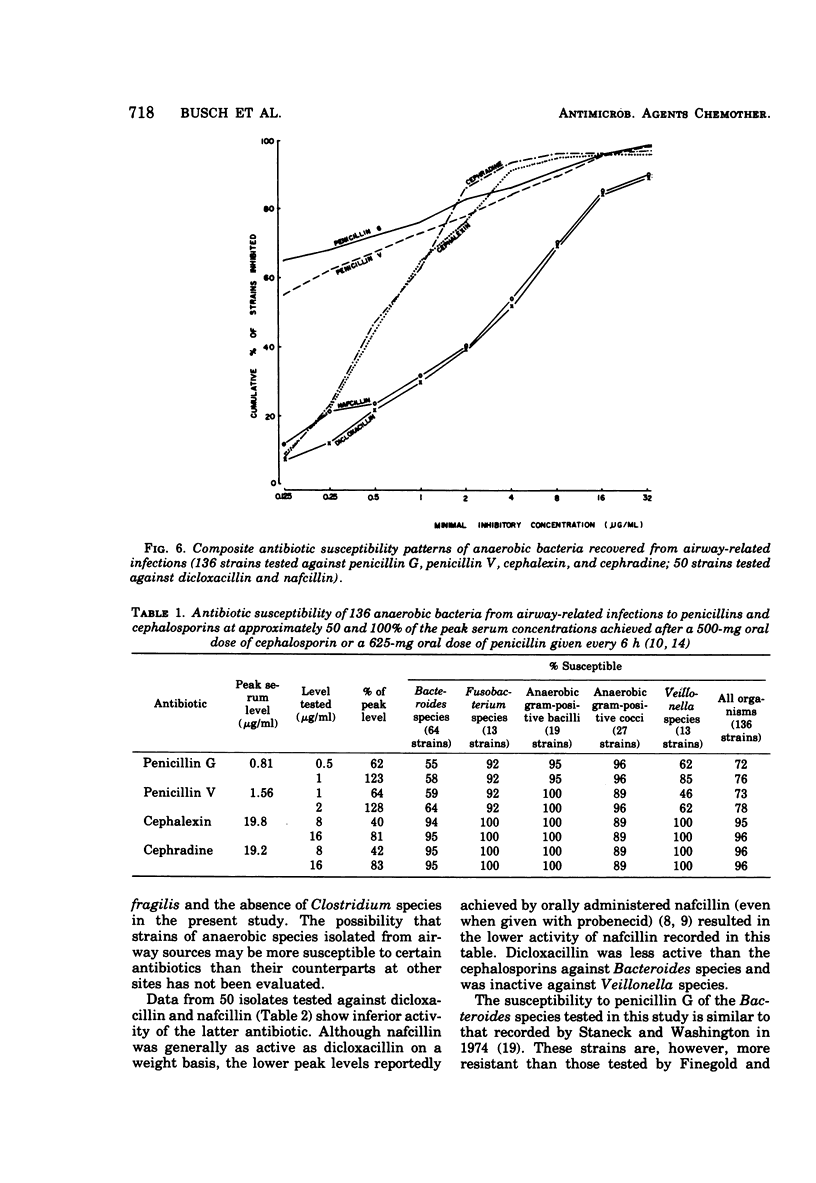
Anaerobic bacteria recovered from airway-related infections were tested by agar dilution against selected penicillins and cephalosporins available for oral administration. Against 136 isolates, penicillins G and V showed comparable activity, particularly when pharmacological differences were considered. Although many isolates were exquisitely susceptible to the penicillins, only 55% of the Bacteroides species and 72% of all isolates were inhibited at 0.5 μg of penicillin G per ml. Results for penicillin V at 1 μg/ml were similar (59 and 73%). The two cephalosporins were more active at achievable levels, inhibiting 94 to 95% of Bacteroides and 95 to 96% of all isolates at 8 μg/ml. These levels represent approximately 50% of the reported peak serum levels after oral administration of 625 mg of the penicillins and 500 mg of the cephalosporins. Dicloxacillin and nafcillin were tested against 50 isolates. The two were comparably active on a weight basis; dicloxacillin was more active when pharmacological differences were considered, but did not match the other penicillins or the cephalosporins.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartlett J. G., Finegold S. M. Anaerobic infections of the lung and pleural space. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1974 Jul;110(1):56–77. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1974.110.1.56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett J. G., Gorbach S. L. Treatment of aspiration pneumonia and primary lung abscess. Penicillin G vs clindamycin. JAMA. 1975 Dec 1;234(9):935–937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finegold S. M., Bartlett J. G., Chow A. W., Flora D. J., Gorbach S. L., Harder E. J., Tally F. P. Management of anaerobic infections. Ann Intern Med. 1975 Sep;83(3):375–389. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-83-3-375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finegold S. M. Infections due to anaerobes. Med Times. 1968 Feb;96(2):174–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAVENKEMPER C. F., BENNETT J. V., BRODIE J. L., KIRBY W. M. DICLOXACILLIN. IN VITRO AND PHARMACOLOGIC COMPARISONS WITH OXACILLIN AND CLOXACILLIN. Arch Intern Med. 1965 Sep;116:340–345. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1965.03870030020005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvengt C., De Schepper P., Lamy F., Hansen J. Cephradine absorption and excretion in fasting and nonfasting volunteers. J Clin Pharmacol New Drugs. 1973 Jan;13(1):36–40. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1973.tb00066.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayser F. H. Methicillin-resistant staphylococci 1965-75. Lancet. 1975 Oct 4;2(7936):650–653. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)90129-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorber B., Swenson R. M. Bacteriology of aspiration pneumonia. A prospective study of community- and hospital-acquired cases. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Sep;81(3):329–331. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-81-3-329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C. Antimicrobial activity and human pharmacology of amoxicillin. J Infect Dis. 1974 Jun;129(0):suppl–suppl:S131. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.supplement_2.s123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pien F. D., Thompson R. L., Martin W. J. Clinical and bacteriologic studies of anaerobic gram-positive cocci. Mayo Clin Proc. 1972 Apr;47(4):251–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staneck J. L., Washington J. A., 2nd Antimicrobial susceptibilities of anaerobic bacteria: recent clinical isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Sep;6(3):311–315. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.3.311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter V. L., Finegold S. M. Susceptibility of Anaerobic bacteria to carbenicillin, cefoxitin, and related drugs. J Infect Dis. 1975 Apr;131(4):417–422. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.4.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter V. L., Finegold S. M. Susceptibility of anaerobic bacteria to 23 antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Oct;10(4):736–752. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.4.736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tally F. P., Jacobus N. V., Bartlett J. G., Gorbach S. L. Susceptibility of anaerobes to cefoxitin and other cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Feb;7(2):128–132. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.2.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


