Abstract
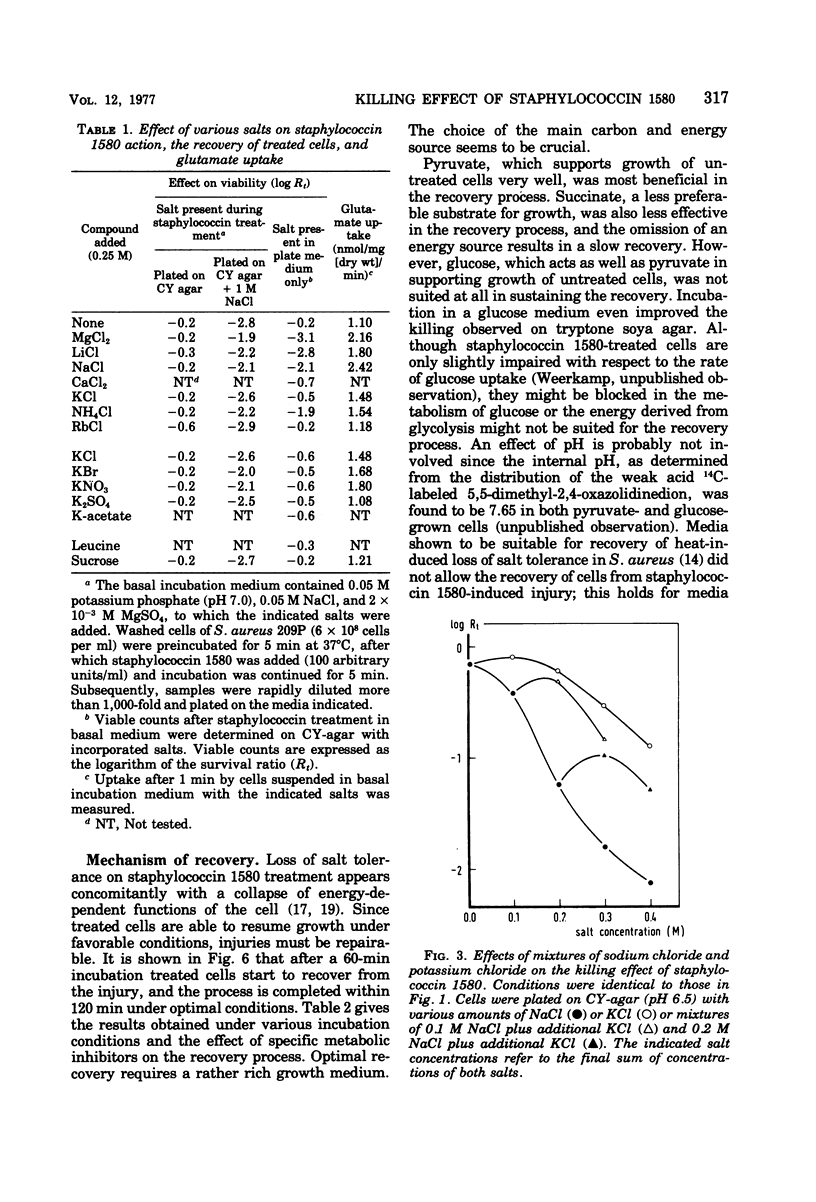
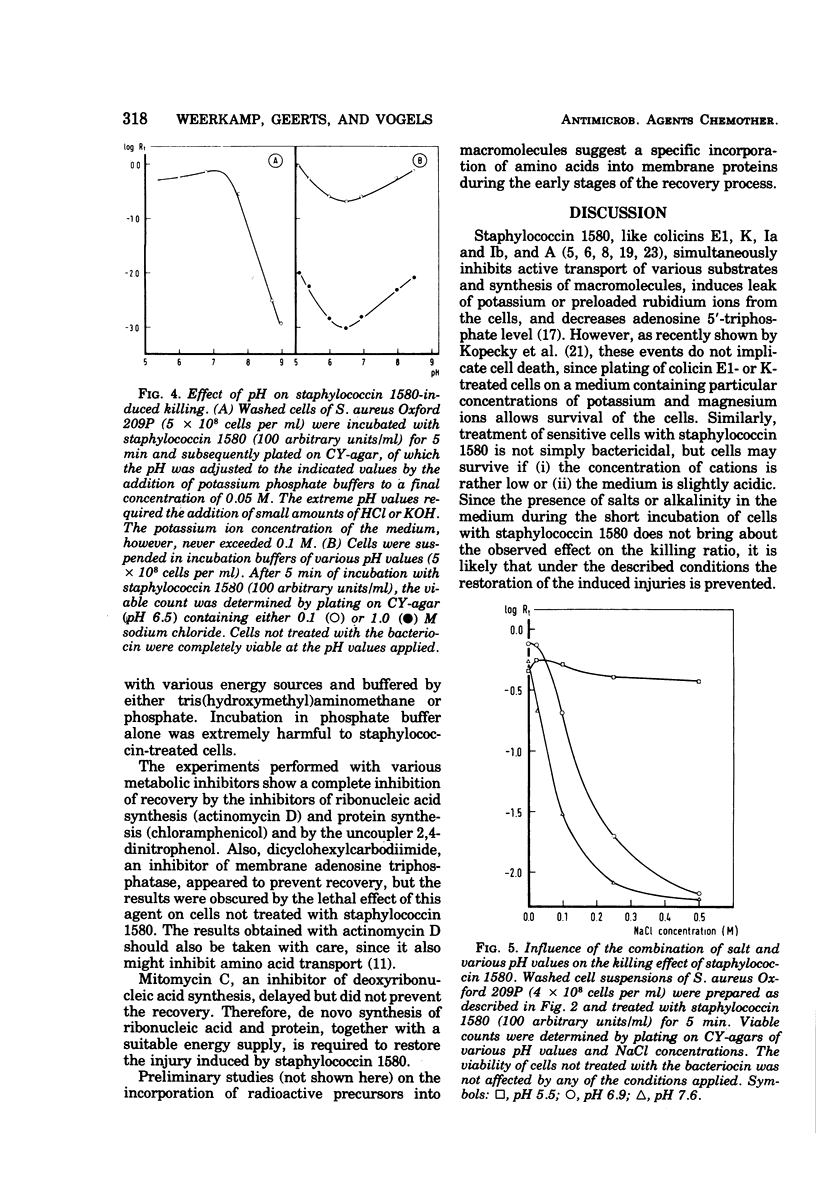
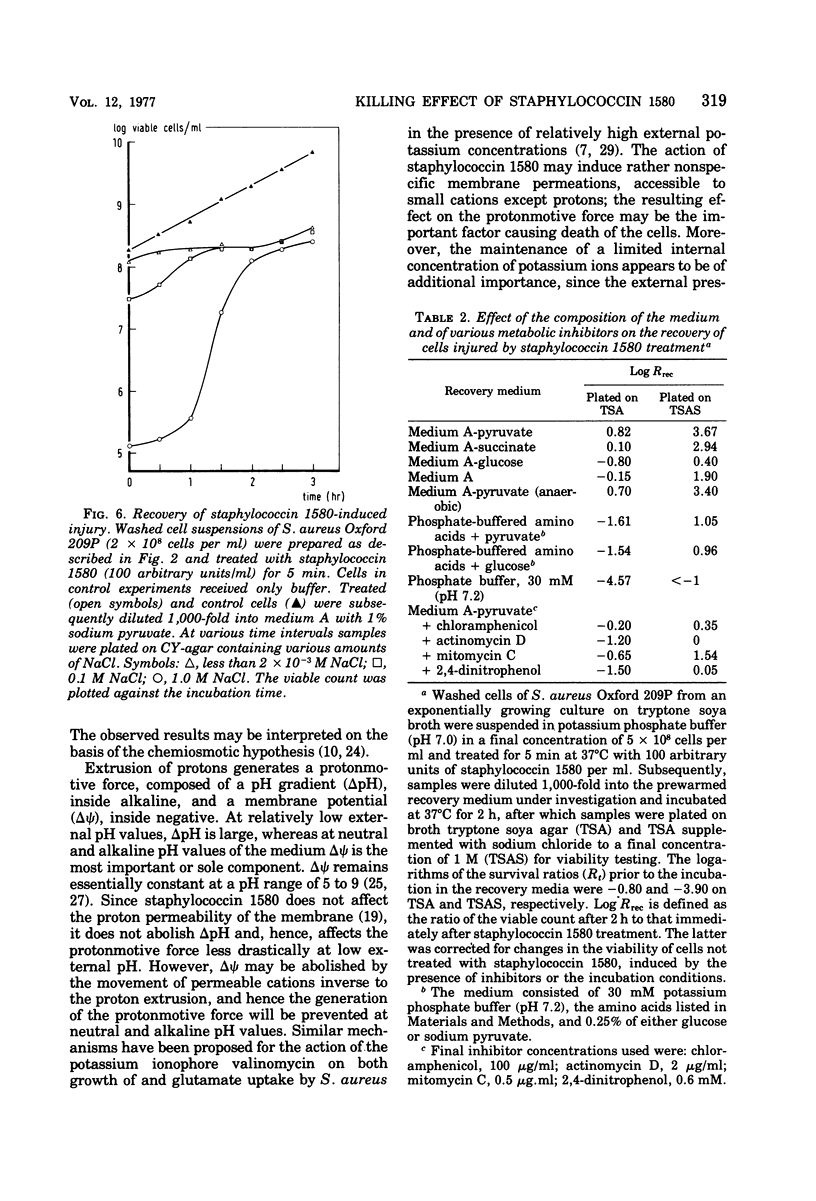
Treatment of sensitive cells with staphylococcin 1580, a bacteriocin of Staphylococcus epidermidis, rapidly induced gross changes in the permeability of the membrane. However, only a small fraction of the cells was killed when treated cells were plated on media containing low amounts of salts. Killing was greatly enhanced by increasing the amounts of small cations incorporated in the plate medium and raising the alkalinity of the medium. The effect of cations correlated inversely with the ion radius. These conditions are shown to affect the repair mechanism of the sublethally injured cells rather than the interaction of staphylococcin 1580 with the cells. A model is proposed in which the killing effect of staphylococcin 1580 is a result of the inability of cells to maintain the protonmotive force at neutral or alkaline pH as a result of the permeation of cations. Recovery of sublethal damage appears to be a complex process requiring protein and probably also ribonucleic acid synthesis and the addition of a suitable energy source.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clarke D. J., Morris J. G. Action of Buytricin 7423 on Clostridium pasteurianum: changes in intracellular adenosine triphosphate concentration. Biochem Soc Trans. 1975;3(3):389–391. doi: 10.1042/bst0030389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dajani A. S., Wannamaker L. W. Bacteriocin of phage type 71 S. aureus. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 Jul 31;236(0):389–394. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb41505.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dajani A. S., Wannamaker L. W. Kinetic studies on the interaction of bacteriophage type 71 staphylococcal bacteriocin with susceptible bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):738–742. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.738-742.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dandeu J. P. Chemical and immunological study of colicins e(1), k, a, and q. Infect Immun. 1971 Jan;3(1):1–9. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.1.1-9.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields K. L., Luria S. E. Effects of colicins E1 and K on cellular metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):64–77. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.64-77.