Abstract
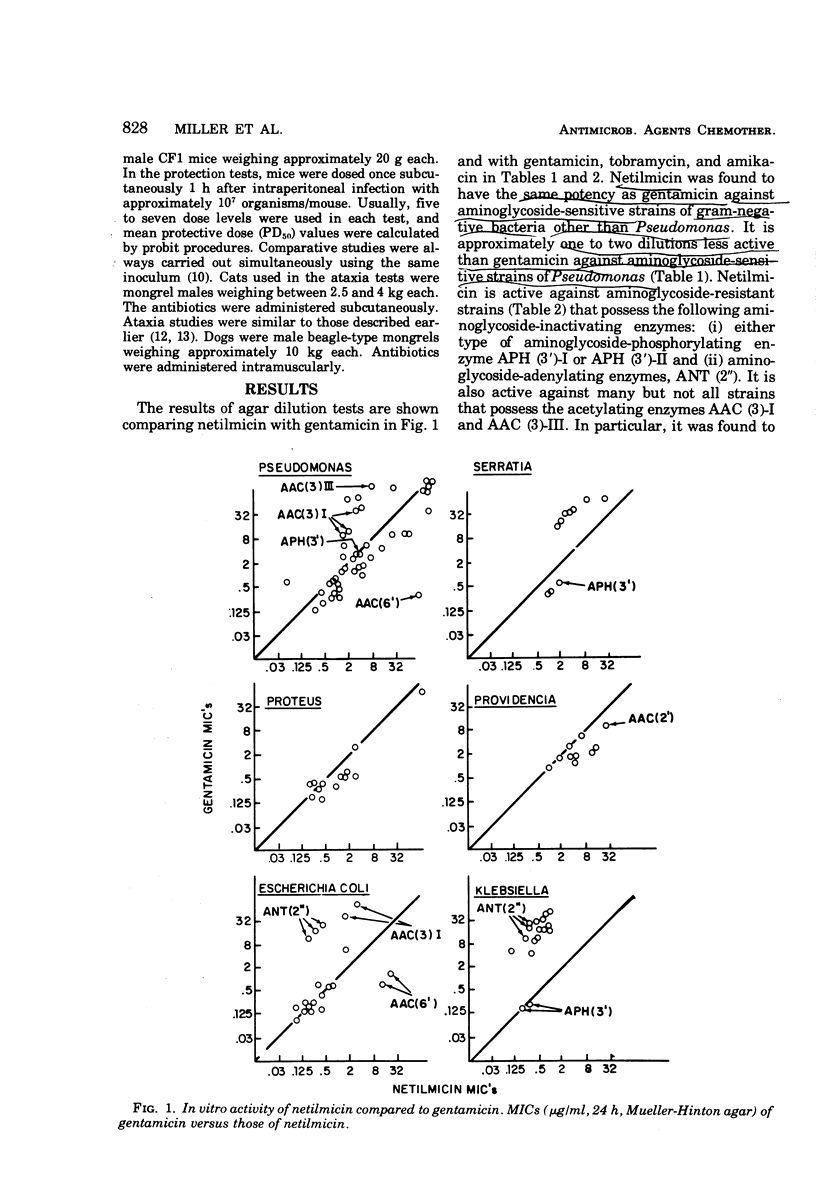
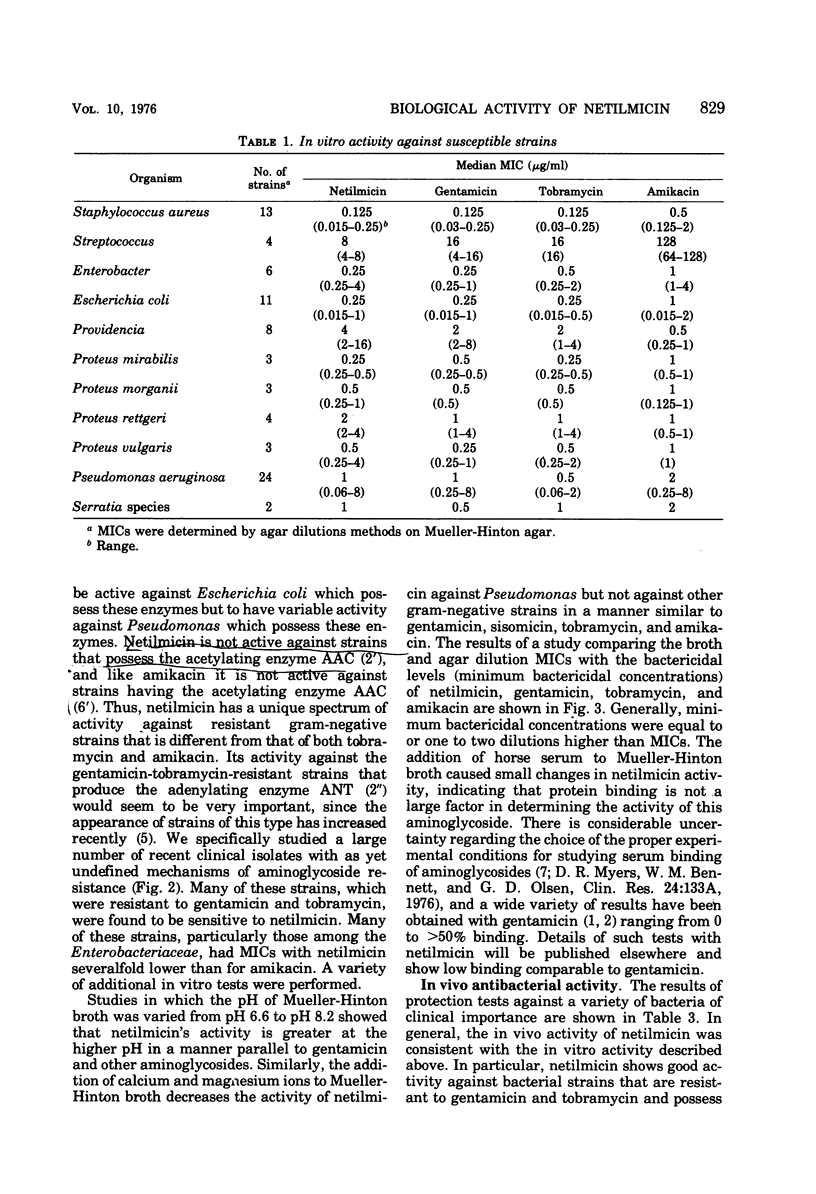
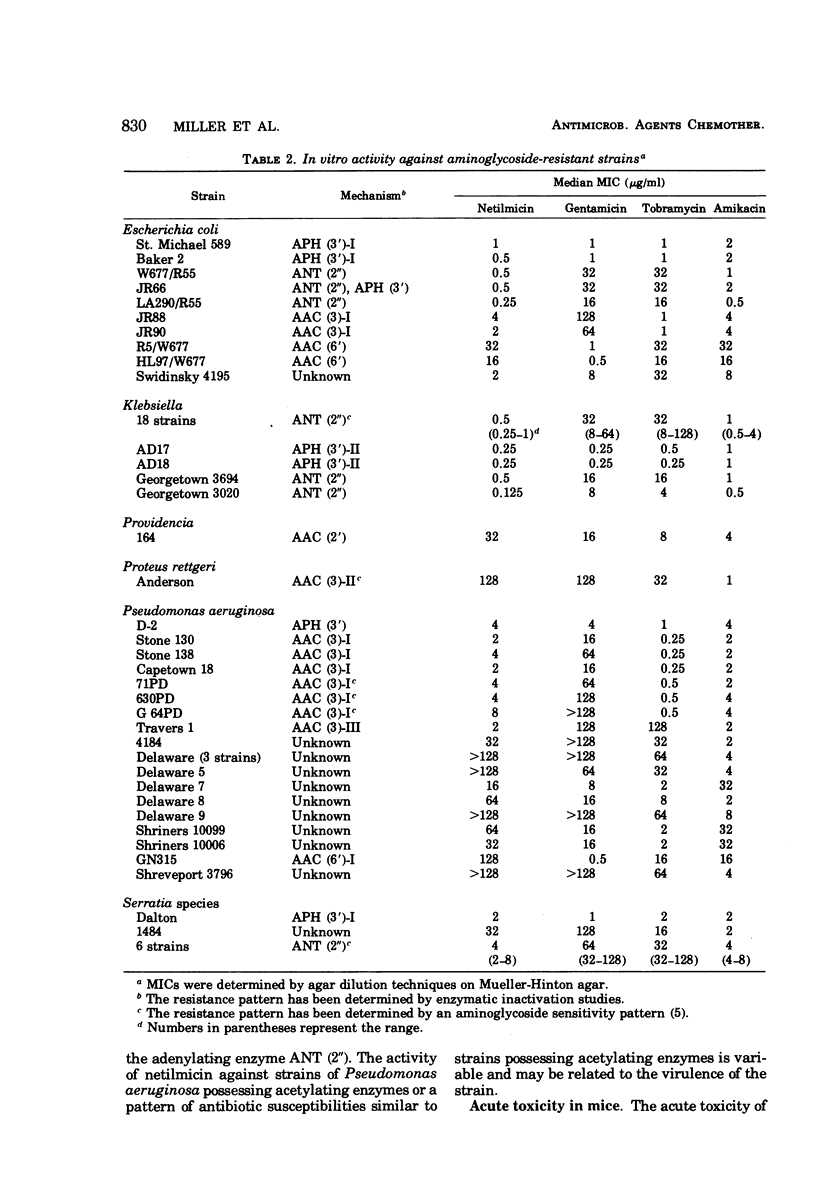
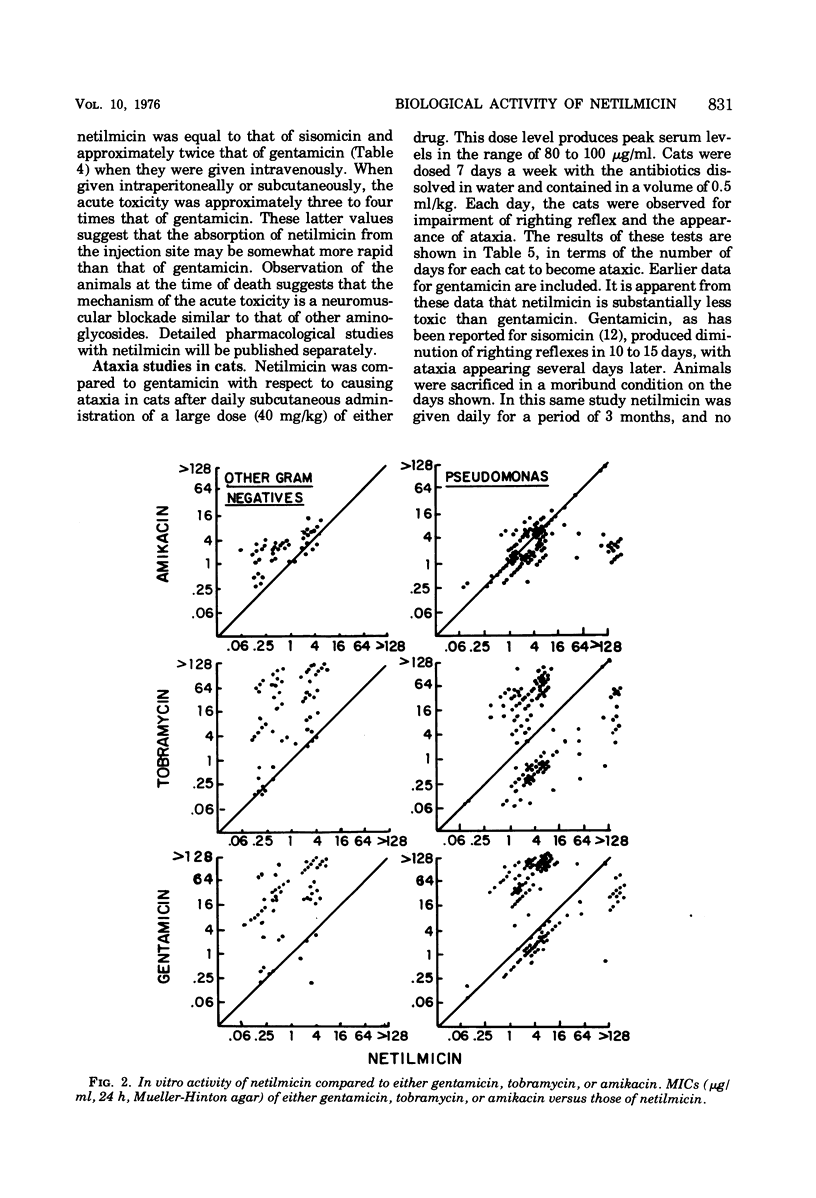
Netilmicin (Sch 20569) is a new broad-spectrum semisynthetic aminoglycoside derived from sisomicin. Netilmicin was compared to gentamicin, tobramycin, and amikacin in a variety of in vitro test systems as well as in mouse protection tests. Netilmicin was found to be similar in activity to gentamicin against aminoglycoside-susceptible strains in both in vitro and in vivo tests. Netilmicin was also active against many aminoglycoside-resistant strains of gram-negative bacteria, particularly those known to possess adenylating enzymes (ANT 2′) or those with a similar resistance pattern. Netilmicin was found to be markedly less toxic than gentamicin in chronic studies in cats, although gentamicin appeared less toxic in acute toxicity tests in mice. The