Abstract
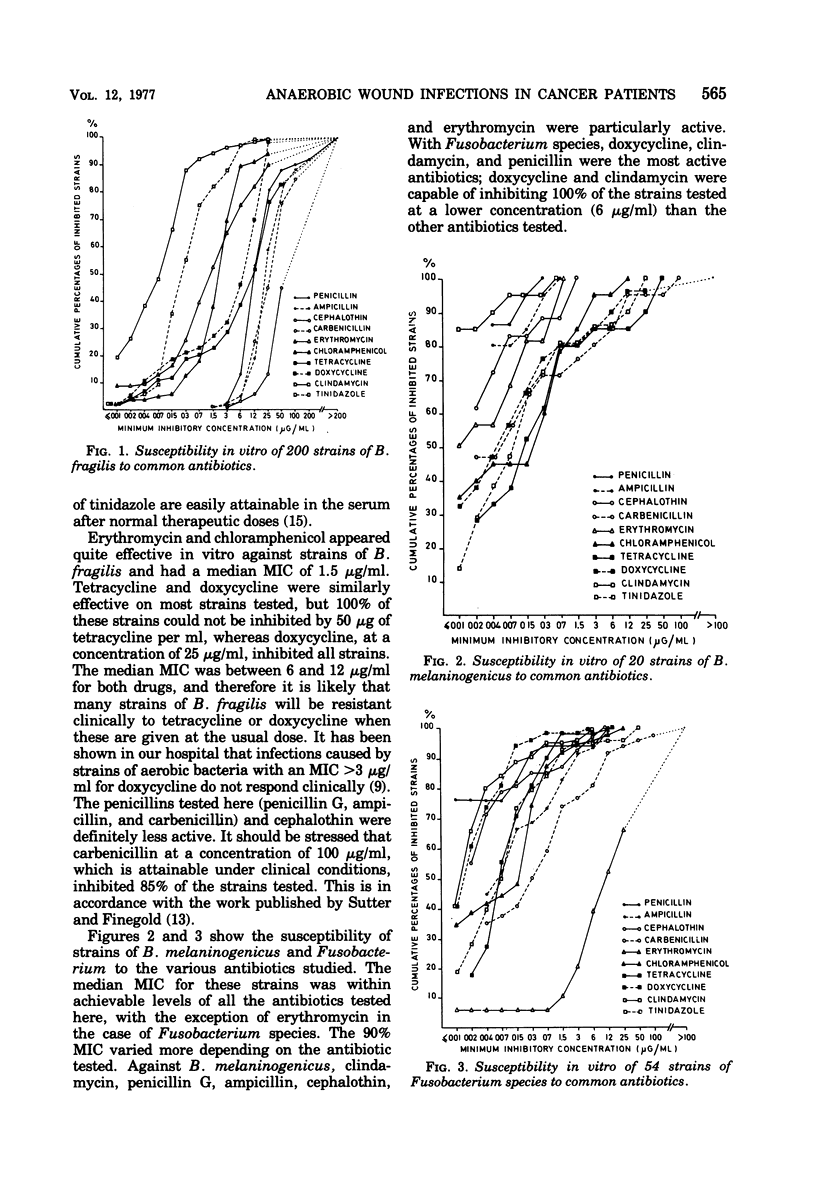
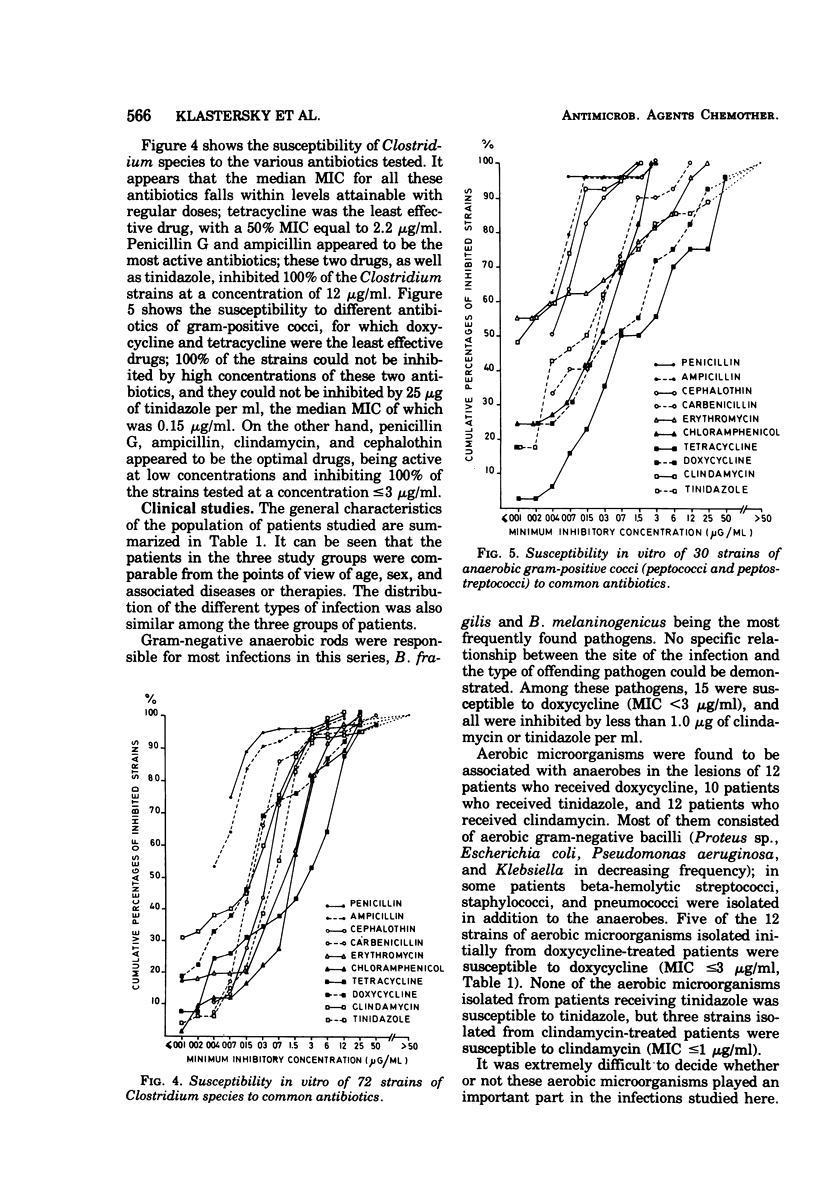
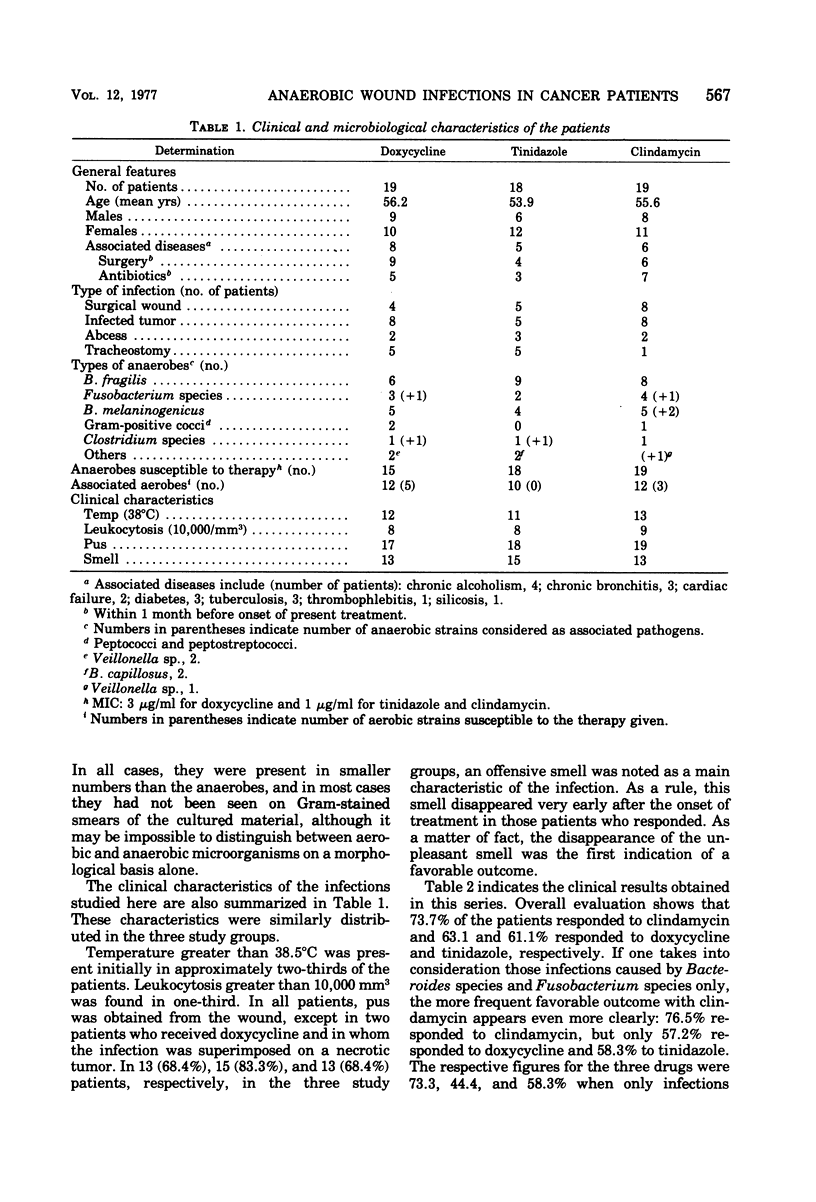
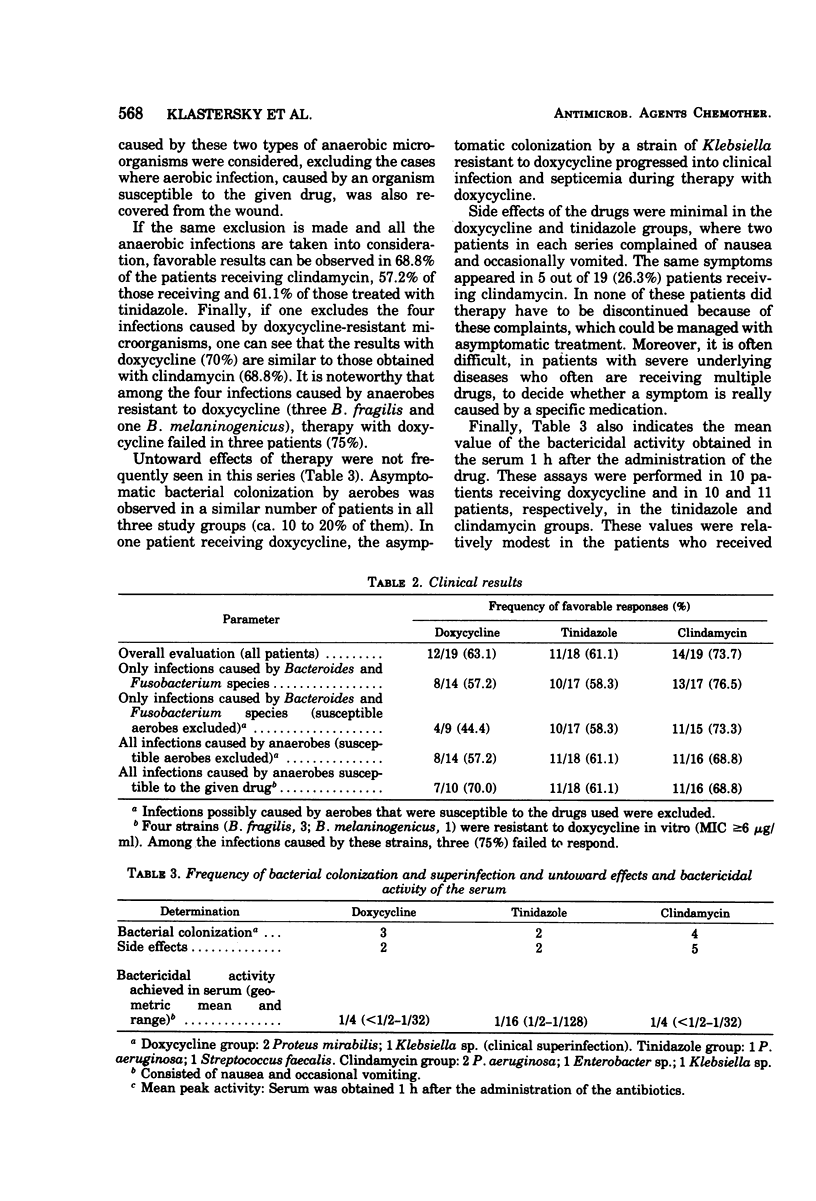
Clindamycin, tinidazole (a parent compound to metronidazole), and doxycycline were compared in vitro against 376 anaerobic bacteria isolated from clinical specimens. Bacteriostatic tests indicated that clindamycin was the most active drug, on a weight basis, against these strains except for Clostridium species. The three drugs were compared as therapies for anaerobic wound infections in cancer patients. In a randomized double-blind study, no statistically significant differences between clindamycin and tinidazole could be documented. Doxycycline was less active presumably because of the lack of clinical response in three out of four patients infected with doxycycline-resistant strains. No major untoward effects were observed. The bactericidal dilution of the serum was predictive of the clinical outcome.