Abstract
Background
The human pathogen Vibrio cholerae normally enters the developmental program of natural competence for transformation after colonizing chitinous surfaces. Natural competence is regulated by at least three pathways in this organism: chitin sensing/degradation, quorum sensing and carbon catabolite repression (CCR). The cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) receptor protein CRP, which is the global regulator of CCR, binds to regulatory DNA elements called CRP sites when in complex with cAMP. Previous studies in Haemophilus influenzae suggested that the CRP protein binds competence-specific CRP-S sites under competence-inducing conditions, most likely in concert with the master regulator of transformation Sxy/TfoX.
Results
In this study, we investigated the regulation of the competence genes qstR and comEA as an example of the complex process that controls competence gene activation in V. cholerae. We identified previously unrecognized putative CRP-S sites upstream of both genes. Deletion of these motifs significantly impaired natural transformability. Moreover, site-directed mutagenesis of these sites resulted in altered gene expression. This altered gene expression also correlated directly with protein levels, bacterial capacity for DNA uptake, and natural transformability.
Conclusions
Based on the data provided in this study we suggest that the identified sites are important for the expression of the competence genes qstR and comEA and therefore for natural transformability of V. cholerae even though the motifs might not reflect bona fide CRP-S sites.
Keywords: Natural competence, Transformation, Vibrio cholerae, cAMP receptor protein, Quorum sensing
Background
Vibrio cholerae is a Gram-negative bacterium that often lives in aquatic environments in association with the chitinous exoskeleton of zooplankton [1,2]. Chitin, a polymer of β-1,4-linked N-acetylglucosamine, is one of the most abundant biopolymers in nature [3]. In addition to its role as a nutrient source, chitin also induces natural competence for transformation in V. cholerae [4] and other Vibrio species (reviewed by [5]).
Natural competence is a mode of horizontal gene transfer, which is based on the ability of a bacterium to take up free DNA from the environment and recombine it with the bacterial genome resulting in natural transformation. In V. cholerae, chitin leads to the up-regulation of tfoX [4,6] (Figure 1). This gene encodes a protein that is the master regulator of transformation and a homolog of Sxy, which was first described in Haemophilus influenzae [7,8]. Indeed, tfoX expression is sufficient to induce natural competence and transformation in V. cholerae even in the absence of chitin [4,9,10]. In our current working model, the components of a type IV pilus combined with a few other competence proteins (such as ComEA, ComEC, and ComF) make up the majority of the DNA-uptake machinery. This machinery is responsible for binding to and pulling extracellular DNA into the periplasm of V. cholerae and subsequently, into the cytoplasm [5,11-14] as previously suggested for other naturally competent bacteria (reviewed for example by [15-19]).
Figure 1.
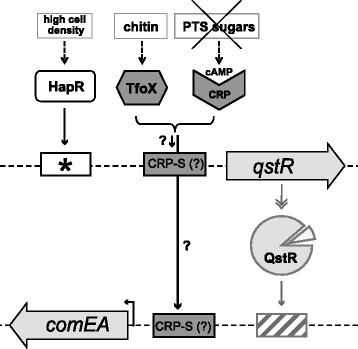
Proposed working model describing the transcriptional regulation of the competence genes qstR and comEA within the network of natural competence for transformation of V. cholerae . qstR and comEA are tightly regulated by three different pathways: quorum sensing, chitin-sensing/degradation, and carbon catabolite repression (signals indicated on top; from left to right). Upon growth on chitin or artifical induction, TfoX is produced within the cell. Furthermore, unsaturated PTS systems lead to the activation of the enzyme adenylate cyclase, which synthesizes cAMP. cAMP then forms a complex with CRP. Based on work performed in H. influenzae [20,21], we hypothesized that CRP-cAMP might bind to the putative CRP-S sites described here and that such binding would be dependent on TfoX. However, full expression of those genes requires a QS-dependent secondary activator (HapR and QstR, respectively). At high cell density the master regulator of QS, HapR, is produced and allows the expression of qstR by directly binding to its promoter (indicated by an asterisk marking a HapR binding site identified in vitro; [22]. The transcriptional regulator QstR, which might require a cofactor for its full activity (indicated by the triangle), positively regulates the comEA gene potentially by binding to a QstR-specific binding motif (indicated by the dashed box and so far unidentified). The question marks indicate the subjects addressed in this study.
In addition to TfoX expression, pathways that regulate quorum sensing (QS) and carbon catabolite repression (CCR) are also necessary to induce the competence regulon of V. cholerae [11,23] (Figure 1). QS is a process of bacterial communication and is based on the production and secretion of small molecules called autoinducers (reviewed by [24]). V. cholerae produces and secretes at least two different autoinducers: the intra-species cholera autoinducer 1 (CAI-1) and the universal autoinducer 2 (AI-2) [24-28]. At high cell density, the concentration of autoinducers is sufficient to lead to the production of HapR, the master regulator of QS that is known to regulate virulence repression [25,29,30], biofilm formation [31] and natural competence for transformation [4,5,9-11,22,32-35] (Figure 1). In the absence of HapR, the extracellular DNA is degraded by the action of the nuclease Dns, preventing DNA uptake [9,11,33]. HapR regulates natural transformation by direct repression of dns and concomitantly with TfoX-mediated induction, directly drives the expression of qstR, which encodes the newly identified transcription factor QstR [22] (Figure 1). Notably, the contribution of QstR to natural transformation was recently confirmed by Dalia et al. using a genome-wide transposon sequencing (Tn-seq) screen [36].
The third pathway involved in the regulation of natural competence for transformation is CCR [4,23]. This term indicates the mechanism by which, in the presence of a preferred carbon source such as glucose, the expression of genes necessary for the metabolism of other carbon sources is repressed [37]. The major players in CCR are the phosphoenolpyruvate-carbohydrate phosphotransferase system (PTS), adenylate cyclase (CyaA), the metabolite 3′,5′-cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) and the CRP protein. Unsaturated PTS transporters enhance the synthesis of cAMP by CyaA. High levels of cAMP trigger the formation of an active complex of CRP and cAMP, which binds the promoters of the target genes (e.g., those genes encoding proteins that are involved in the transport and utilization of alternative carbon sources). Conversely, when the PTS is saturated cAMP is not produced and the CRP-cAMP complex cannot form. Central metabolism and transport of the carbon sources are not the exclusive targets of CCR; cAMP and the CRP protein, as well as the PTS components (independent of cAMP), also control biofilm formation in V. cholerae [38-40]. With respect to natural competence for transformation, the presence of PTS sugars significantly decreases the transformability of V. cholerae; moreover, knockout strains for crp or cyaA are non-transformable [23].
The role and function of the CRP protein have been primarily studied in E. coli (reviewed by [41,42]). CRP, formerly known as catabolite activator protein (CAP), forms a dimer of two identical subunits. Each CRP subunit contains an N-terminal cAMP binding domain, a flexible hinge region and a C-terminal helix-turn-helix DNA binding motif. CRP recognizes and binds 22 bp-long symmetrical sequences called CRP sites. Under physiological conditions, CRP is likely present either as a free apo-CRP dimer (in the absence of cAMP) or as a dimer with each subunit bound to a molecule of cAMP. V. cholerae CRP and E. coli CRP (EcCRP) share 95% identity in amino acid sequence [43]. As with EcCRP, V. cholerae CRP displayed a biphasic dependence on cAMP levels in vitro. Moreover V. cholerae CRP is able to activate the transcription of E. coli gal promoters [44,45]. These findings strongly suggest that the CRP protein functions similarly in these two bacterial species.
