Abstract
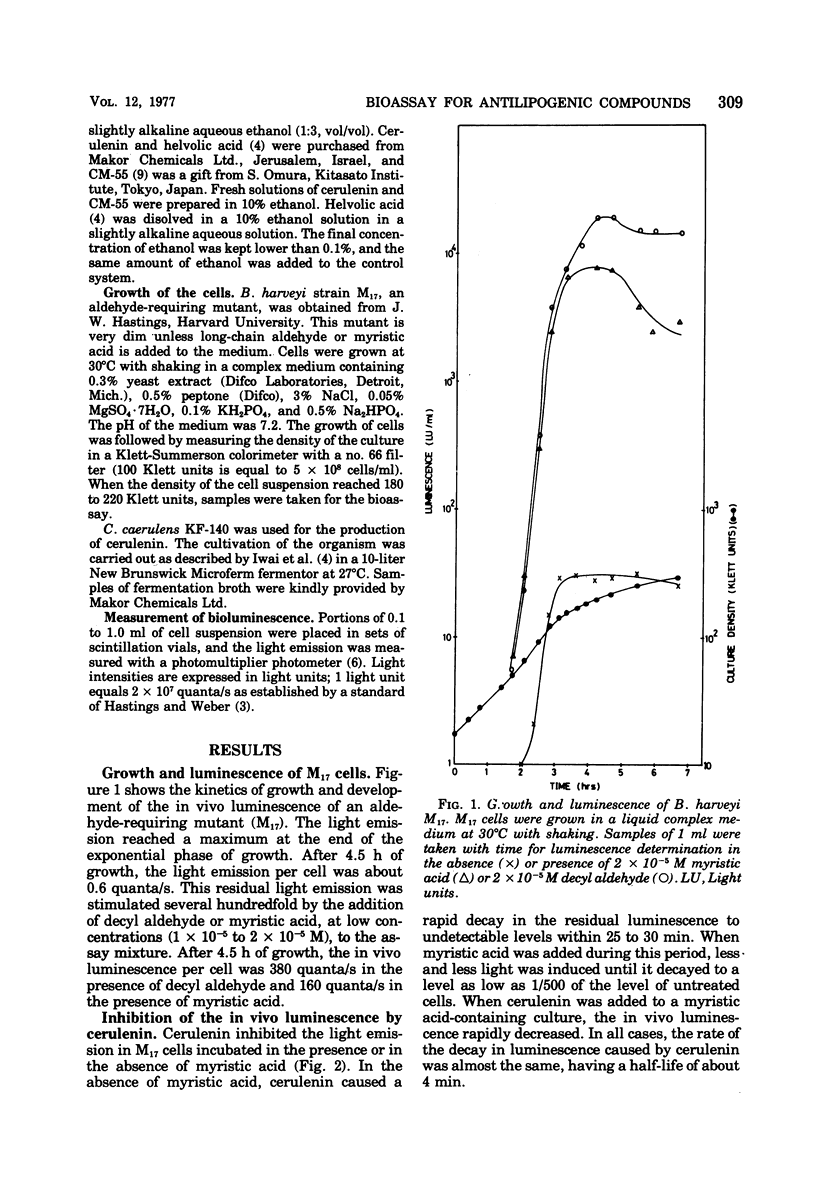
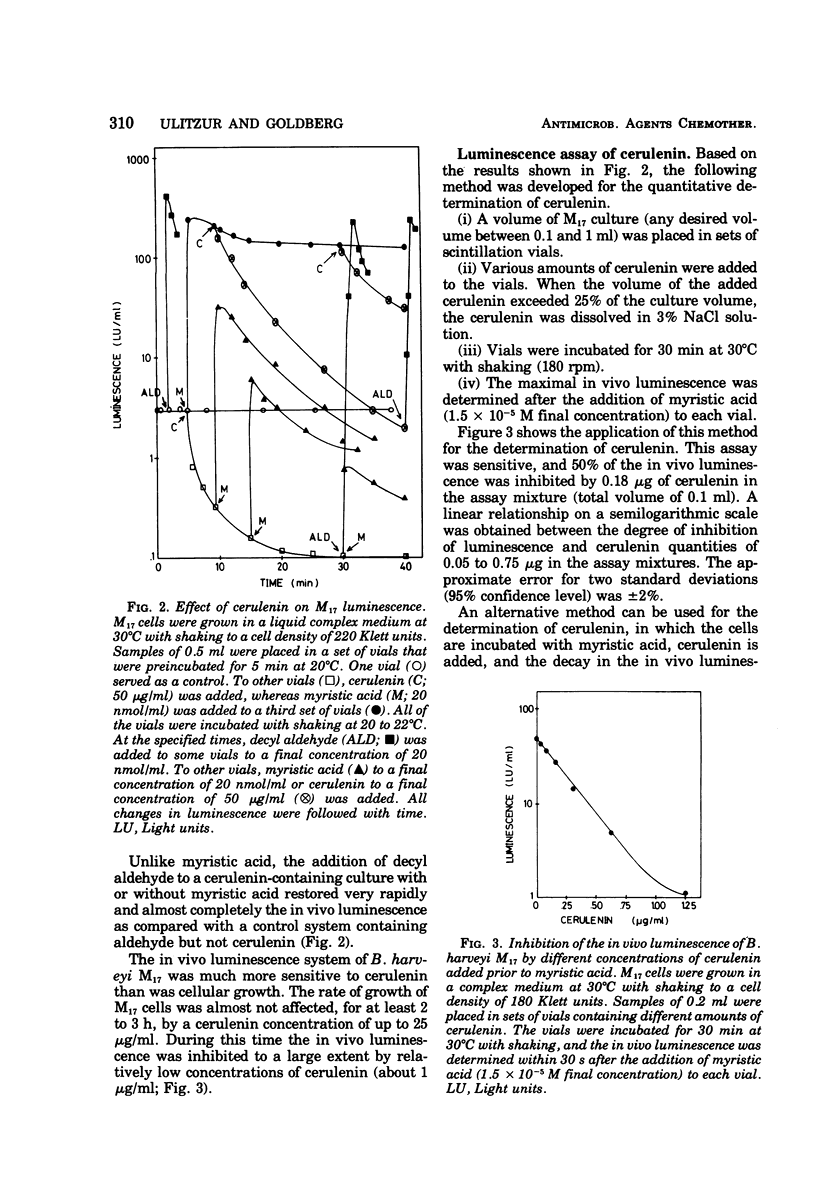
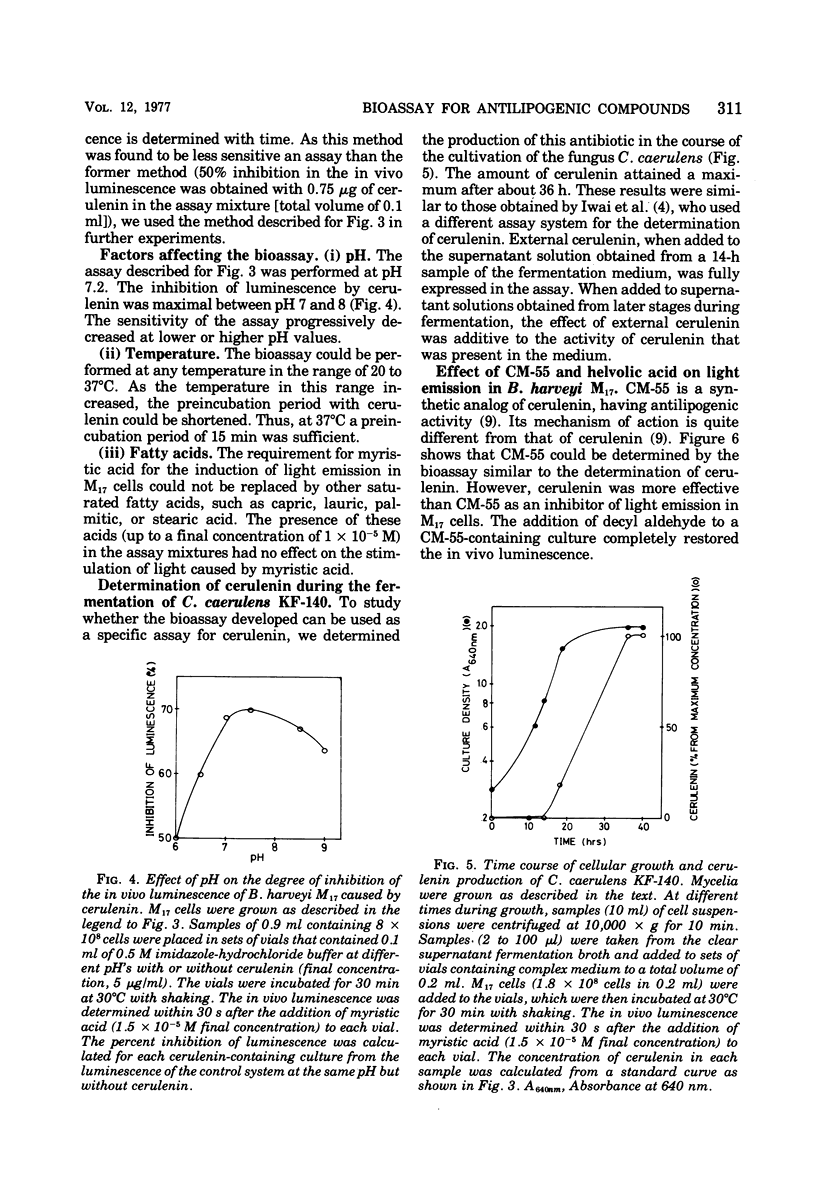
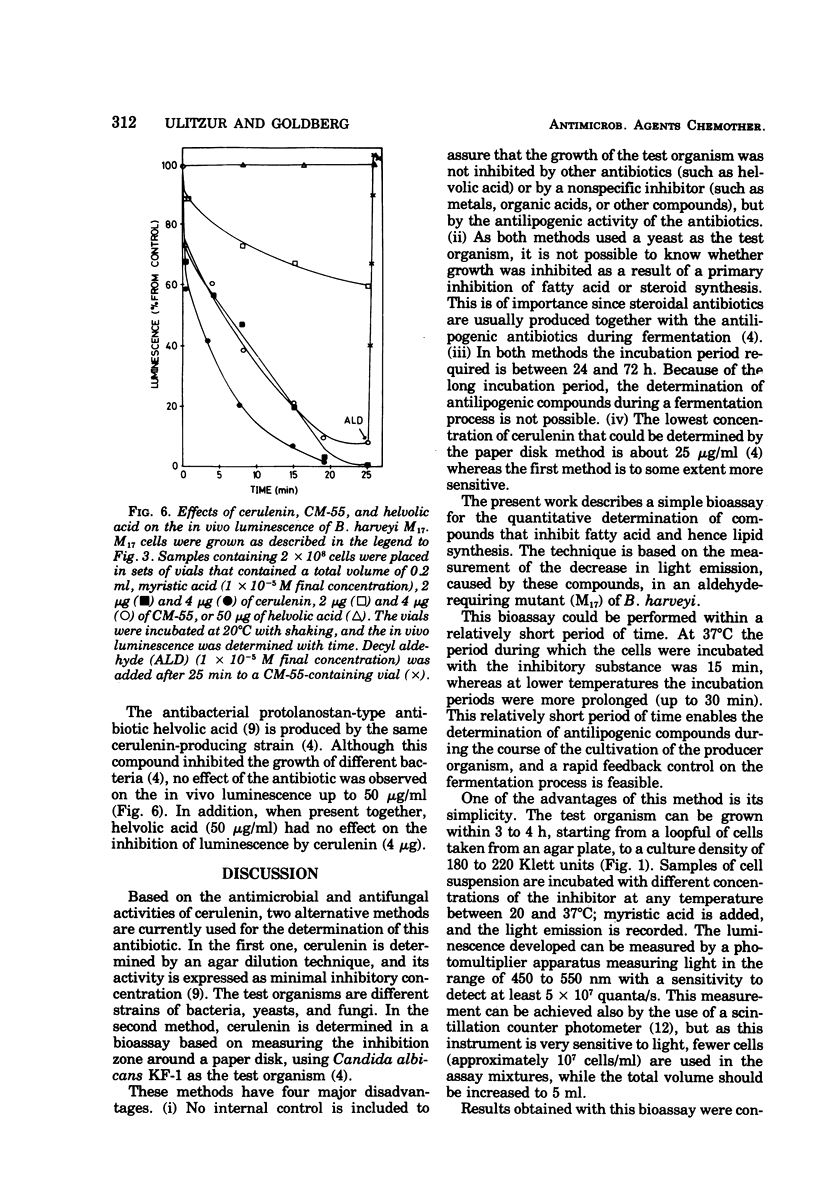
A sensitive and rapid bioassay for the determination of the antilipogenic compounds cerulenin and CM-55 is described. The bioassay is based on the inhibitory effect of cerulenin and CM-55 on the in vivo luminescence of an aldehyde-requiring mutant of the marine bacterium Beneckea harveyi. A total quantity as low as 0.1 μg of cerulenin can be determined within 15 min with an error of ±2%. The bioassay, as presented, is specific for compounds that are known to inhibit fatty acid biosynthesis and, as such, it might be used as a general screening method for the detection of antilipogenic compounds.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arison B. H., Omura S. Revised structure of cerulenin. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1974 Jan;27(1):28–30. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.27.