concentrations of netilmicin and gentamicin in serum were compared in dogs after intramuscular dosing, and the pharmacokinetics including peak concentrations in serum were found to be similar.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gordon R. C., Regamey C., Kirby W. M. Serum protein binding of the aminoglycoside antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Sep;2(3):214–216. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.3.214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabins S. A., Nathan C., Cohen S. In vitro comparison of netilmicin, a semisynthetic derivative of sisomicin, and four other aminoglycoside antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jul;10(1):139–145. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.1.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noriega E. R., Leibowitz R. E., Richmond A. S., Rubinstein E., Schaefler S., Simberkoff M. S., Rahal J. J., Jr Nosocomial infection caused by gentamicin-resistant, streptomycin-sensitive Klebsiella. J Infect Dis. 1975 May;131 (Suppl):S45–S50. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.supplement.s45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price K. E., Pursiano T. A., DeFuria M. D. Activity of BB-K8 (amikacin) against clinical isolates resistant to one or more aminoglycoside antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Feb;5(2):143–152. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.2.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahal J. J., Jr, Simberkoff M. S., Kagan K., Moldover N. H. Bactericidal efficacy of Sch 20569 and amikacin against gentamicin-sensitive and -resistant organisms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Apr;9(4):595–599. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.4.595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waitz J. A., Moss E. L., Jr, Oden E. M., Wagman G. H., Weinstein M. J. Biological activity of Sch 14342, an aminoglycoside antibiotic coproduced in the gentamicin fermentation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Dec;2(6):464–469. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.6.464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waitz J. A., Moss E. L., Jr, Oden E. M., Weinstein M. J. Antibiotic 6640. 3. Biological studies with antibiotic 6640, a new broad-spectrum aminoglycoside antibiotic. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1970 Nov;23(11):559–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waitz J. A., Moss E. L., Jr, Weinstein M. J. Aspects of the chronic toxicity of gentamicin sulfate in cats. J Infect Dis. 1971 Dec;124 (Suppl):S125–S129. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.supplement_1.s125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