In H. influenzae, the expression of the competence genes requires the CRP-cAMP complex [46,47] along with the master regulator of transformation Sxy [7] (TfoX in V. cholerae). The competence regulon of H. influenzae consists of genes characterized by the presence of competence regulatory elements (CRE) [48,49]. Due to their Sxy dependency, these specific competence-related CRP binding sites were later renamed CRP-S sites to distinguish them from the canonical Sxy-independent CRP-N sites [20]. Indeed, Cameron and Redfield suggested that in H. influenzae, and most likely in other competent Gram-negative bacteria, the induction of competence genes is under the control of CRP and Sxy/TfoX acting in concert at the CRP-S site [20]. Based on previously published expression data from V. cholerae [4,6] Cameron and Redfield also predicted a 22-bp CRP-S and CRP-N consensus motif for the Vibrionaceae family in silico, which was nnntTTnAAnTnnnTCGAAnnn for CRP-S and tnntGTGAnnnnnnTCACanan for CRP-N (the most common bases are indicated in upper case, the less likely bases in lower case; 'n' refers to any base even though minor preference might be valid for some of these positions; for details see [20]).
In this study, we tested the role of QstR as an activator of comEA. We demonstrated that overexpression of qstR was sufficient to increase the abundance of the comEA transcripts, although not to the same level observed under competence-inducing conditions. We therefore hypothesized that TfoX and CRP-cAMP were also involved in driving the expression of comEA and qstR (Figure 1). In agreement with this hypothesis, we identified putative CRP-S sites in the promoter regions of qstR and comEA, which were not part of the in silico predicted Vibrionaceae CRP-S sites described above [20]. We investigated the importance of these motifs using site-directed mutagenesis, followed by the analysis of the respective mutants. Our results suggest that these sites are important for the transcriptional regulation of the respective competence genes but might not represent bona fide CRP-S sites.
Methods
Bacterial strains and plasmids
Vibrio cholerae strains and plasmids used in this study are listed in Table 1. Escherichia coli strains DH5α [50] and One Shot PIR1 or PIR2 (Invitrogen) were employed as hosts for cloning. E. coli strain S17-1λpir [51] was used as a mating donor for plasmid transfer between E. coli and V. cholerae.
Table 1.
Strains and plasmids used in this study
| Strains or plasmids | Genotype*/Description | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| V. cholerae strains | ||
| A1552 | Wild-type, O1 El Tor Inaba, RifR | [52] |
| A1552-LacZ-Kan | A1552 strain with aph cassette in lacZ gene; RifR, KanR | [53,54] |
| A1552-TntfoX | A1552 containing mini-Tn7-araC-PBAD-tfoX; RifR, GentR | [10] |
| ΔhapR | A1552ΔVC0583, RifR | [4] |
| ΔhapR-TntfoX | A1552ΔhapR containing mini-Tn7-araC-PBAD-tfoX; RifR, GentR | [10] |
| ΔcomEA | A1552ΔVC1917 (=A1552VC1917 in (Ref)), RifR | [4] |
| ΔcomEA-TntfoX | A1552ΔcomEA containing mini-Tn7-araC-PBAD-tfoX; RifR, GentR | [22] |
| ΔqstR | A1552ΔVC0396, RifR | [22] |
| ΔqstR-TntfoX | A1552ΔqstR containing mini-Tn7-araC-PBAD-tfoX; RifR, GentR | [22] |
| ΔCRP-S | CRP-S site upstream of comEA deleted in strain A1552-TntfoX using the TransFLP method; RifR, GentR | This study |
| CRP-S_inv | CRP-S site upstream of comEA inverted in strain A1552-TntfoX using the TransFLP method; RifR, GentR | This study |
| CRP-N | CRP-S site upstream of comEA changed for a CRP-N site (see scheme in Figure 4) in strain A1552-TntfoX using the TransFLP method; RifR, GentR | This study |
| [frdA] site | CRP-S site upstream of comEA changed for the in silico predicted CRP-N site preceding the frdA gene in strain A1552-TntfoX (see scheme in Figure 4) using the TransFLP method; RifR, GentR | This study |
| CRP-0 | CRP-S site upstream of comEA changed in the 3′ conserved region (see scheme in Figure 4) in strain A1552-TntfoX using the TransFLP method; RifR, GentR | This study |
| WT_qstR (FRT control) | Extended TransFLP scar [53,55] added upstream of qstR without changing the CRP-S site (control) in strain A1552-TntfoX; RifR, GentR | This study |
| ΔHapR-site_qstR | HapR-binding site determined in vitro [22] deleted from strain A1552-TntfoX using the TransFLP method; RifR, GentR | This study |
| ΔCRP-S_qstR | CRP-S site upstream of qstR deleted in strain A1552-TntfoX (see scheme in Figure 4) using the TransFLP method; RifR, GentR | This study |
| [frdA] site_qstR | CRP-S site upstream of qstR changed for the in silico predicted CRP-N site preceding the frdA gene (see scheme in Figure 4) in strain A1552-TntfoX using the TransFLP method; RifR, GentR | This study |
| CRP-0_qstR | CRP-S site upstream of qstR changed in the 3′ conserved region (see scheme in Figure 4) in strain A1552-TntfoX using the TransFLP method; RifR, GentR | This study |
| Plasmids | ||
| pBR322 | AmpR, TcR | [56] |
| pBAD/Myc-HisA | pBR322-derived expression vector; araBAD promoter (PBAD); AmpR | Invitrogen |
| p_qstR | qstR gene cloned into pBAD/Myc-HisA; arabinose inducible; AmpR | [22] |
| pUX-BF13 | oriR6K, helper plasmid with Tn7 transposition function; AmpR | [57] |
| pGP704::Tn7 | pGP704 with mini-Tn7 | [58] |
| pGP704-mTn7-araC-tfoX | pGP704 with mini-Tn7 carrying araC and PBAD-driven tfoX; AmpR | [10] |
| pBR-Tet_MCSI | pBR322 derivative deleted for Tet promoter and part of tet R gene; new MCS included; AmpR | [10] |
| pBR-Tet_MCSII | pBR322 derivative deleted for Tet promoter and part of tet R gene; new MCS included; AmpR | [22] |
| pBR-[own]comEA | comEA gene preceded by 900 bp of upstream region cloned into pBR-Tet_MCSII; AmpR | [22] |
| pBR-[−700]comEA | comEA gene preceded by 700 bp of upstream region; plasmid generated by inverse PCR of pBR-[own]comEA; AmpR | This study |
| pBR-[−500]comEA | comEA gene preceded by 500 bp of upstream region; plasmid generated by inverse PCR of pBR-[own]comEA; AmpR | This study |
| pBR-[−300]comEA | comEA gene preceded by 300 bp of upstream region; plasmid generated by inverse PCR of pBR-[own]comEA; AmpR | This study |
| pBR-[−134]comEA | comEA gene preceded by 134 bp of upstream region cloned into NotI site of pBR-Tet_MCSII; AmpR | This study |
| pBR-[−100]comEA | comEA gene preceded by 100 bp of upstream region; plasmid generated by inverse PCR of pBR-[own]comEA; AmpR | This study |
| pBR-[−40]comEA | comEA gene preceded by 40 bp of upstream region; plasmid generated by inverse PCR of pBR-[own]comEA; AmpR | This study |
*VC numbers according to [59].
