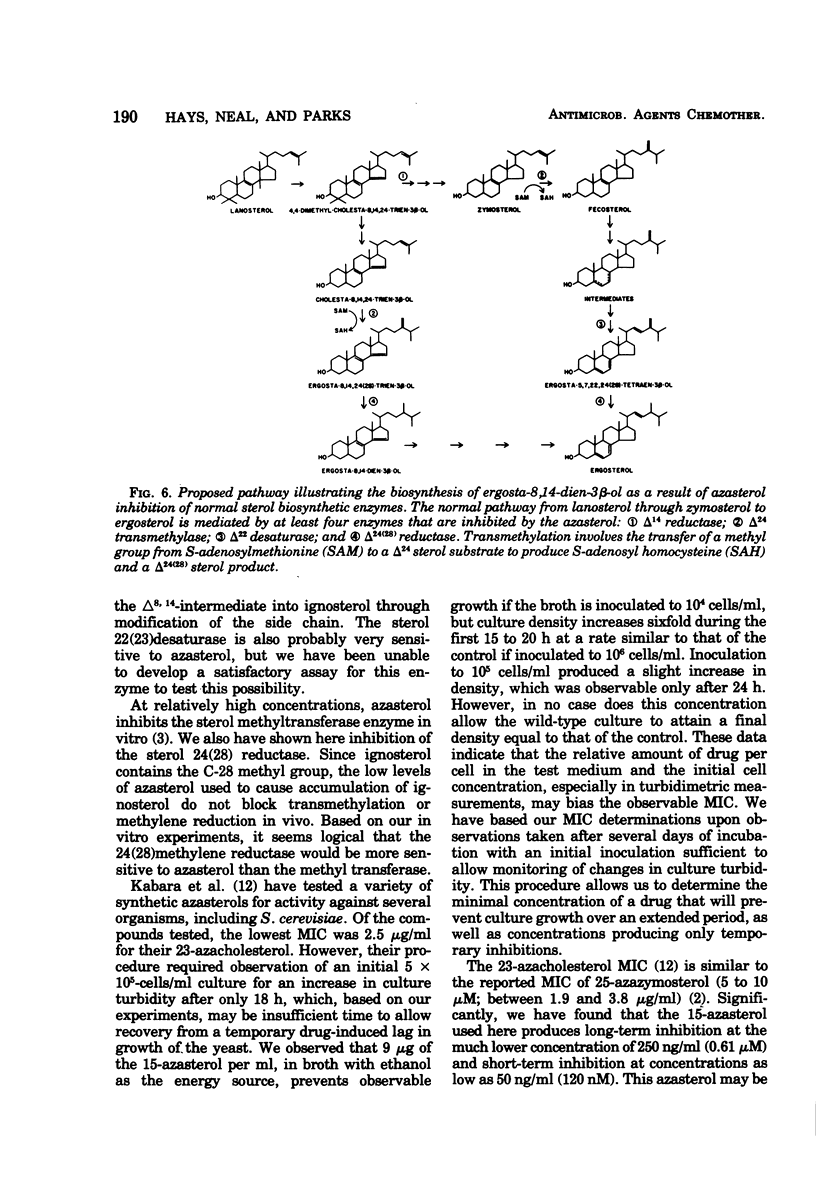
Abstract
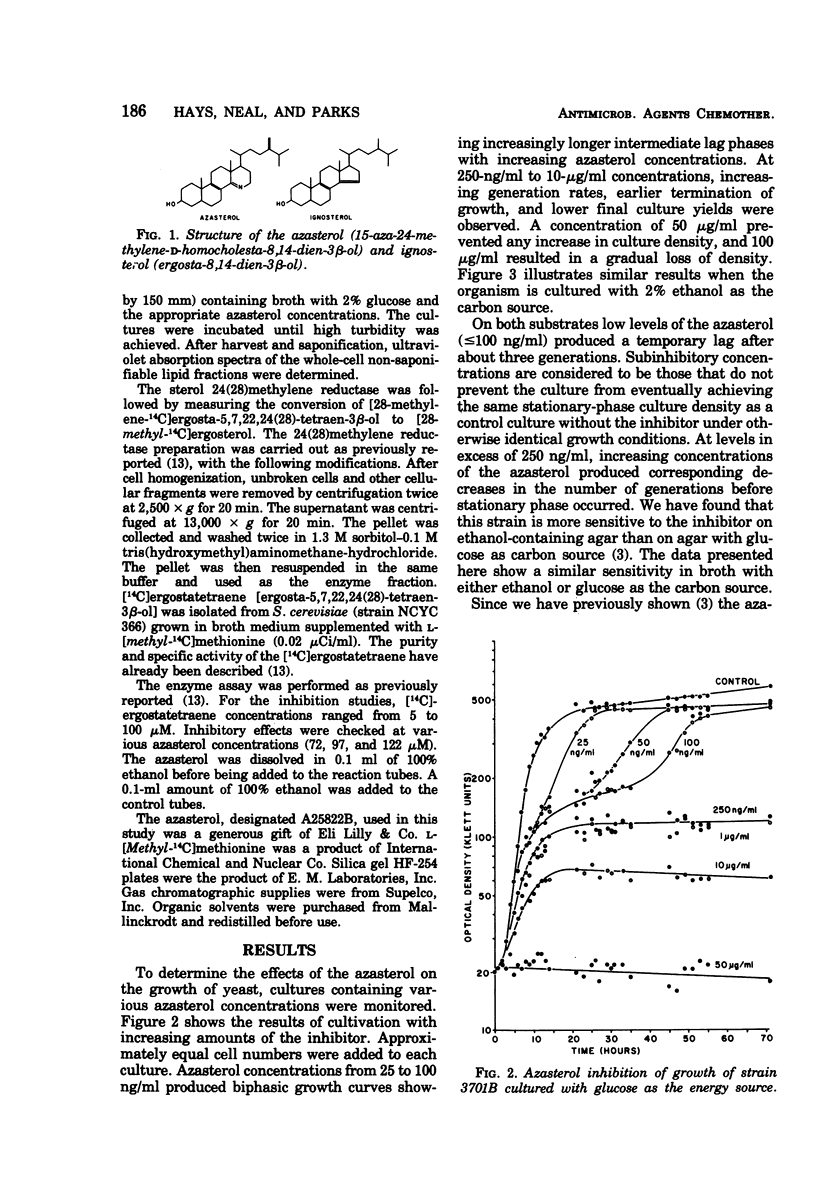
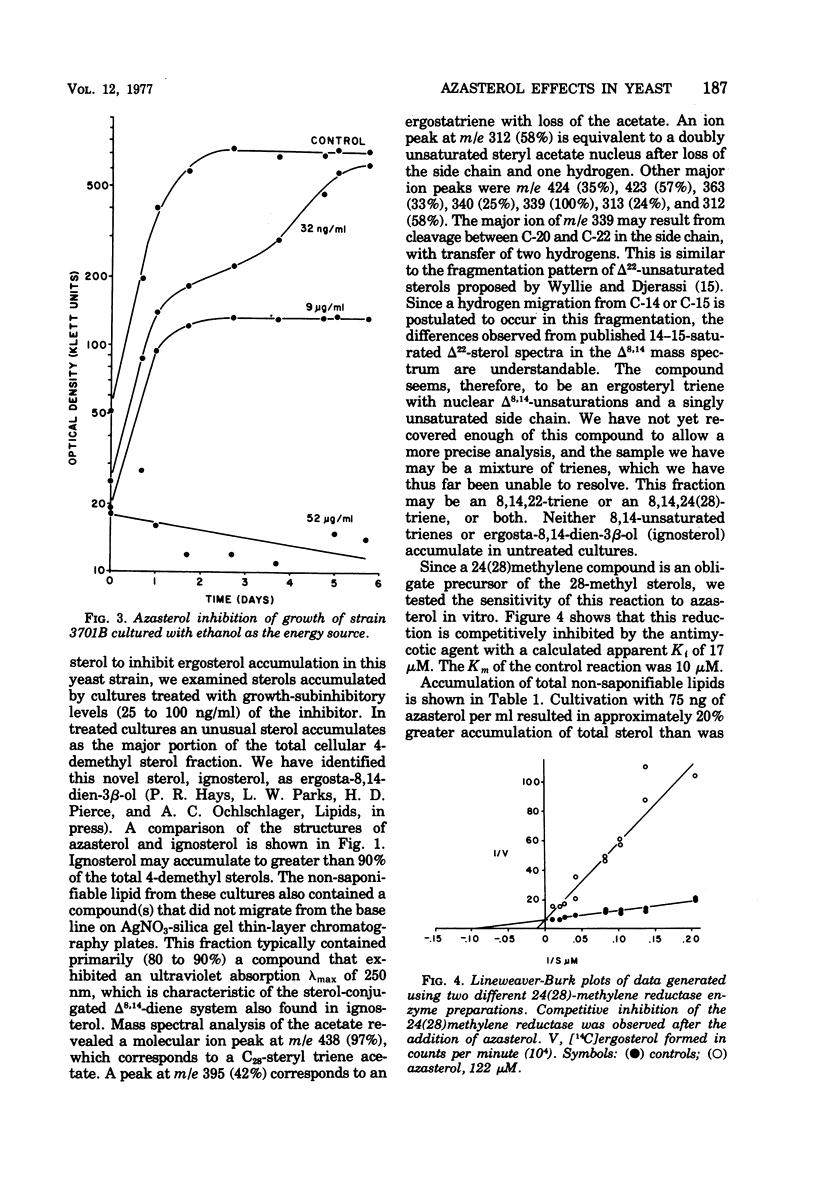
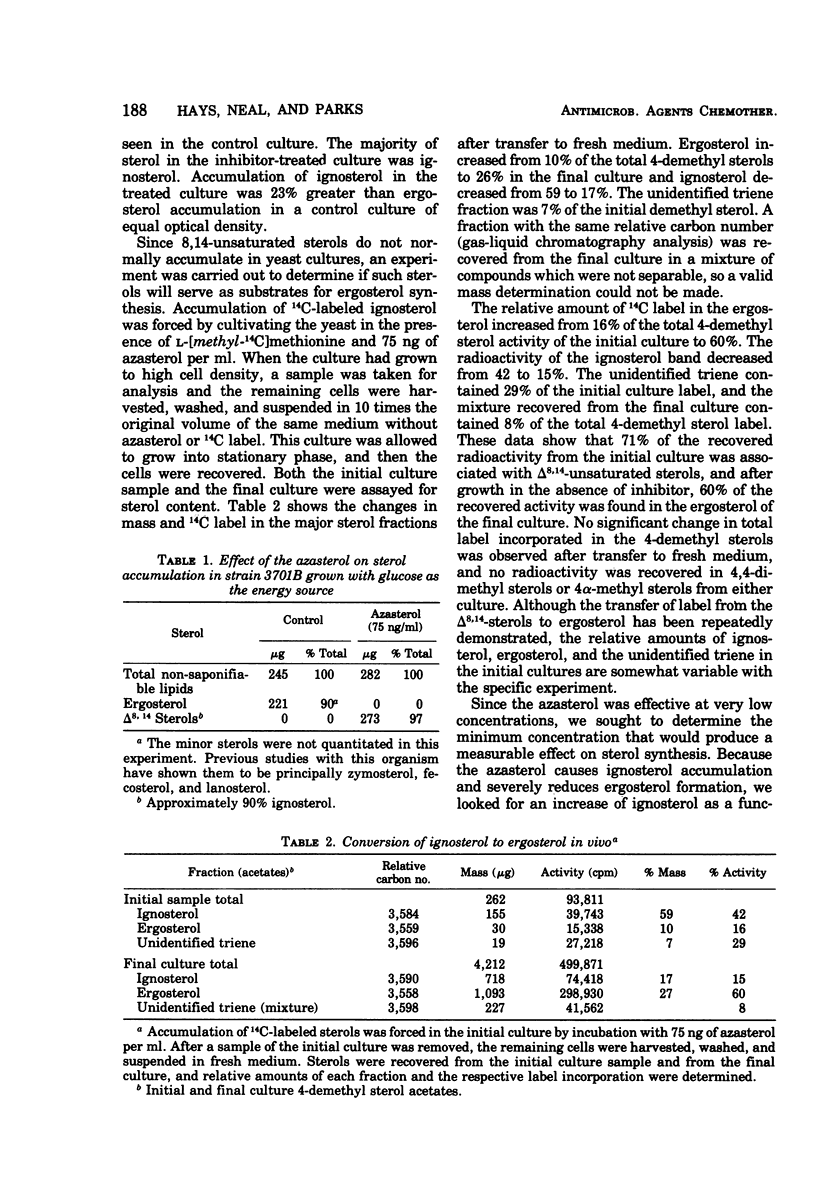
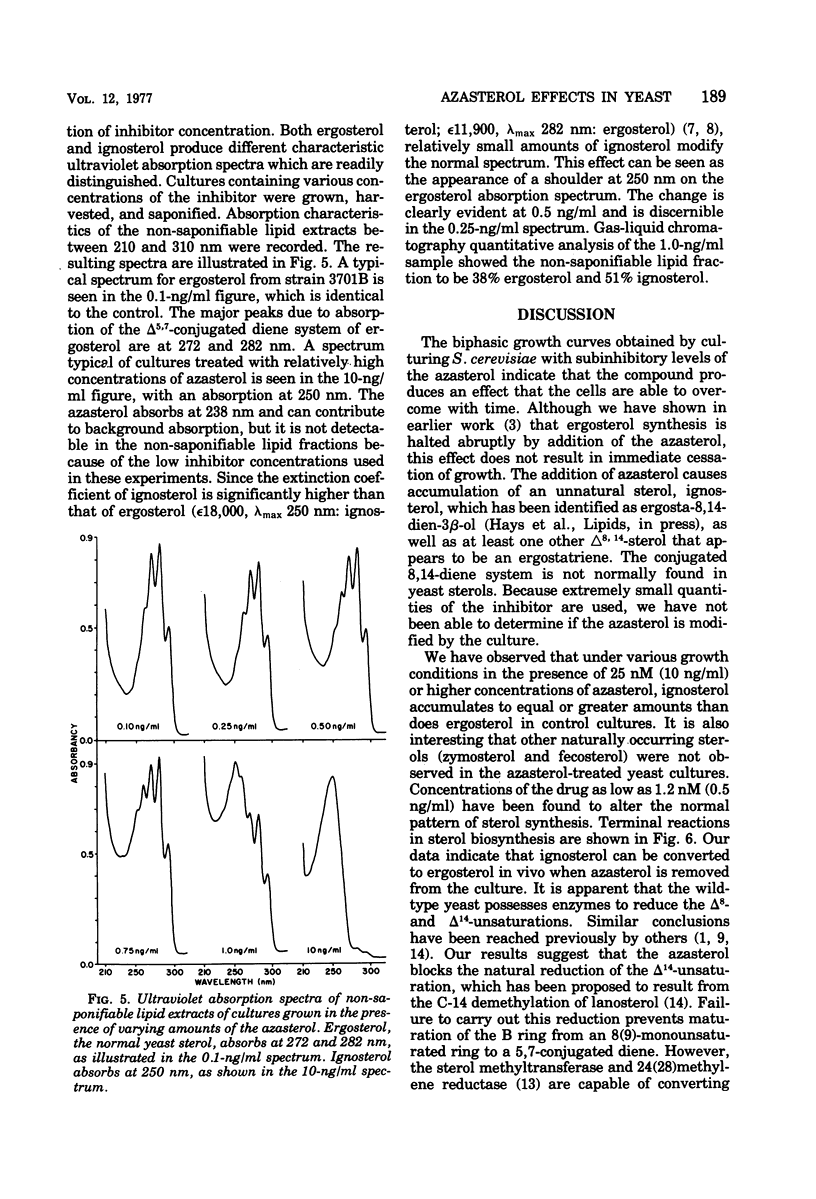
The yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae has been studied during cultivation with a naturally occurring antimycotic azasterol. At very low concentrations (1.0 to 10.0 ng/ml), where growth retardation is not observed, an unusual sterol, ergosta-8,14-dien-3β-ol, accumulates in high concentrations. Upon removal of the azasterol from the culture, the 8,14-diene is converted to ergosterol. Much smaller amounts of another 8,14-sterol, but with an additional unsaturation, have also been observed. Total sterol accumulation is higher in cultures containing subinhibitory levels of the antimycotic agent than the amounts of normal sterol accumulation in control cultures. With