Abstract
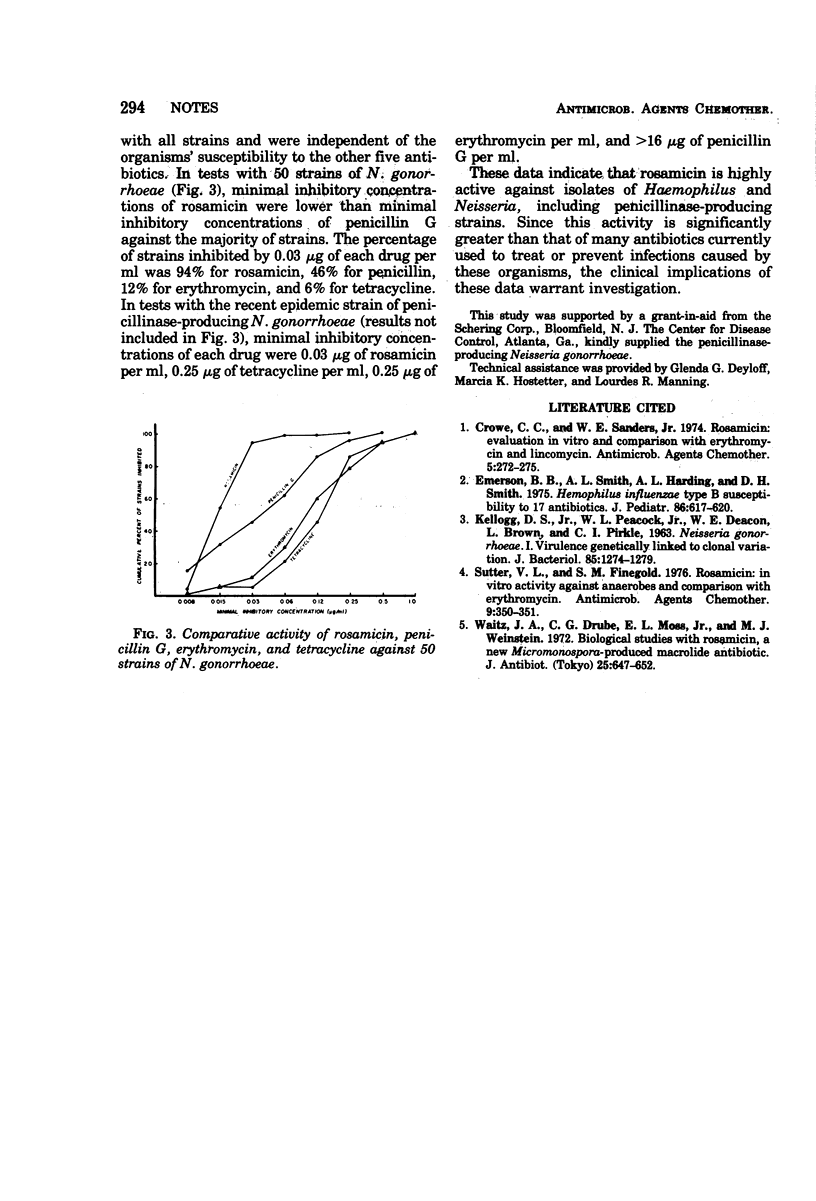
Rosamicin was significantly more active against Haemophilus and Neisseria than are many antibiotics currently used to treat or prevent infection caused by these organisms. This enhanced activity was also observed against penicillinase-producing strains.