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alpern R. J., Dowell V. R., Jr Clostridium septicum infections and malignancy. JAMA. 1969 Jul 21;209(3):385–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett J. G., Sutter V. L., Finegold S. M. Treatment of anaerobic infections with lincomycin and clindamycin. N Engl J Med. 1972 Nov 16;287(20):1006–1010. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197211162872002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow A. W., Montgomerie J. Z., Guze L. B. Parenteral clindamycin therapy for severe anaerobic infections. Arch Intern Med. 1974 Jul;134(1):78–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow A. W., Patten V., Guze L. B. Susceptibility of anaerobic bacteria to metronidazole: relative resistance of non-spore-forming gram-positive baccilli. J Infect Dis. 1975 Feb;131(2):182–185. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.2.182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeHaan R. M., Metzler C. M., Schellenberg D., Vandenbosch W. D. Pharmacokinetic studies of clindamycin phosphate. J Clin Pharmacol. 1973 May-Jun;13(5):190–209. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1973.tb00208.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fass R. J., Scholand J. F., Hodges G. R., Saslaw S. Clindamycin in the treatment of serious anaerobic infections. Ann Intern Med. 1973 Jun;78(6):853–859. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-78-6-853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felner J. M., Dowell V. R., Jr "Bacteroides" bacteremia. Am J Med. 1971 Jun;50(6):787–796. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(71)90187-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klastersky J., Daneau D., Swings G., Weerts D. Antibacterial activity in serum and urine as a therapeutic guide in bacterial infections. J Infect Dis. 1974 Feb;129(2):187–193. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.2.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph E. D., Kirby W. M. Unique bactericidal action of metronidazole against Bacteroides fragilis and Clostridium perfringens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Oct;8(4):409–414. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.4.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinkovics J. G., Smith J. P. Septicemia with bacteroides in patients with malignant disease. Cancer. 1970 Mar;25(3):663–671. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197003)25:3<663::aid-cncr2820250323>3.0.co;2-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter V. L., Finegold S. M. Susceptibility of Anaerobic bacteria to carbenicillin, cefoxitin, and related drugs. J Infect Dis. 1975 Apr;131(4):417–422. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.4.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welling P. G., Monro A. M. The pharmacokinetics of metronidazole and tinidazole in man. Arzneimittelforschung. 1972 Dec;22(12):2128–2132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