Media and growth conditions
V. cholerae and E. coli strains were grown at either 30°C or at 37°C. Overnight cultures were grown in LB medium under aerobic conditions. Thiosulfate Citrate Bile Salts Sucrose (TCBS) agar plates were used to counterselect E. coli strains after triparental mating with V. cholerae strains. The TCBS agar plates were prepared following the manufacturer’s instructions (Fluka). For plasmid maintenance or selection of transformants/transconjugants, antibiotics were added to the growth media at concentrations of 50 or 100 μg ml−1 for ampicillin, 75 μg ml−1 for kanamycin, and 50 μg ml−1 for gentamicin.
Construction of V. cholerae mutant strains
Chromosomally-encoded site-directed mutants were generated using the previously described TransFLP method [53,55,60]. The extended FRT scar was located downstream of the native comEA gene and upstream of the native qstR gene. In the latter case, a control strain was designed that was not modified in a site-directed manner but solely contained the integrated FRT scar upstream qstR (strain WT_qstR (FRT control)). This strain behaved as the WT with respect to the expression pattern, natural transformation, DNA uptake, and general growth behavior (described below).
Construction of plasmids
The majority of the plasmids carrying the comEA gene preceded by a certain length of its upstream region were made through inverse PCR, using the plasmid pBR-[own]comEA [22] as template and the oligonucleotides listed in Table 2. The plasmid pBR-[−134]comEA was constructed by cloning the PCR-amplified insert [−134]comEA into the NcoI site of pBR-Tet_MCSII [22].
Table 2.
Primers used in this study
| Primer name | Sequence | Description |
|---|---|---|
| (in 5′ to 3′ direction) | ||
| Rev[VC1917]-NotI | GCGGCCGCGAGCTCTAGAGGTTTCTTAG | For inverse PCR leading to plasmids: |
| pBR-[−700]comEA, | ||
| pBR-[−500]comEA, | ||
| pBR-[−300]comEA, | ||
| pBR-[−100]comEA, | ||
| pBR-[−40]comEA | ||
| Fwd[VC1917]-700 | AGAGCTCGCGGCCGCAGGTGTTAACCACTCCTGCGGTAC | Inverse PCR to generate |
| pBR-[−700]comEA | ||
| Fwd[VC1917]-500 | AGAGCTCGCGGCCGCCAACAAGCACTTGAACTGGGTAAC | Inverse PCR to generate |
| pBR-[−500]comEA | ||
| Fwd[VC1917]-300 | AGAGCTCGCGGCCGCTATCGTTGTGATTGAGTTGAGC | Inverse PCR to generate |
| pBR-[−300]comEA | ||
| VC1917-134-NotI | GCGGCGGCCGCATTCTTAGTGTAATTGATATG | PCR to generate |
| pBR-TET_MCS after | ATCATGCGCACCCGTGGCCAGGACCC | pBR[−134]comEA, |
| Fwd[VC1917]-100 | AGAGCTCGCGGCCGCGGGCTACAGCAGTAGCCCGTTC | Inverse PCR to generate |
| pBR[−100]comEA | ||
| Fwd[VC1917]-40 | AGAGCTCGCGGCCGCCGCTATCATAAGCCCTCAACAAC | Inverse PCR to generate |
| pBR[−40]comEA | ||
| gyrA-157-fwd | AATGTGCTGGGCAACGACTG | qRT-PCR for gyrA transcription [10] |
| gyrA_332_bwd | GAGCCAAAGTTACCTTGGCC | |
| comEA_50_fwd | CGACATTACCGTTACTGGCC | qRT-PCR for comEA transcription [10] |
| comEA_224_bwd | CCGTTGGCTTCTCGATAATCG | |
| comEC_1029_fwd | GGTCGCGATTGTTCTCTACC | qRT-PCR for comEC transcription [10] |
| comEC_1186_bwd | CCAAATTGTACAGAACTGCCG | |
| VC0396_188_fwd | GCCTGATTCGCCAGCAATTG | qRT-PCR for qstR transcription [22] |
| VC0396_356_bwd | CCAAGACCGTGGGCAATAAAG | |
| hapR-230-fwd | CCAACTTCTTGACCGATCAC | qRT-PCR for hapR transcription [22] |
| hapR-399-bwd | GGTGGAAACAAACAGTGGCC | |
| hapA_175_fwd | ACGGTACAGTTGCCGAATGG | qRT-PCR for hapA transcription [22] |
| hapA_358_bwd | GCTGGCTTTCAATGTCAGGG | |
| comEA_284_rev | CGCACTGTCGCTTCACCAATCC | 5′RACE: synthesis of first strand cDNA of comEA |
| comEA_217_rev | CTTCTCGATAATCGACAATGGCCTGAGC | 5′RACE: PCR amplification of Poly(A) cDNA comEA |
| oligo dT-Anchor primer (Roche) | GACCACGCGTATCGATGTCGAC | |
| F-EcoRI_Anchor_P | CCAAGAATTCGACCACGCGTATCGATGTCGAC | 5′RACE: PCR fragment of Poly(A) cDNA comEA cloned into plasmid pBR-Tet_MCSI |
| R-BamHI_comEA_217 | CCAAGGATCCCTTCTCGATAATCGACAATGGCCTGAGC | |
| T7RNA-pol-750-down | GCTGAGGCTATCGCAACCCGTGC | DNA uptake assay: amplification of donor DNA; primer specific for E. coli BL21(DE3); [9,13] |
| T7 RNAP-end-bw | TTACGCGAACGCGAAGTCCGACTCTAAG | |
| lacZ-missing-fw | GCCGACTTTCCAATGATCCACAATGGG | DNA uptake assay: amplification of acceptor DNA; primer specific for V. cholerae A1552 and lacZ+ derivatives of it; [9,13] |
| lacZ-missing-bw | CCCTCGCTATCCCATTTGGAAATGCC |
Natural transformation assay (chitin-dependent and chitin-independent)
Natural transformation assays were performed as previously described, growing V. cholerae strains on chitin flakes with a medium change on day two [54], or in LB medium supplemented with 0.02% arabinose to express an inducible chromosomal copy of tfoX (preceeded by a PBAD promoter; [10]). The same growth conditions were used for in trans over-expression of the plasmid-encoded qstR gene. Notably, V. cholerae does not contain any obvious homolog of the low-affinity high-capacity arabinose transporter AraE, which is involved in the all-or-none induction of genes preceeded by the arabinose-inducible promoter PBAD in E. coli [61]. Statistical analyses of transformation data were carried out on log-transformed data [62] using a two-tailed Student’s t-test.