Full text
PDF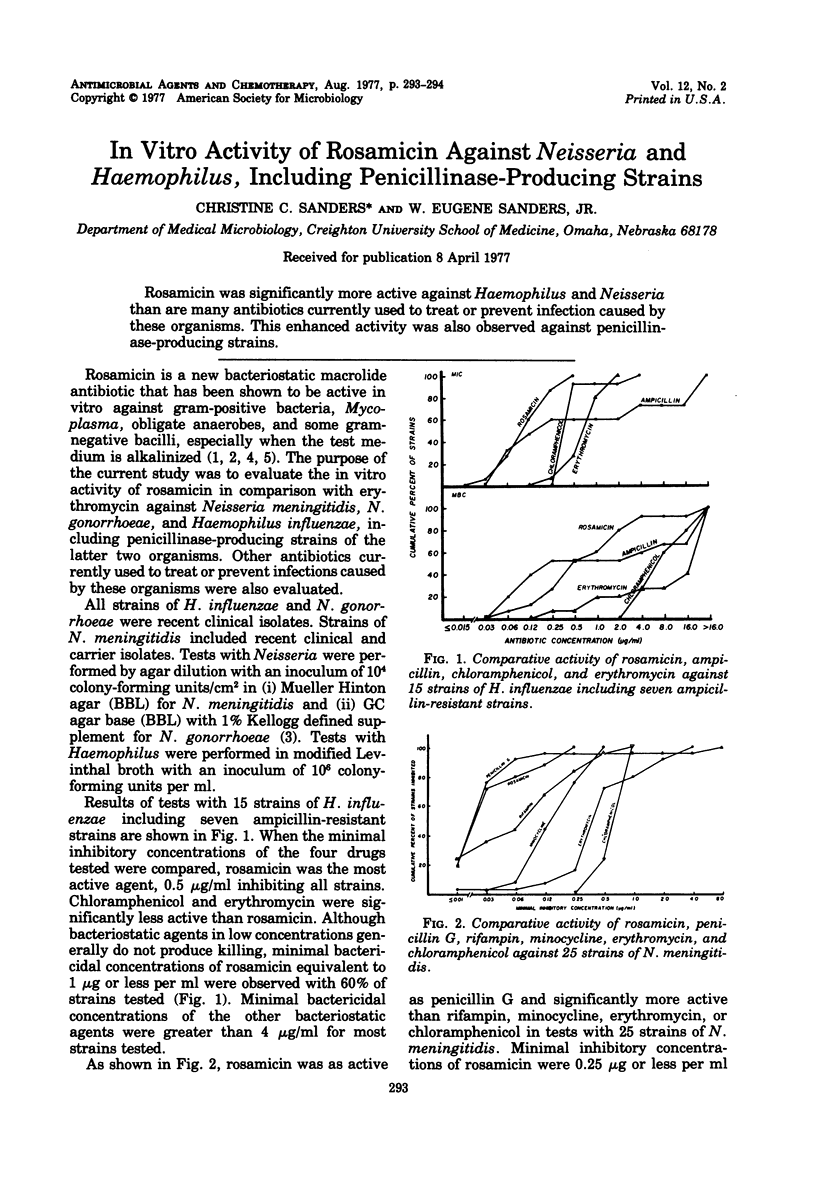
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Crowe C. C., Sanders W. E., Jr Rosamicin: evaluation in vitro and comparison with erythromycin and lincomycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Mar;5(3):272–275. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.3.272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson B. B., Smith A. L., Harding A. L., Smith D. H. Hemophilus influenzae type B susceptibility to 17 antibiotics. J Pediatr. 1975 Apr;86(4):617–620. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(75)80166-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLOGG D. S., Jr, PEACOCK W. L., Jr, DEACON W. E., BROWN L., PIRKLE D. I. NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE. I. VIRULENCE GENETICALLY LINKED TO CLONAL VARIATION. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jun;85:1274–1279. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.6.1274-1279.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter V. L., Finegold S. M. Rosamicin: in vitro activity against anaerobes and comparison with erythromycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Feb;9(2):350–351. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.2.350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waitz J. A., Drube C. G., Moss E. L., Jr, Weinstein M. J. Biological studies with rosamicin, a new Micromonospora-produced macrolide antibiotic. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1972 Nov;25(11):647–652. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.25.647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


