Abstract
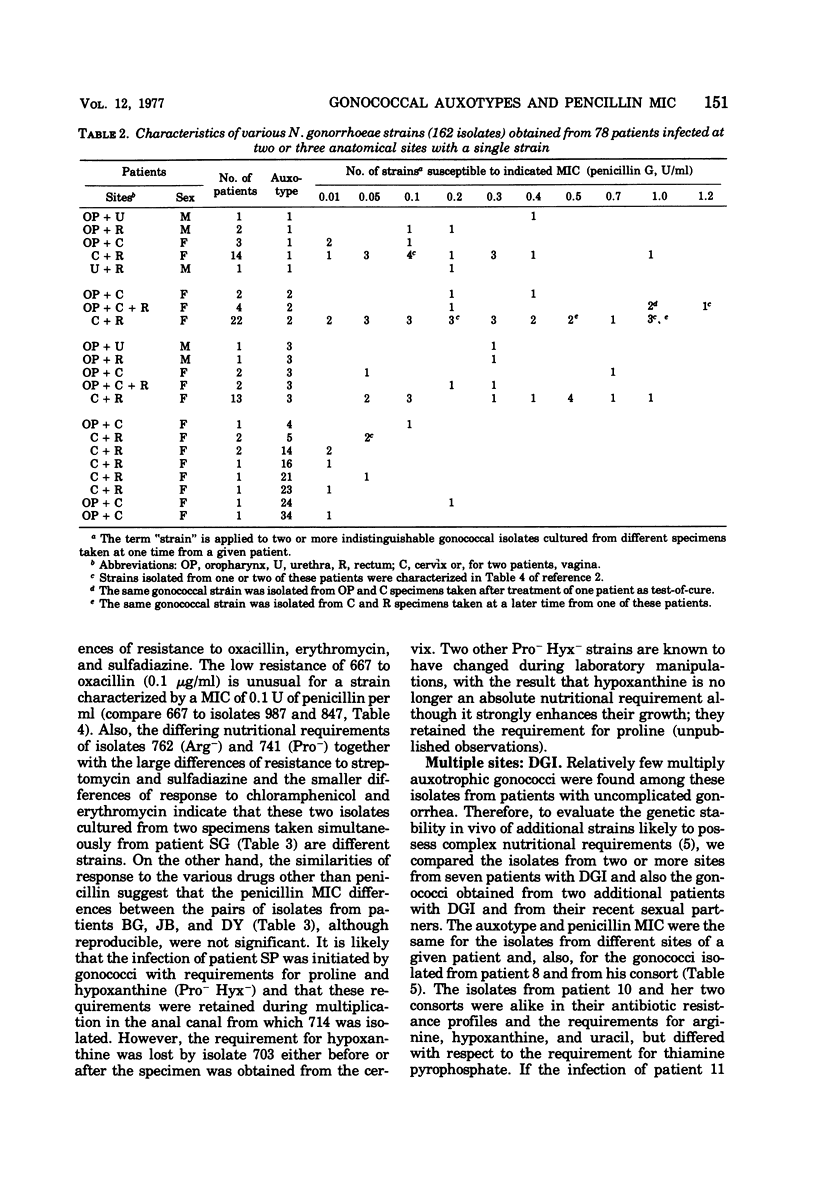
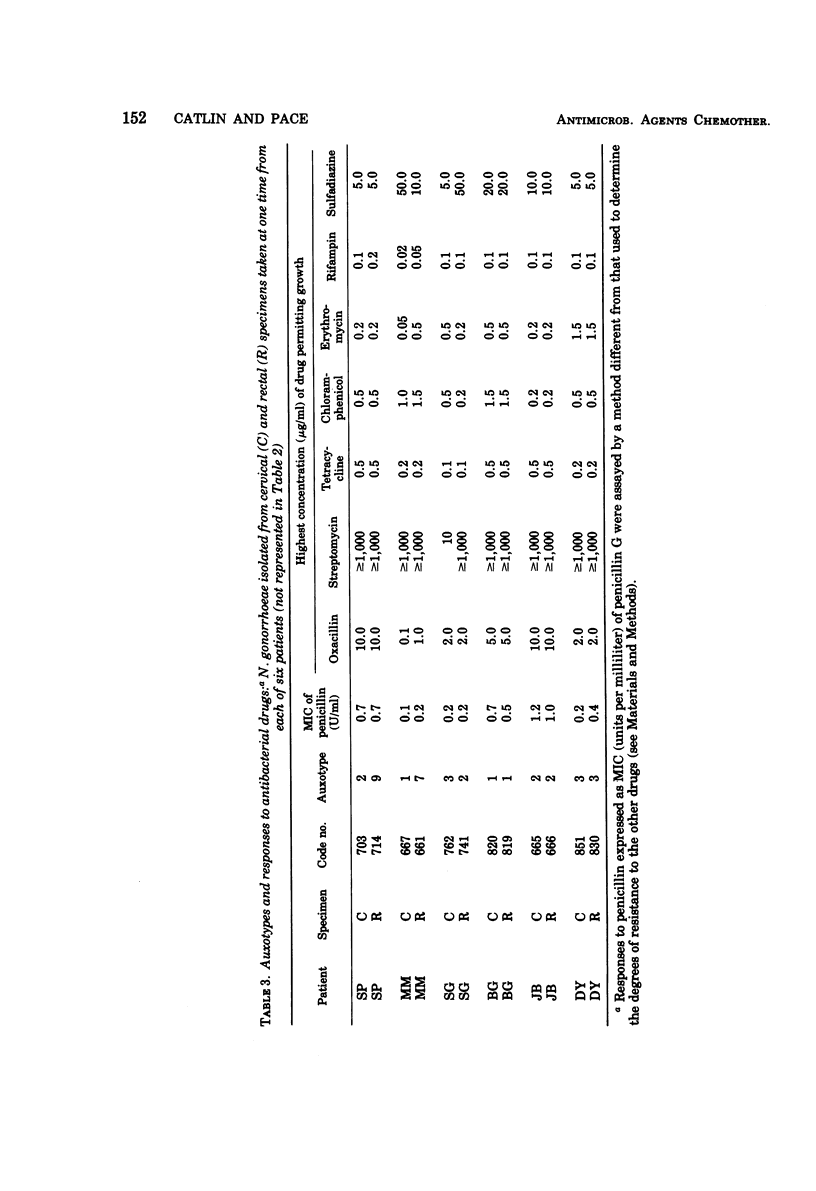
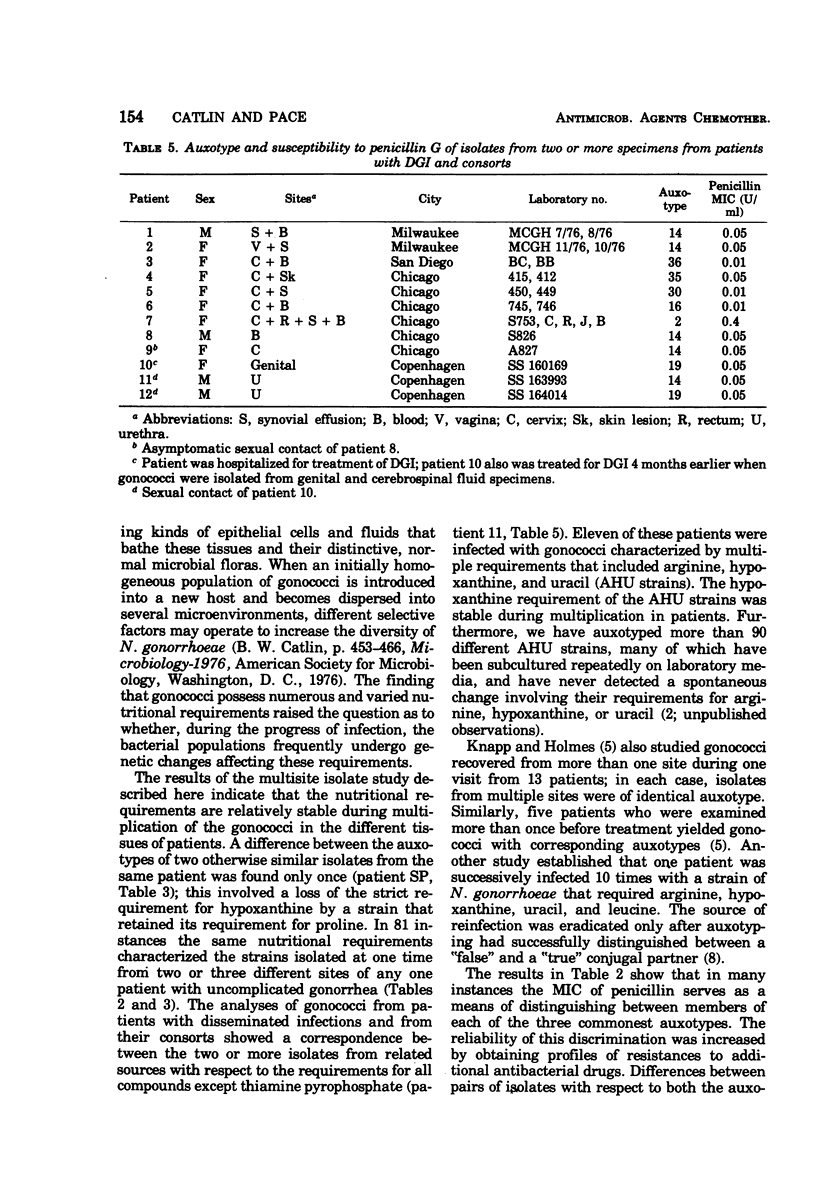
A system of auxotyping described in 1973 is based on the differing nutritional requirement patterns of Neisseria gonorrhoeae strains. Our ongoing evaluation of the reliability of auxotyping has involved a study of the constancy of characteristics of gonococci isolated at one time from two or more sites of a given subject. The auxotypes and minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of penicillin G were determined for 181 isolates obtained from 84 patients with uncomplicated gonorrhea, for 16 isolates from 8 couples with uncomplicated gonorrhea, and for 21 isolates from 12 other patients, 9 with disseminated gonococcal infection and three consorts. The penicillin MIC served to distinguish between many members of auxotypes 1, 2, and 3, which are commonly involved in uncomplicated gonorrhea. Thus, for proline-requiring gonococci (auxotype 2) the MIC ranged from 0.01 to 1.2 IU of penicillin per ml. The profile of gonococcal responses to seven other antibacterial drugs provided useful additional information where the extent of phenotypic similarity was in doubt. In all but seven instances, the gonococci isolated from different sites of the same patient, or from a consort, had the same nutritional requirements and penicillin MIC. The gonococci isolated from one patient with disseminated gonococcal infection and from one of her two sexual contacts had nutritional requirements for arginine, hypoxanthine, uracil, and thiamine pyrophosphate, whereas the strain isolated from her second contact differed in having no requirement for thiamine pyrophosphate. The paired cervical and rectal isolates from one patient with uncomplicated gonorrhea differed only with respect to a requirement for hypoxanthine. Pairs of isolates from three patients differed slightly in degree of susceptibility to penicillin. In the remaining two instances, however, numerous differences between the isolates from the endocervix and the anal canal of a given patient indicated the presence of concomitant infections with different strains of N. gonorrhoeae.