between 10 and 100 ng of azasterol per ml a transitory cessation of growth is observed from which the culture is able to recover. At much higher concentrations growth inhibition and even cell lysis results. Competitive inhibition of sterol 24(28)methylene reductase is demonstrated.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akhtar M., Brooks W. A., Watkinson I. A. The intermediary role of a steroid 8,14-dien-3-beta-ol system in ergosterol biosynthesis. Biochem J. 1969 Nov;115(2):135–137. doi: 10.1042/bj1150135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avruch L., Fischer S., Pierce H., Jr, Oehlschlager A. C. The induced biosynthesis of 7-dehydrocholesterols in yeast: potential sources of new provitamin D3 analogs. Can J Biochem. 1976 Jul;54(7):657–665. doi: 10.1139/o76-095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey R. B., Hays P. R., Parks L. W. Homoazasterol-mediated inhibition of yeast sterol biosynthesis. J Bacteriol. 1976 Dec;128(3):730–734. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.3.730-734.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey R. B., Parks L. W. Yeast sterol esters and their relationship to the growth of yeast. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):606–612. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.606-612.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeck L. D., Hoehn M. M., Westhead J. E., Wolter R. K., Thomas D. N. New azasteroidal antifungal antibotics from Geotrichum flavo-brunneum. I. Discovery and fermentation studies. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1975 Feb;28(2):95–101. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.28.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlin J. W., Chaney M. O., Chen S., Demarco P. V., Jones N. D., Occolowitz J. L. Structure of antibiotic A 25822 B, a novel nitrogen-containing C28-sterol with antifungal properties. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1974 Dec;27(12):992–993. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.27.992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabara J. J., Holzschu D. L., Catsoulacos D. P. Structure-function activity of azasterols and nitrogen-containing steroids. Lipids. 1976 Oct;11(10):755–762. doi: 10.1007/BF02533051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neal W. D., Parks L. W. Sterol 24(28) methylene reductase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1375–1378. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1375-1378.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkinson I. A., Wilton D. C., Munday K. A., Akhtar M. The formation and reduction of the 14,15-double bond in cholesterol biosynthesis. Biochem J. 1971 Jan;121(1):131–137. doi: 10.1042/bj1210131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Kruijff B., Demel R. A. Polyene antibiotic-sterol interactions in membranes of Acholeplasma laidlawii cells and lecithin liposomes. 3. Molecular structure of the polyene antibiotic-cholesterol complexes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Feb 26;339(1):57–70. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90332-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Kruyff B., van Dijck P. W., Godlbach R. W., Demel R. A., van Deenen L. L. Influence of fatty acid and sterol composition on the lipid phase transition and activity of membrane-bound enzymes in Acholeplasma laidlawii. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 22;330(3):269–282. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90232-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