Whole-cell duplex PCR assay to test for DNA uptake
DNA uptake was verified using a whole-cell duplex PCR assay as previously described [9,13]. Briefly, the respective V. cholerae strains were induced for competence as described above before genomic DNA of E. coli strain BL21(DE3) was added at a final concentration of 2 μg/ml. After a 2 h incubation step the cells were harvested and DNase I-treated. Any excess nuclease was removed by washing of the cells with PBS buffer. ~3×106 bacteria served as template in a whole-cell duplex PCR. The two primer pairs were specific for the donor DNA derived from E. coli BL21(DE3) and for gDNA of the V. cholerae acceptor strain (at a 10-fold lower concentration), respectively [9,13].
SDS-PAGE and Western blotting
Proteins were separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and then subjected to western blotting as previously described [10]. The primary antibody against ComEA (GP 1248; see below) and horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated goat anti-rabbit secondary antibody (Sigma-Aldrich, Switzerland) were diluted at 1:5,000 and 1:20,000, respectively. Luminescent signals were produced and detected by Western Lightning-ECL (PerkinElmer) and chemiluminescence-detecting film (Amersham Hyperfilm ECL, GE Healthcare).
Generation of the antibodies against ComEA
Rabbit anti-ComEA antibodies were raised against synthetic peptides and produced by Eurogentec (Belgium). The antibody was tested in Western blot analysis against the comEA knockout strain to exclude potential cross-reactions with proteins migrating towards the same position as the target protein.
Quantitative reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR)
V. cholerae strains were grown in LB medium supplemented with 0.02% arabinose to induce the qstR gene or natural competence. RNA preparation, DNase treatment, reverse transcription, and qPCR were performed as previously described [10,22,23].
5′ Rapid amplification of cDNA ends (5′RACE)
V. cholerae wild-type strain A1552-TntfoX was induced to competence as described above. Cell harvesting and RNA preparation were performed as previously published [22]. The 5′/3′ RACE Kit 2nd Generation (Roche) was used to identify the transcription start of the comEA gene. All steps were performed according to the manufacturer’s protocol unless stated otherwise. Total RNA (2 μg) and the gene-specific primer comEA_284_rev were used to synthesize the first strand cDNA of comEA. The cDNA was then purified using the High Pure PCR Product Purification Kit (Roche, Switzerland). After addition of the Poly(A) tail to the 3′ end, the first strand cDNA was amplified by PCR with the gene-specific primer comEA_217_rev and oligo dT-Anchor primer. The PCR products were visualized on an agarose gel and purified. The double-stranded cDNA of comEA was further amplified by PCR with the primers F-EcoRI_Anchor_P and R-BamHI_comEA_217. The PCR products were cloned into the EcoRI/BamHI sites of the plasmid pBR-Tet_MCSI [10]. To determine the transcription start point of comEA, fifteen of those plasmids were sequenced. 12 out of those 15 sequences pointed to the C at position −24 bp upstream the comEA start codon as transcriptional start site.
Results
Regulation of comEA by QstR and TfoX/CRP-cAMP
From previous studies it was known that the expression of comEA is dependent on a) the master regulator of transformation, TfoX; b) the CRP-cAMP complex; and c) the transcription factor QstR [4,22,23] (Figure 1). Indeed, we previously demonstrated that the QstR protein is required for proper expression of the two competence genes, comEA and comEC [22], both of which are essential for DNA uptake and natural transformation [12]. We also speculated that QstR might require a cofactor for proper binding to the respective promoter regions [22]. Here, we asked whether TfoX only regulates comEA indirectly through its influence on QstR, or whether it also has a role in directly regulating the expression of comEA (Figure 1). To do so, we measured the transcripts of comEA in the absence of natural competence induction (e.g., in the absence of a chitin surface and without artificial induction of the gene encoding the main regulator of transformation, TfoX) but with in trans overexpression of qstR. Using this approach, we observed an increased level of comEA expression, whereas expression of the upstream acting regulatory gene hapR and the competence-unrelated but HapR-activated gene hapA did not change as expected (Figure 2). However, the relative expression of comEA appeared lower than what was measured when natural competence was concomitantly induced even though the expression of qstR was significantly higher due to the multi-copy effect of the expression in trans (compare to [22] and data shown below).
Figure 2.
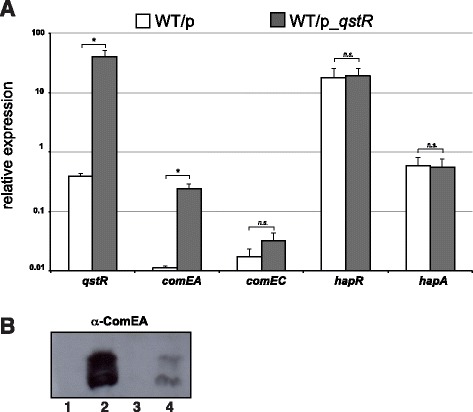
QstR drives the expression of comEA in the absence of competence induction. (A) qRT-PCR data showing the relative expression of the indicated genes in wild-type V. cholerae strain A1552 (WT) carrying an empty vector (p) as control or a plasmid encoding qstR (p_qstR; ara-inducible). Strains were grown to high cell density, and the growth medium was supplemented with arabinose to induce expression of qstR in the absence of competence-induction (e.g., independent of TfoX). Data are the average of three biological replicates. Error bars indicate standard deviation. Statistically significant differences were determined by Student’s t-tests. *P < 0.05, n.s. = not significant. (B) Detection of the ComEA protein (with and without the N-terminal signal sequence peptide; upper and lower band, respectively) by Western blot analysis using protein-specific antibodies. Total protein was extracted from the indicated strains after growth to high cell density. Lanes: 1, V. cholerae strain A1552-TntfoX, competence-non-induced; 2, A1552-TntfoX competence-induced; 3, wild-type strain A1552 carrying plasmid pBAD/Myc-HisA (vector control); 4, A1552 containing plasmid p_qstR in trans. Strains indicated in lanes 3 and 4 were grown in the presence of 0.02% arabinose to induce the PBAD promoter, which is located on the plasmid.
Next, we investigated the production of the ComEA protein in order to evaluate whether the transcript levels would also reflect the protein levels. Apart from the strains used to measure the comEA transcripts, we also included wild-type strains harboring an inducible copy of tfoX on the chromosome as previously described [10] and grew the strains under both competence-inducing and non-inducing conditions. Total protein extracts were prepared from bacterial strains that had reached the high cell density state. As shown in Figure 2B, the ComEA protein was readily detectable in the competence-induced strain (lane 2) and absent in the same strain that was grown without competence induction (lane 1). Moreover, we detected low levels of ComEA in the wild-type strain when qstR was overexpressed but competence (e.g., tfoX) was not induced (lane 4), which was not the case for the vector control (lane 3). This result strengthened the evidence that QstR per se is able to drive the expression of comEA in the absence of competence induction. However, the protein was more abundant in the wild-type strain under competence-inducing conditions, suggesting that full comEA expression requires more than the QstR protein alone, which is consistent with the proposed dual regulation of comEA by TfoX / CRP-cAMP complex and QstR (Figure 1).