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brooks G. F., Israel K. S., Petersen B. H. Bactericidal and opsonic activity against Neisseria gonorrhoeae in sera from patients with disseminated gonococcal infection. J Infect Dis. 1976 Nov;134(5):450–462. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.5.450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carifo K., Catlin B. W. Neisseria gonorrhoeae auxotyping: differentiation of clinical isolates based on growth responses on chemically defined media. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Sep;26(3):223–230. doi: 10.1128/am.26.3.223-230.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catlin B. W. Genetic transformation of biosynthetically defective Neisseria gonorrhoeae clinical isolates. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):203–209. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.203-209.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catlin B. W. Nutritional profiles of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Neisseria meningitidis, and Neisseria lactamica in chemically defined media and the use of growth requirements for gonococcal typing. J Infect Dis. 1973 Aug;128(2):178–194. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.2.178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp J. S., Holmes K. K. Disseminated gonococcal infections caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae with unique nutritional requirements. J Infect Dis. 1975 Aug;132(2):204–208. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.2.204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. E., Jr, Billings T. E., Hackney J. F., Thayer J. D. Primary isolation of N. gonorrhoeae with a new commercial medium. Public Health Rep. 1967 Apr;82(4):361–363. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masterton G., Schofield C. B. Doxycycline HCl (Vibramycin) as a single dose oral treatment of gonococcal and nonspecific urethritis in men. Br J Vener Dis. 1972 Apr;48(2):121–125. doi: 10.1136/sti.48.2.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morello J. A., Lerner S. A., Bohnhoff M. Characteristics of atypical Neisseria gonorrhoeae from disseminated and localized infections. Infect Immun. 1976 May;13(5):1510–1516. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.5.1510-1516.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYN A., BENTZON M. W. SENSITIVITY TO ANTIBIOTICS OF GONOCOCCAL STRAINS ISOLATED BY REPEATED CULTURING FROM THE SAME PATIENT. Acta Derm Venereol. 1963;43:394–398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYN A., BENTZON M. W., THAYER J. D., WILKINSON A. E. RESULTS OF COMPARATIVE EXPERIMENTS USING DIFFERENT METHODS FOR DETERMINING THE SENSITIVITY OF NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE TO PENICILLIN G. Bull World Health Organ. 1965;32:477–502. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYN A., KORNER B., BENTZON M. W. Effects of penicillin, streptomycin, and tetracycline on N. gonorrhoeae isolated in 1944 and in 1957. Br J Vener Dis. 1958 Dec;34(4):227–239. doi: 10.1136/sti.34.4.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyn A., Benzon M. W. A study of the relationships between the sensitivities of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to sodium penicillin G, four semi-synthetic penicillins, spiramycin, and fusidic acid. Br J Vener Dis. 1968 Jun;44(2):140–150. doi: 10.1136/sti.44.2.140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMIDT H., LARSEN S. O. Comparison of the in vitro sensitivity of gonococcal strains isolated from patients and from their contacts. Acta Derm Venereol. 1962;42:294–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoolnik G. K., Buchanan T. M., Holmes K. K. Gonococci causing disseminated gonococcal infection are resistant to the bactericidal action of normal human sera. J Clin Invest. 1976 Nov;58(5):1163–1173. doi: 10.1172/JCI108569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver P. S., Darling W. M. Penicillin-insensitive gonococci in the Bolton area. Preponderance in young women and immigrants. Br J Vener Dis. 1971 Oct;47(5):367–372. doi: 10.1136/sti.47.5.367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE L. A., KELLOGG D. S., Jr NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE IDENTIFICATION IN DIRECT SMEARS BY A FLUORESCENT ANTIBODY-COUNTERSTAIN METHOD. Appl Microbiol. 1965 Mar;13:171–174. doi: 10.1128/am.13.2.171-174.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