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Agnolo G., Rosenfeld I. S., Awaya J., Omura S., Vagelos P. R. Inhibition of fatty acid synthesis by the antibiotic cerulenin. Specific inactivation of beta-ketoacyl-acyl carrier protein synthetase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Nov 29;326(2):155–156. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(73)90241-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nealson K. H., Hastings J. W. The inhibition of bacterial luciferase by mixed function oxidase inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 10;247(3):888–894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura S., Horiuchi T., Omura S., Hata T. The action mechanism of cerulenin. I. Effect of cerulenin on sterol and fatty acid biosynthesis in yeast. J Biochem. 1972 May;71(5):783–796. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno T., Awaya J., Kesado T., Nomura S., Omura S. Mechanism of action of CM-55, a synthetic analogue of the antilipogenic antibiotic cerulenin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Oct;6(4):387–392. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.4.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omura S. The antibiotic cerulenin, a novel tool for biochemistry as an inhibitor of fatty acid synthesis. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Sep;40(3):681–697. doi: 10.1128/br.40.3.681-697.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono T., Kesado T., Awaya J., Omura S. Target of inhibition by the anti-lipogenic antibiotic cerulenin of sterol synthesis in yeast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Apr 23;57(4):1119–1124. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90812-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley P. E. Determination of subpicomole levels of NADH and FMN using bacterial luciferase and the liquid scintillation spectrometer. Anal Biochem. 1971 Feb;39(2):441–453. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90434-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vance D., Goldberg I., Mitsuhashi O., Bloch K. Inhibition of fatty acid synthetases by the antibiotic cerulenin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Aug 7;48(3):649–656. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90397-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


