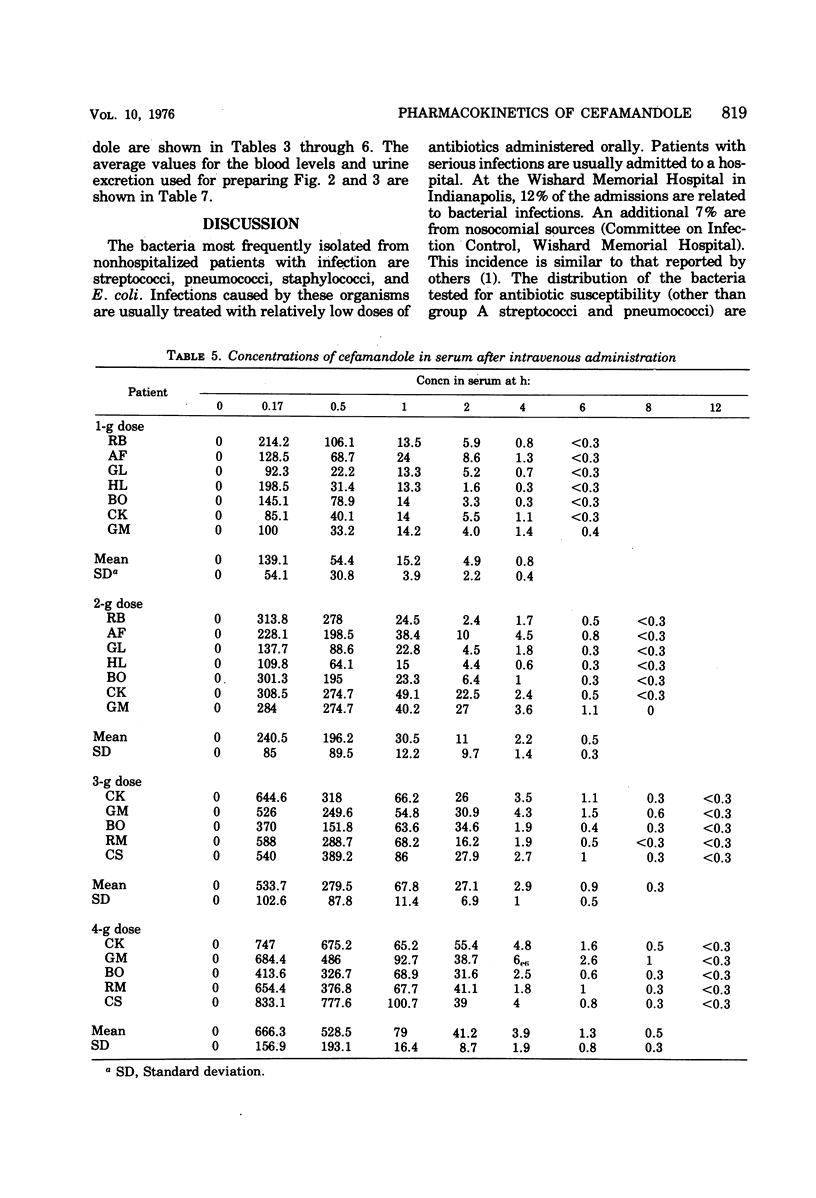
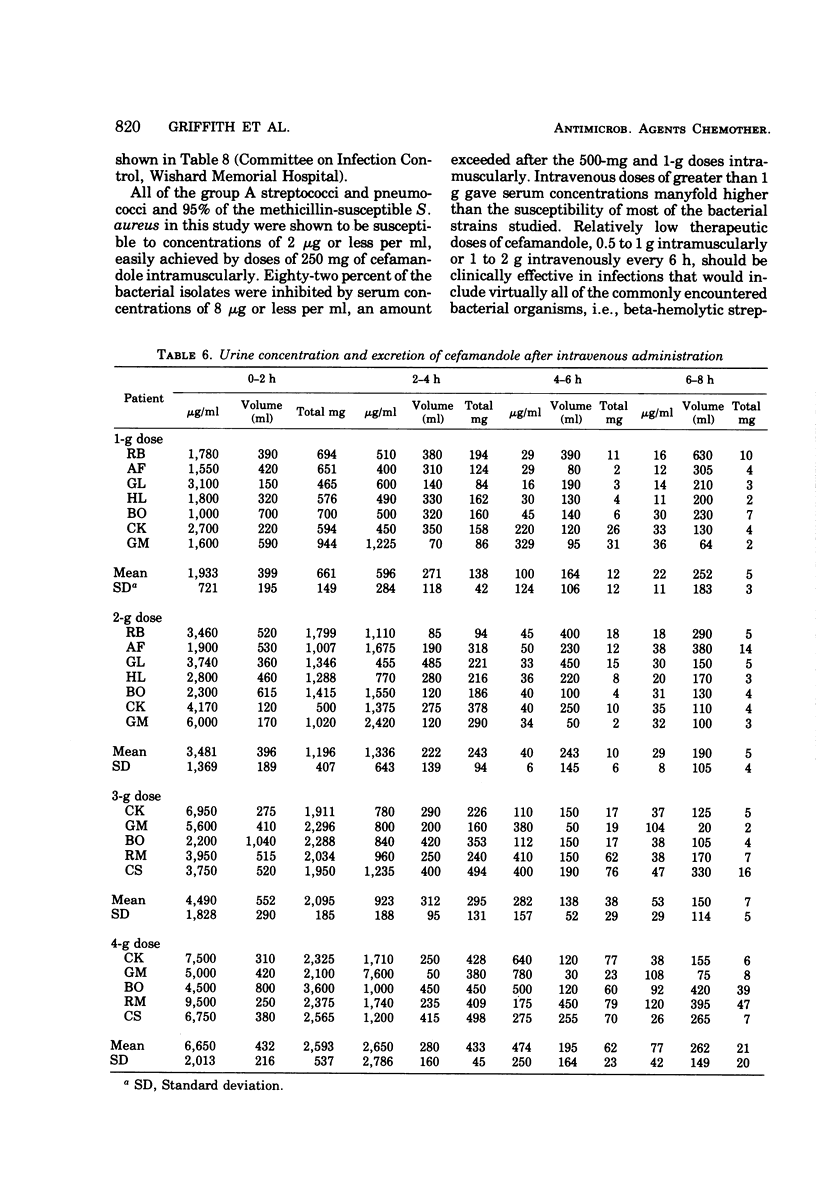
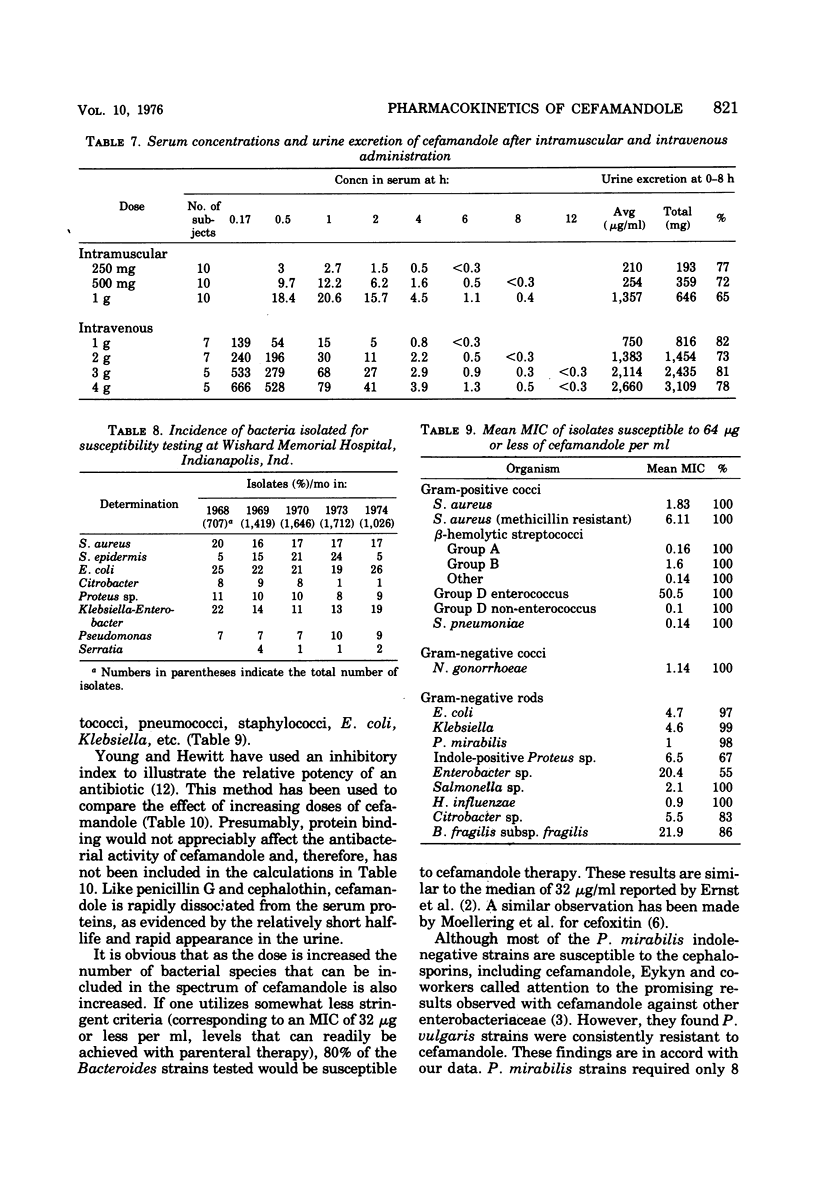
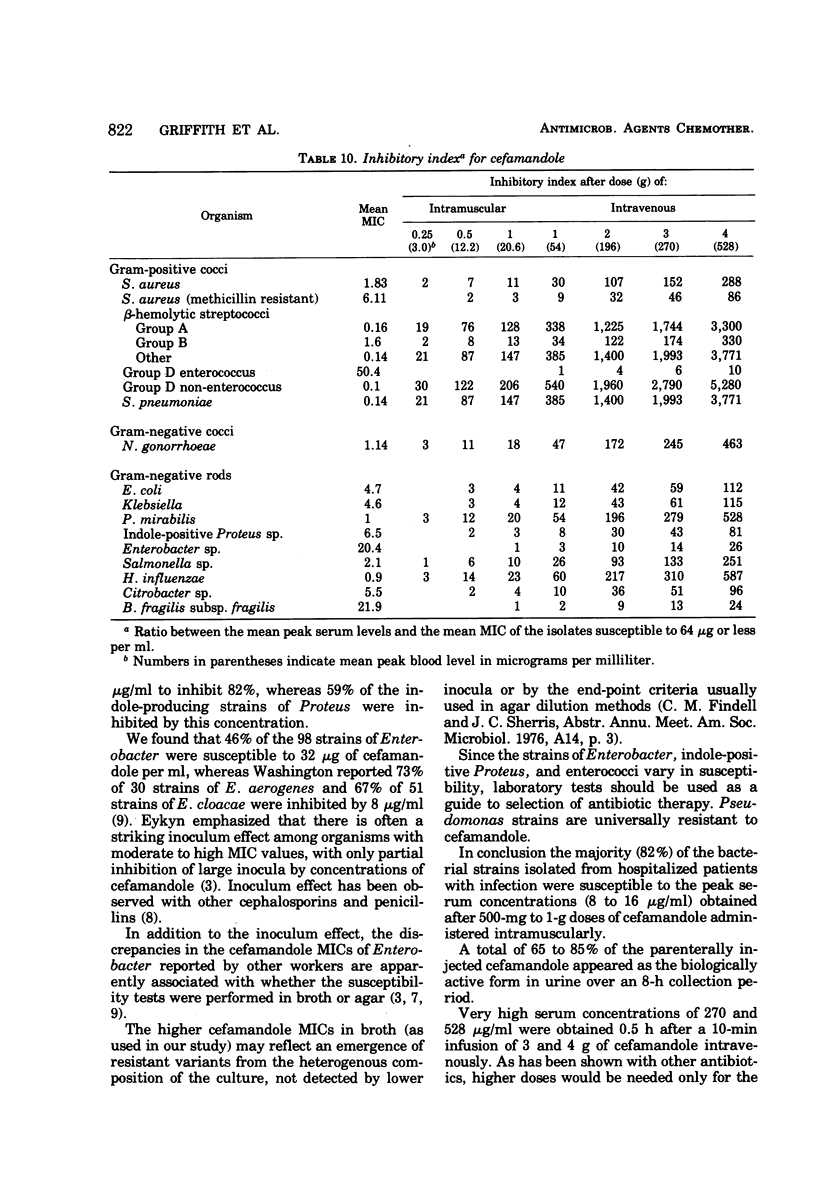
Abstract
Cefamandole has a broader spectrum and greater potency than the other cephalosporins. It includes Haemophilus influenzae, most strains of Enterobacter, and many strains of indole-positive Proteus and Bacteroides, with a lower minimal inhibitory concentration for Escherichia coli, Klebsiella, etc. Concentrations of drug in the serum after the parenteral injection of cefamandole exceed manyfold the minimal inhibitory concentrations of over 82% of the bacteria studied. Approximately 65 to 85% is excreted in a biologically active form in the urine. This antibiotic offers advantages of antibacterial effectiveness and at the same time retains the safety of penicillin G and cephalothin in animals.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ernst E. C., Berger S., Barza M., Jacobus N. V., Tally F. P. Activity of cefamandole and other cephalosporins against aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 May;9(5):852–855. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.5.