Narrowing down the promoter region driving the expression of comEA
To better understand how the expression of comEA is regulated, we first mapped the putative promoter region of this gene. To do so we constructed eight plasmids carrying the gene and its upstream region, which we incrementally shortened (Figure 3). The plasmids were originated using direct or inverse PCR and plasmid pBR-[own]comEA as template [22]; Table 1). This plasmid contains the comEA gene and a 900 bp sequence that is upstream of the start codon and therefore includes the promoter region [22]. All eight constructs were tested for their ability to restore the transformability of the V. cholerae comEA-minus strain (∆comEA) in trans after chitin-dependent induction of competence (Figure 3). ∆comEA strains harboring plasmid-encoded comEA and at least 134 bp of its upstream region were complemented and showed transformation frequencies comparable to the wild-type strain. Neither of the bacterial strains harboring either 100 bp or 40 bp of the comEA upstream region rescued transformability, nor did the strain carrying the empty vector (Figure 3). We concluded that 134 bp of sequence upstream of the comEA start codon are sufficient to drive comEA expression.
Figure 3.
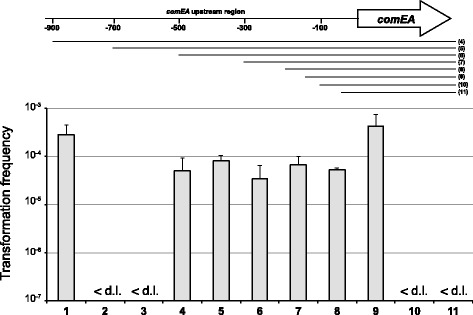
Localization of the putative promoter region of comEA . Schematic representation of comEA with 900 bp of its upstream region (not to scale). To localize the promoter, the upstream region of comEA was incrementally shortened. The numbers indicate the bp upstream of the start codon of the open reading frame, which itself is indicated by the arrow. The cloned fragments are indicated by the lines below the genomic region view, and the numbers in the brackets on the right correspond to the lane numbers in the graph. Fragment lengths upstream of comEA (numbered 4–11): 900 bp, 700 bp, 500 bp, 300 bp, 203 bp, 134 bp, 100 bp, 40 bp. Graph: V. cholerae strains harboring the plasmid-encoded comEA plus the indicated upstream regions were tested for their transformability. The transformation assay was performed in a chitin-dependent manner, and the transformation frequencies of the strains are shown on the y-axis. Strains tested: wild-type A1552 (lane 1); ΔcomEA (lane 2); ΔcomEA/p (vector control; lane 3) and ΔcomEA containing plasmids according to the schematic above the graph (lanes 4–11). The data are the average of at least three independent experiments and the error bars reflect the standard deviation. <d.l.: below detection limit.
Prediction of putative promoter elements within the comEA upstream region
Next, we localized the transcription start site of the comEA transcript using 5′ RACE (Rapid amplification of cDNA ends). As schematized in Figure 4A, we could map the transcription start site at −24 bp upstream the start codon. In E. coli, the majority of the promoters consist of two conserved hexanucleotides, which are located at approximately −35 and −10 from the transcription start site. The consensus of a “typical” promoter of E. coli has been summarized as follows: TTGACA-(N15–19)-TATAAT-(N5–7)-start [63] (N = any nucleotide). The −35 and −10 regions are specifically recognized and bound by the σ subunit of the RNA polymerase (RNAP) holoenzyme [64], and the most commonly used σ factor in E. coli is σ70 [65]. Comparing the sequence upstream of the transcription start site of comEA with the consensus of the E. coli σ70-activated promoter [65], we identified the putative −35 and −10 regions of the comEA promoter, TTTCCA-(N16)-TATCAT-(N7)-start, as shown in Figure 4A. These regions were also predicted using the BPROM program, which works to recognize bacterial σ70 promoters [66]. Moreover, we manually screened the upstream region of comEA and identified a motif similar to the in silico predicted consensus of the Vibrionaceae CRP-S site [20] (Figure 4A and B). As described above, the CRP-S site is hypothesized to represent a CRP binding motif where the protein binds to in conjunction with TfoX. This putative CRP-S site is 22 bp in length and located between −79 bp and −58 bp upstream of the comEA start codon (Figure 4A).
Figure 4.

The transcriptional start site of comEA and the putative CRP-S site. (A) Sequence of the upstream region of comEA. Numbers in black below the nucleotide sequence indicate the position relative to the start codon (ATG, as indicated); numbers in red above the nucleotide sequence refer to the position relative to the transcription start site at position −24 (highlighted by the arrow and +1). The putative −10 and −35 regions are also highlighted in bold and underlined. The newly identified putative CRP-S site is centered at position −44.5 (sequence surrounded by the gray box). (B) Putative CRP-S sites identified in the upstream region of comEA and qstR and their site-directed mutagenesis. The conserved bases of the putative CRP-S site are indicated in bold (compared to the motif in silico predicted by Cameron and Redfield for other competence genes of Vibrionaceae [20]). The putative CRP-S site upstream of comEA and qstR was entirely deleted in the constructs ΔCRP-S and ΔCRP-S_qstR, respectively. Changes made to generate the indicated CRP-S motif variants are underlined.
Investigation of the putative CRP-S site upstream of comEA
To understand the importance of this putative CRP-S site, we modified its sequence using site-directed mutagenesis at the original chromosomal locus. The sequences of the putative CRP-S site upstream of comEA, as well the site-directly changed CRP sites are represented in Figure 4B. Specifically, we either deleted the entire putative CRP-S site (ΔCRP-S), inverted it (CRP-S_inv), changed it to the consensus of the canonical CRP binding site, which works independently of TfoX (CRP-N), or to the in silico predicted CRP-N motif of the V. cholerae fumarate reductase gene [20] ([frdA] site), or we altered it to a motif that differed considerably from the original CRP-S consensus in the 3′ half of the motif (designated CRP-0) (Figure 4B). When we tested these modified strains, we observed a perfect correlation between natural transformability (Figure 5A) and the expression levels of comEA (Figure 5B). The (non-) functionality of the CRP-S motifs in driving comEA expression was also confirmed by testing DNA uptake using a recently developed whole-cell duplex PCR assay [9,12,13] (Figure 5C). Notably, all of these assays confirmed that the absence of the CRP-S site lowered the comEA expression level followed by reductions in ComEA-mediated DNA uptake ability and eventual transformation (Figure 5). Interestingly, the mutant carrying the inverted CRP-S site turned out to be only mildly impaired in transformation (Figure 5A) due to reduced expression of comEA (Figure 5B) and reduced DNA uptake (Figure 5C). Most importantly, the replacement of the CRP-S site by both CRP-N derivatives (CRP-N and [frdA] site) resulted in similar phenotypes as those seen with the CRP-S-minus strain. The CPR-0 motif mutant on the other hand displayed the highest expression level for comEA, which resulted in increased DNA uptake and transformation (Figure 5).
Figure 5.