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields K. L., Luria S. E. Effects of colicins E1 and K on transport systems. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):57–63. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.57-63.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gale E. F., Llewellin J. M. The role of hydrogen and potassium ions in the transport of acidic amino acids in Staphylococcus aureus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Apr 14;266(1):182–205. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90134-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilchrist M. J., Konisky J. Effects of colicin Ia on transport and respiration in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 10;250(7):2457–2462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould J. M., Cramer W. A., van Thienen G. The effect of colicin E1 on proton extrusion and the H+/0 ration in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Oct 18;72(4):1519–1525. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80186-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M. Chemiosmotic interpretation of active transport in bacteria. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 Feb 18;227:297–311. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb14395.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holden J. T., Utech N. M. Actinomycin D inhibition of amino acid transport in Streptococcus faecalis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 May 2;135(2):351–354. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(67)90129-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes A., Hurst A. Magnesium requirement of Staphylococcus aureus for repair from sublethal heat injury. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Aug;22(8):1202–1205. doi: 10.1139/m76-177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst A., Hughes A., Duckworth M., Baddiley J. Loss of D-alanine during sublethal heating of Staphylococcus aureus S6 and magnesium binding during repair. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Aug;89(2):277–284. doi: 10.1099/00221287-89-2-277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iandolo J. J., Ordal Z. J. Repair of thermal injury of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):134–142. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.1.134-142.