Abstract
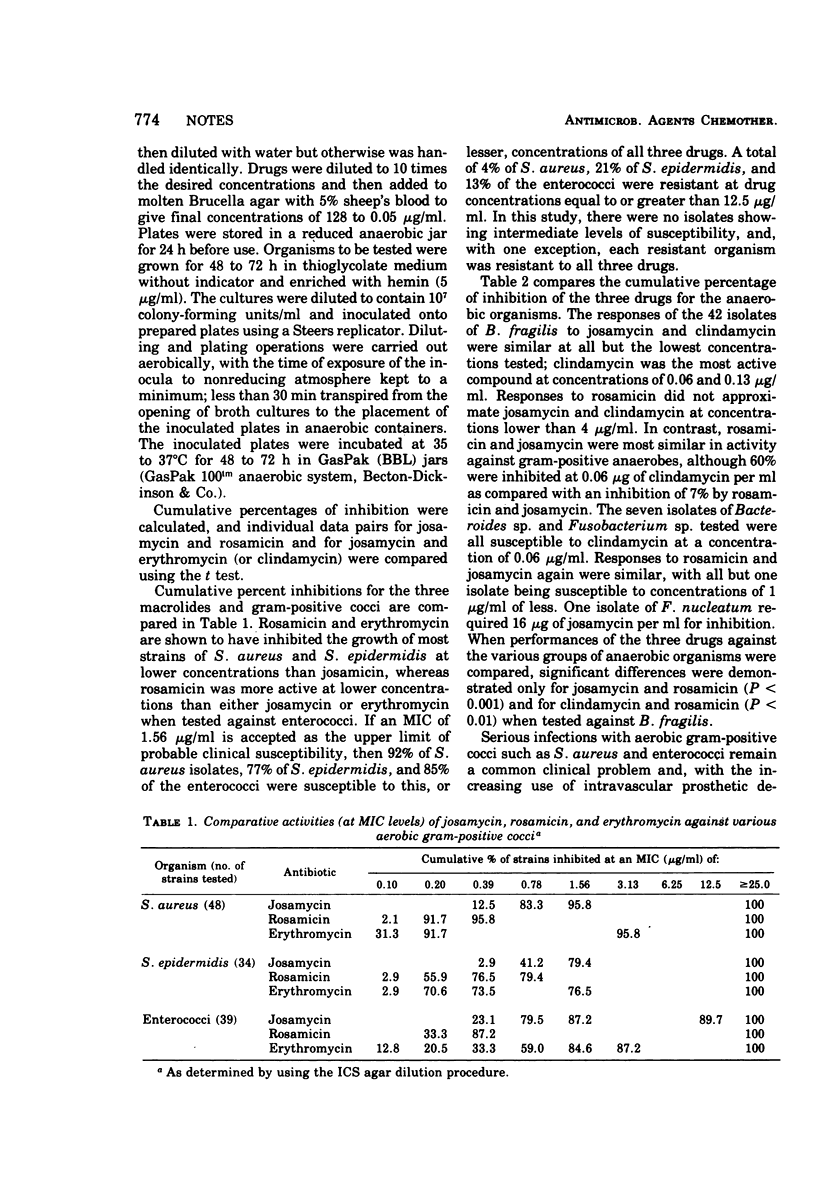
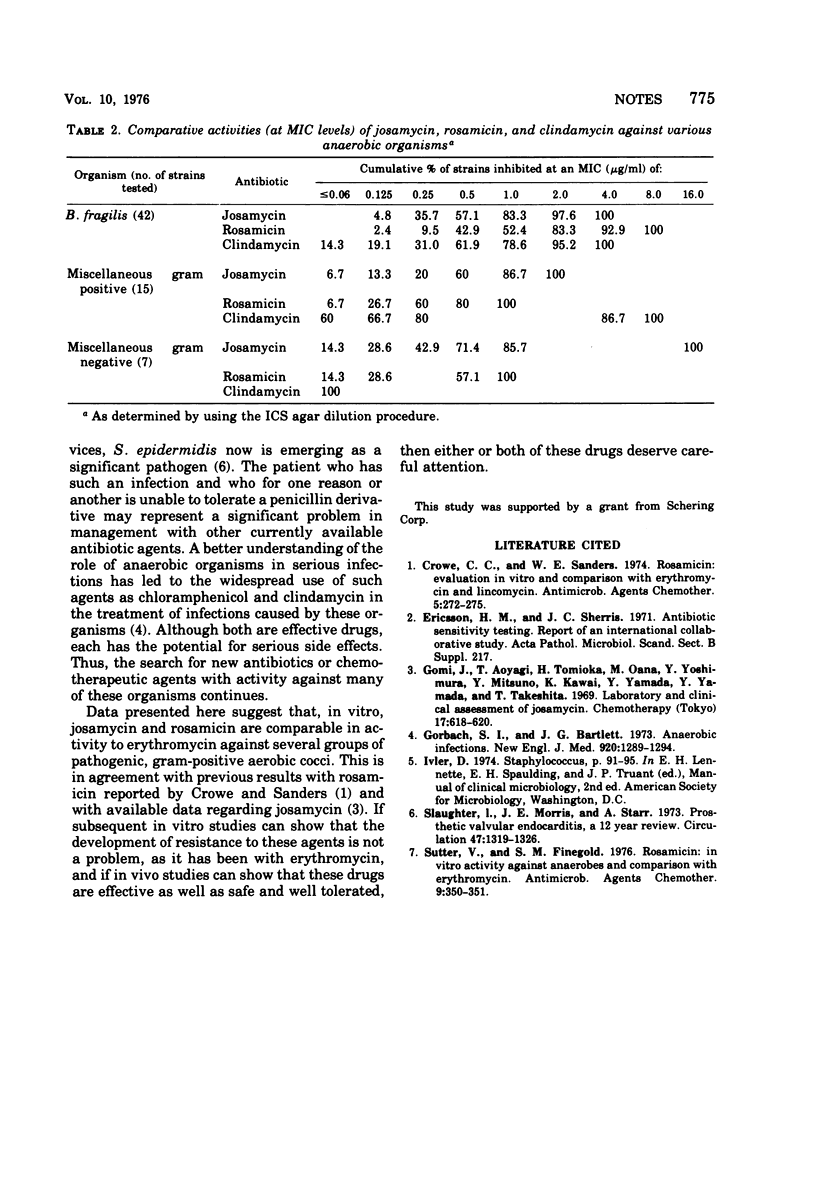
The macrolide antibiotics josamycin and rosamicin were compared in vitro with erythromycin for activity against Staphylococcus aureus, S. epidermidis, and enterococci and with clindamycin for activity against a variety of anaerobic organisms. Rosamicin and erythromycin were similar in activity and superior to josamycin against aerobic cocci. Most isolates of S. aureus (96%), S. epidermidis (79%), and the enterococci (87%) were inhibited by 1.56 μg of either of the new macrolide compounds per ml. Clindamycin was the most active compound against the anaerobic organisms.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Crowe C. C., Sanders W. E., Jr Rosamicin: evaluation in vitro and comparison with erythromycin and lincomycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Mar;5(3):272–275. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.3.272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericsson H. M., Sherris J. C. Antibiotic sensitivity testing. Report of an international collaborative study. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;217(Suppl):1+–1+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slaughter L., Morris J. E., Starr A. Prosthetic valvular endocarditis. A 12-year review. Circulation. 1973 Jun;47(6):1319–1326. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.47.6.1319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter V. L., Finegold S. M. Rosamicin: in vitro activity against anaerobes and comparison with erythromycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Feb;9(2):350–351. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.2.350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