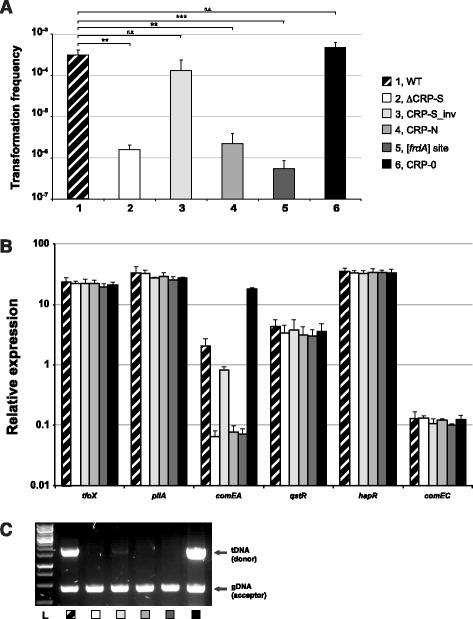
Variants of the putative CRP-S motif preceding comEA are altered with respect to natural transformation. (A) Natural transformability of the indicated strains was tested under tfoX-inducing but chitin-independent conditions as previously described [10]. The frequencies are indicated on the Y-axis. Lane numbers are according to the legend shown on the right. The graph shows the average of at least three independent biological replicates (±SD as indicated by the error bar). Statistically significant differences were determined by Student’s t-tests. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, n.s. = not significant. (B) The same strains used in panel A were tested for the relative expression of tfoX (arabinose-induced), pilA, comEA, qstR, hapR, and comEC. The values are given on the Y-axis. Data are averages from at least three independent experiments ± SD. (C) The ability of the wild-type and mutant V. cholerae strains to take up DNA was tested using a whole-cell duplex PCR assay. The lower fragments reflect the quantity of acceptor bacteria and serve as internal controls. The upper band indicates internalized transforming DNA (tDNA). L, ladder.
The CRP-S site upstream of qstR
From the data presented above, we hypothesized that the putative CRP-S motif indeed plays a role in the regulation of comEA, but potentially not in the same way that would be expected from a bona fide CRP-S site. Notable, expression of comEA also requires QstR, which links the QS pathway with the competence genes [22]. Because qstR expression occurs in a TfoX-dependent manner [22], we speculated that the gene might also be preceded by a putative CRP-S site. Indeed, upon closer inspection we identified such a motif in the upstream region of qstR (−87 bp to −65 bp upstream from the ATG start codon of the ORF) (Figure 4). To investigate the contribution of this site to qstR expression and natural transformability, we either deleted the putative CRP-S motif or used site-directed modifications as indicated in Figure 4. All of these variants were chromosomally-encoded and replaced the original putative CRP-S site. As a control for the genetic engineering method that we used to exchange the motif (TransFLP; [53,55,60], we also included a strain in which the FRT scar preceding the putative qstR promoter region was present without an altered CRP-S motif. This strain (WT_qstR (FRT control)) showed WT behavior with respect to all measured phenotypes (e.g., expression of qstR, natural transformation, and DNA uptake; Figure 6). Moreover, we also included a strain in which the in vitro-identified HapR-binding site [22] was deleted (strain ΔHapR-site_qstR). Notably, this strain was severely impaired in transformation due to very low qstR and comEA expression, undetectable ComEA protein levels, and a DNA uptake ability, which was below the detection limit of the assay (Figure 6). With respect to the putative CRP-S site, we observed similar phenotypes as those observed in the mutants that were modified in the upstream region of the comEA gene (described above). That is, both deleting the motif and changing it to an frdA-derived CRP-N site ([frdA] site_qstR) abolished qstR and comEA expression, ComEA production, DNA uptake and, consequently, natural transformability. Remarkably, the change to a CRP-0 site again slightly exaggerated those same phenotypes (Figure 6).
Figure 6.
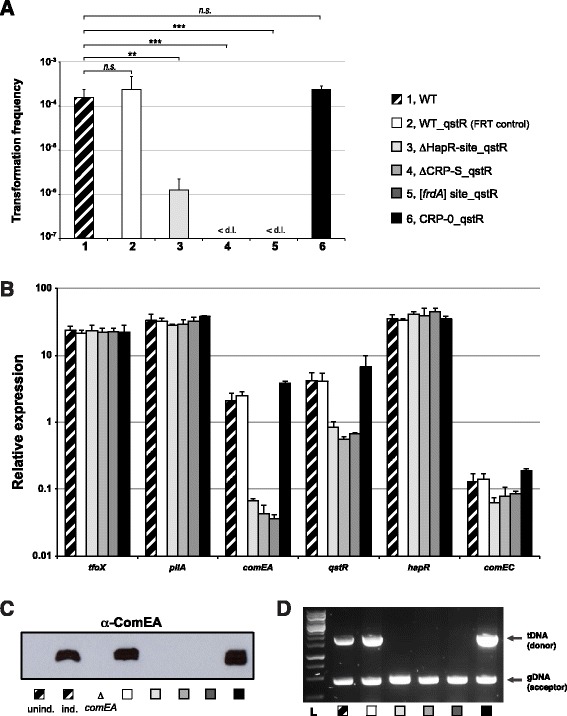
Altering the promoter region of qstR affects natural transformation. Variants lacking either the HapR-binding site or the putative CRP-S site or containing site-directly changed CRP-S motifs were tested for natural transformability, relative expression of the selected genes, ComEA protein production, and DNA uptake (panels A-D) as described for the previous figures. The tested strains are indicated in the legend, and all experiments were performed at least three independent times. Error bars represent the standard deviation. Statistically significant differences with respect to natural transformation were determined by Student’s t-tests. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, n.s. = not significant. The value of the detection limit was used for the statistics of non-transformable strains.
Discussion
In bacteria, gene transcription begins only after 1) binding of the RNA polymerase (RNAP) holoenzyme to the promoter region and 2) formation of an open complex of the DNA. Promoters that are non-constitutively active (e.g., those of the competence genes) require one or several activating protein(s), such as the CRP protein, that directly interact with the RNAP and assist the holoenzyme in the steps preceding transcriptional initiation [67]. Using comEA and qstR as important genes of the competence regulon of V. cholerae, this study contributes to the understanding of the regulatory network driving natural competence. For comEA we showed that the region up to 134 bp upstream of the start codon is sufficient to drive comEA expression in this organism. But what initiates transcription of comEA? Trying to answer this question, we followed a common assumption, namely that the expression of the competence genes of V. cholerae is TfoX- and CRP-cAMP-dependent and that competence genes are preceeded by so-called CRP-S sites as previously suggested for H. influenzae [48,49]. And indeed, we demonstrated that the deletion of a newly identified motif with striking resemblance to the in silico predicted CRP-S sites [20] had a negative effect on natural transformability. Moreover, we also identified and investigated a putative CRP-S site upstream qstR, which likewise was required for qstR expression and natural transformability. Interestingly, our site-directed mutagenesis approach resulted in unexpected but interesting phenotypes. CRP-mediated activation at the CRP-S site is expected to be different from that at the canonical CRP binding site (CRP-N site; Sxy/TfoX-independent). We therefore assumed that exchanging the putative CRP-S site for a CRP-N motif would enhance competence gene expression. Notably, and in contrast to this assumption, the expression of comEA and qstR was significantly reduced when preceeded by a CRP-N site (Figures 5 and 6). Moreover, opposite results were observed for the strains carrying the CRP-0 motif variants. Despite the fact that this mutation affects the most highly conserved bases of the in silico predicted CRP-S consensus (those in the 3′ part of the motif), the comEA/qstR genes were expressed at higher levels, which correlated well with increased levels of ComEA protein, enhanced DNA uptake, and higher transformation frequencies (Figures 5 and 6). We therefore speculate that the CRP-0 mutation could either be a better binding site for the RNAP or favor the escape of the RNAP complex from the promoter in order to begin transcription. However, based on these unexpected phenotypes we concluded that the identified motifs indeed play a role in driving the expression of qstR and comEA but that they do not qualify as bona fide CRP-S sites.