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ionesco H., Wolff A. Sur le mode d'action de la bactériocine N5 purifiée de Clostridium perfringens. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1975 Dec 22;281(24):2033–2036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jetten A. M., Vogels G. D. Effects of colicin A and staphylococcin 1580 on amino acid uptake into membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli and staphylococcus aureus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jul 18;311(4):483–495. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90124-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jetten A. M., Vogels G. D. Mode of action of a Staphylococcus epidermidis bacteriocin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Dec;2(6):456–463. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.6.456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jetten A. M., Vogels G. D. Nature and properties of a Staphylococcus epidermidis bacteriocin. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):243–250. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.243-250.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jetten A. M., Vogels G. D., de Windt F. Production and purification of a Staphylococcus epidermidis bacteriocin. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):235–242. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.235-242.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knepper J. E., Lusk J. E. Disappearance of specific proteins from the membranes of colicin-treated cells. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 10;251(23):7577–7580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopecky A. L., Copeland D. P., Lusk J. E. Viability of Escherichia coli treated with colicin K. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4631–4634. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer J., Brandis H. Mode of action of two streptococcus faecium bacteriocins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Feb;7(2):117–120. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.2.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levisohn R., Konisky J., Nomura M. Interaction of colicins with bacterial cells. IV. Immunity breakdown studied with colicins Ia and Ib. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):811–821. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.811-821.