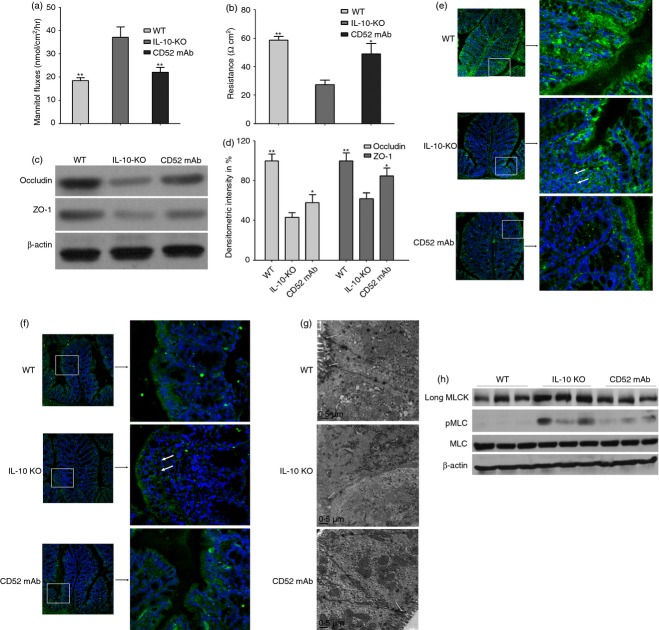
Figure 2.
Effect of CD52 monoclonal antibody (mAb) on intestinal permeability, tight junction (TJ) structure and composition, long myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) expression and activity in the proximal colon of interleukin-deficient (IL-10−/−) mice 4 weeks after the final drug administration. Measurements of colonic mannitol flux (a) and electrical resistance (b) in wild-type (WT), IL-10−/− (IL-10-KO) and CD52 mAb treatment (CD52 mAb) mice (n = 6). (c) Representative Western blots of colonic lysates for occludin and zona occludens 1 (ZO-1) in WT mice, IL-10−/− mice or CD52 mAb-treated mice. (d) Densitometric analysis of occludin and ZO-1 (n = 4 to 6). Representative immunofluorescence (green) of occludin (e) and ZO-1 (f) in the proximal colon of mice in three groups (200 × magnification, n = 3 or 4). Nuclei are blue, and arrows show the staining of TJ proteins. (g) Representative transmission electron micrograph of mucosa in three groups (n = 3 or 4), Arrows indicate TJ. (h) Representative Western blots of long MLCK, pMLC, and total MLC (MLC) of isolated colonic epithelia (n = 3). Data in this figure are representative of at least three independent experiments. Data were presented as means ± SEM. *P < 0·05 and **P < 0·01 versus IL-10-KO group.