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eykyn S., Jenkins C., King A., Phillips I. Antibacterial activity of cefamandole, a new cephalosporin antibiotic, compared with that of cephaloridine, cephalothin, and cephalexin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Jun;3(6):657–661. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.6.657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby W. M., Regamey C. Pharmacokinetics of cefazolin compared with four other cephalosporins. J Infect Dis. 1973 Oct;128(Suppl):S341–S346. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.supplement_2.s341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moellering R. C., Jr, Dray M., Kunz L. J. Susceptibility of clinical isolates of bacteria to cefoxitin and cephalothin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Sep;6(3):320–323. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.3.320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C. Cefamandole, a cephalosporin antibiotic with an unusually wide spectrum of activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Aug;6(2):177–182. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.2.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabath L. D., Garner C., Wilcox C., Finland M. Effect of inoculum and of beta-lactamase on the anti-staphylococcal activity of thirteen penicillins and cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Sep;8(3):344–349. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.3.344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washington J. A. The in vitro spectrum of the cephalosporins. Mayo Clin Proc. 1976 Apr;51(4):237–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein L., Kaplan K. The cephalosporins. Microbiological, chemical, and pharmacological properties and use in chemotherapy of infection. Ann Intern Med. 1970 May;72(5):729–739. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-72-5-729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Hewitt W. L. Activity of five aminoglycoside antibiotics in vitro against gram-negative bacilli and Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Dec;4(6):617–625. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.6.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