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. Performance and conservation of osmotic work by proton-coupled solute porter systems. J Bioenerg. 1973 Jan;4(1):63–91. doi: 10.1007/BF01516051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padan E., Zilberstein D., Rottenberg H. The proton electrochemical gradient in Escherichia coli cells. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Apr 1;63(2):533–541. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10257.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plate C. A., Suit J. L., Jetten A. M., Luria S. E. Effects of colicin K on a mutant of Escherichia coli deficient in Ca 2+, Mg 2+-activated adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 10;249(19):6138–6143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos S., Schuldiner S., Kaback H. R. The electrochemical gradient of protons and its relationship to active transport in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1892–1896. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ring K., Ehle H., Foit B. Effect of alkali ions on the active transport of neutral amino acids into Streptomyces hydrogenans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 May 21;433(3):615–629. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90285-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryabova I. D., Gorneva G. A., Ovchinnikov Y. A. Effect of valinomycin on ion transport in bacterial cells and on bacterial growth. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Aug 5;401(1):109–118. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90345-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel R., Slade H. D. Alteration of macromolecular synthesis and membrane permeability by a Streptococcus sanguis bacteriocin. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Mar;81(1):275–277. doi: 10.1099/00221287-81-1-275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomochika K. Energy dependency on the salt-resistance of Staphylococcus aureus: Effects of various inhibitors on the growth in high salinity condition. Acta Med Okayama. 1975 Jun;29(3):171–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upreti G. C., Hinsdill R. D. Production and mode of action of lactocin 27: bacteriocin from a homofermentative Lactobacillus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Feb;7(2):139–145. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.2.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