Upon visual inspection we did not identify other motifs resembling the CRP-S site within the putative promoter region of comEA. A sequence (TGCGA-N6-AAGCA) centered at −115.5 from the transcription start point and located between −147 bp and −132 bp upstream the comEA start codon, was recently discussed (though never experimentally addressed) by Antonova et al. The authors suggested that this sequence serves as a potential CRE element (competence regulatory element [49]; the former name for CRP-S sites) [68]. Although we cannot exclude that this sequence is indeed a CRP binding motif, this site is not essential for the transcription of comEA, as it was not part of the construct that in trans complemented the respective knockout strain (e.g. comEA preceded by 134 bp of its upstream region; Figure 3). Furthermore, the localization of this putative CRP-S site within the open reading frame of the adjacent gene (VC1918) also leads to questions regarding its functionality with respect to the regulation of comEA.
Conclusion
Given the absence of any obvious alternative CRP-S site within the 134 bp upstream of comEA we raised the possibility that TfoX and CRP-cAMP only indirectly regulate comEA via the intermediate transcriptional regulator QstR. Indeed, we have previously shown that QstR is necessary for the expression of comEA and comEC but not of the DNA-uptake pilus-encoding genes [12,22]. However, upon artificial induction of qstR in trans only low levels of comEA transcript were measured in accordance with the production of low levels of the ComEA protein (Figure 2). Two hypothesis are therefore possible: either the proteins TfoX and/or CRP-cAMP are somehow involved in the production of the previously suggested co-factor of QstR [22], or a direct regulation of comEA by TfoX/CRP-cAMP still occurs but involves a CRP-S binding site that significantly differs form the consensus that was in silico predicted for the Vibrionaceae [20]. Further studies involving chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by high-throughput DNA sequencing (ChIP-seq) will be required to ultimately establish the in vivo binding sites of CRP-cAMP, QstR, and potentially also of TfoX in naturally competent V. cholerae cells.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for technical assistance by Tiziana Scrignari and to all of the members of the Blokesch laboratory for discussion of the project. We also acknowledge useful comments from the participants of the Cold Spring Harbor Meeting on Bacteria, Archaea & Phages in August 2012 where we first presented our work on the putative CRP-S site upstream of comEA. This work was supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation (SNSF) grants 31003A_127029 and 31003A_143356.
Footnotes
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
MLS and MB designed the study; MLS, SB, and MB performed the experiments, and MLS and MB wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Contributor Information
Mirella Lo Scrudato, Email: mirella.loscrudato@epfl.ch.
Sandrine Borgeaud, Email: sandrine.borgeaud@epfl.ch.
Melanie Blokesch, Email: melanie.blokesch@epfl.ch.
References
- 1.Nalin DR, Daya V, Reid A, Levine MM, Cisneros L. Adsorption and growth of Vibrio cholerae on chitin. Infect Immun. 1979;25(2):768–770. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.2.768-770.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Pruzzo C, Vezzulli L, Colwell RR. Global impact of Vibrio cholerae interactions with chitin. Environ Microbiol. 2008;10(6):1400–1410. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2007.01559.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Gooday GW. Physiology of microbial degradation of chitin and chitosan. Biodegradation. 1990;1:177–190. doi: 10.1007/BF00058835. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Meibom KL, Blokesch M, Dolganov NA, Wu C-Y, Schoolnik GK. Chitin induces natural competence in Vibrio cholerae. Science. 2005;310(5755):1824–1827. doi: 10.1126/science.1120096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Seitz P, Blokesch M. Cues and regulatory pathways involved in natural competence and transformation in pathogenic and environmental Gram-negative bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2013;37(3):336–363. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2012.00353.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Meibom KL, Li XB, Nielsen AT, Wu CY, Roseman S, Schoolnik GK. The Vibrio cholerae chitin utilization program. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(8):2524–2529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0308707101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Redfield RJ. sxy-1, a Haemophilus influenzae mutation causing greatly enhanced spontaneous competence. J Bacteriol. 1991;173(18):5612–5618. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.18.5612-5618.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Zulty JJ, Barcak GJ. Identification of a DNA transformation gene required for com101A+ expression and supertransformer phenotype in Haemophilus influenzae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995;92(8):3616–3620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.8.3616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Suckow G, Seitz P, Blokesch M. Quorum sensing contributes to natural transformation of Vibrio cholerae in a species-specific manner. J Bacteriol. 2011;193(18):4914–4924. doi: 10.1128/JB.05396-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lo Scrudato M, Blokesch M. The regulatory network of natural competence and transformation of Vibrio cholerae. PLoS Genet. 2012;8(6):e1002778. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Blokesch M. A quorum sensing-mediated switch contributes to natural transformation of Vibrio cholerae. Mob Genet Elements. 2012;2(5):224–227. doi: 10.4161/mge.22284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Seitz P, Blokesch M. DNA-uptake machinery of naturally competent Vibrio cholerae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(44):17987–17992. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1315647110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Seitz P, Pezeshgi Modarres H, Borgeaud S, Bulushev RD, Steinbock LJ, Radenovic A, Dal Peraro M, Blokesch M. ComEA Is Essential for the Transfer of External DNA into the Periplasm in Naturally Transformable Vibrio cholerae Cells. PLoS Genet. 2014;10(1):e1004066. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Metzger LC, Blokesch M. Composition of the DNA-uptake complex of Vibrio cholerae. Mob Genet Elements. 2014;4(1):e28142. doi: 10.4161/mge.28142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Fussenegger M, Rudel T, Barten R, Ryll R, Meyer TF. Transformation competence and type-4 pilus biogenesis in Neisseria gonorrhoeae–a review. Gene. 1997;192(1):125–134. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00038-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Chen I, Dubnau D. DNA uptake during bacterial transformation. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2004;2(3):241–249. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Claverys JP, Martin B, Polard P. The genetic transformation machinery: composition, localization, and mechanism. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2009;33(3):643–656. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2009.00164.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Allemand JF, Maier B. Bacterial translocation motors investigated by single molecule techniques. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2009;33(3):593–610. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2009.00166.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Averhoff B. Shuffling genes around in hot environments: the unique DNA transporter of Thermus thermophilus. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2009;33(3):611–626. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2008.00160.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Cameron ADS, Redfield RJ. Non-canonical CRP sites control competence regulons in Escherichia coli and many other gamma-proteobacteria. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34(20):6001–6014. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Cameron ADS, Redfield RJ. CRP binding and transcription activation at CRP-S sites. J Mol Biol. 2008;383(2):313–323. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.08.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Lo Scrudato M, Blokesch M. A transcriptional regulator linking quorum sensing and chitin induction to render Vibrio cholerae naturally transformable. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41(6):3644–3658. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Blokesch M. Chitin colonization, chitin degradation and chitin-induced natural competence of Vibrio cholerae are subject to catabolite repression. Environ Microbiol. 2012;14(8):1898–1912. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2011.02689.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ng WL, Bassler BL. Bacterial quorum-sensing network architectures. Annu Rev Genet. 2009;43:197–222. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-102108-134304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Miller MB, Skorupski K, Lenz DH, Taylor RK, Bassler BL. Parallel quorum sensing systems converge to regulate virulence in Vibrio cholerae. Cell. 2002;110(3):303–314. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00829-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Xavier KB, Bassler BL. Interference with AI-2-mediated bacterial cell-cell communication. Nature. 2005;437(7059):750–753. doi: 10.1038/nature03960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Higgins DA, Pomianek ME, Kraml CM, Taylor RK, Semmelhack MF, Bassler BL. The major Vibrio cholerae autoinducer and its role in virulence factor production. Nature. 2007;450(7171):883–886. doi: 10.1038/nature06284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Xavier KB, Bassler BL. LuxS quorum sensing: more than just a numbers game. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2003;6(2):191–197. doi: 10.1016/S1369-5274(03)00028-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kovacikova G, Skorupski K. Regulation of virulence gene expression in Vibrio cholerae by quorum sensing: HapR functions at the aphA promoter. Mol Microbiol. 2002;46(4):1135–1147. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.03229.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Zhu J, Miller MB, Vance RE, Dziejman M, Bassler BL, Mekalanos JJ. Quorum-sensing regulators control virulence gene expression in Vibrio cholerae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99(5):3129–3134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.052694299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Zhu J, Mekalanos JJ. Quorum sensing-dependent biofilms enhance colonization in Vibrio cholerae. Dev Cell. 2003;5(4):647–656. doi: 10.1016/S1534-5807(03)00295-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Blokesch M, Schoolnik GK. Serogroup conversion of Vibrio cholerae in aquatic reservoirs. PLoS Pathog. 2007;3(6):e81. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0030081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Blokesch M, Schoolnik GK. The extracellular nuclease Dns and its role in natural transformation of Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 2008;190(21):7232–7240. doi: 10.1128/JB.00959-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Antonova ES, Hammer BK. Quorum-sensing autoinducer molecules produced by members of a multispecies biofilm promote horizontal gene transfer to Vibrio cholerae. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2011;322(1):68–76. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2011.02328.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Sun Y, Bernardy EE, Hammer BK, Miyashiro T. Competence and natural transformation in vibrios. Mol Microbiol. 2013;89(4):583–595. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Dalia AB, Lazinski DW, Camilli A. Identification of a membrane-bound transcriptional regulator that links chitin and natural competence inVibrio cholerae. mBio. 2014;5(1):e01028–13. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01028-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Deutscher J, Francke C, Postma PW. How phosphotransferase system-related protein phosphorylation regulates carbohydrate metabolism in bacteria. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2006;70(4):939–1031. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00024-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Liang W, Pascual-Montano A, Silva AJ, Benitez JA. The cyclic AMP receptor protein modulates quorum sensing, motility and multiple genes that affect intestinal colonization in Vibrio cholerae. Microbiology. 2007;153(Pt 9):2964–2975. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.2007/006668-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Fong JC, Yildiz FH. Interplay between cyclic AMP-cyclic AMP receptor protein and cyclic di-GMP signaling in Vibrio cholerae biofilm formation. J Bacteriol. 2008;190(20):6646–6659. doi: 10.1128/JB.00466-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Houot L, Chang S, Absalon C, Watnick PI. Vibrio cholerae phosphoenolpyruvate phosphotransferase system control of carbohydrate transport, biofilm formation, and colonization of the germfree mouse intestine. Infect Immun. 2010;78(4):1482–1494. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01356-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Busby S, Ebright RH. Transcription activation by catabolite activator protein (CAP) J Mol Biol. 1999;293(2):199–213. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1999.3161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Harman JG. Allosteric regulation of the cAMP receptor protein. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 2001;1547(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/S0167-4838(01)00187-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Skorupski K, Taylor RK. Sequence and functional analysis of the gene encoding Vibrio cholerae cAMP receptor protein. Gene. 1997;198(1–2):297–303. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00331-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Mukhopadhyay J, Sur R, Parrack P. Functional roles of the two cyclic AMP-dependent forms of cyclic AMP receptor protein from Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1999;453(1–2):215–218. doi: 10.1016/S0014-5793(99)00719-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Chattopadhyay R, Parrack P. Cyclic AMP-dependent functional forms of cyclic AMP receptor protein from Vibrio cholerae. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2006;447(1):80–86. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2006.01.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Chandler MS. The gene encoding cAMP receptor protein is required for competence development in Haemophilus influenzae Rd. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992;89(5):1626–1630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Dorocicz IR, Williams PM, Redfield RJ. The Haemophilus influenzae adenylate cyclase gene: cloning, sequence, and essential role in competence. J Bacteriol. 1993;175(22):7142–7149. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.22.7142-7149.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Macfadyen LP. Regulation of competence development in Haemophilus influenzae. J Theor Biol. 2000;207(3):349–359. doi: 10.1006/jtbi.2000.2179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Redfield RJ, Cameron ADS, Qian Q, Hinds J, Ali TR, Kroll JS, Langford PR. A novel CRP-dependent regulon controls expression of competence genes in Haemophilus influenzae. J Mol Biol. 2005;347(4):735–747. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2005.01.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Yanisch-Perron C, Vieira J, Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Simon R, Priefer U, Pühler A. A broad host range mobilization system for in vivo genetic engineering: transposon mutagenesis in Gram negative bacteria. Nat Biotechnol. 1983;1:784–791. doi: 10.1038/nbt1183-784. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Yildiz FH, Schoolnik GK. Role of rpoS in stress survival and virulence of Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 1998;180(4):773–784. doi: 10.1128/jb.180.4.773-784.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.De Souza Silva O, Blokesch M. Genetic manipulation of Vibrio cholerae by combining natural transformation with FLP recombination. Plasmid. 2010;64(3):186–195. doi: 10.1016/j.plasmid.2010.08.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Marvig RL, Blokesch M. Natural transformation of Vibrio cholerae as a tool-optimizing the procedure. BMC Microbiol. 2010;10:155. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-10-155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Blokesch M. TransFLP – a method to genetically modify V. cholerae based on natural transformation and FLP-recombination. J Vis Exp. 2012;68:e3761. doi: 10.3791/3761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Bolivar F, Rodriguez RL, Greene PJ, Betlach MC, Heyneker HL, Boyer HW, Crosa J, Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(77)90000-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Bao Y, Lies DP, Fu H, Roberts GP. An improved Tn7-based system for the single-copy insertion of cloned genes into chromosomes of Gram-negative bacteria. Gene. 1991;109(1):167–168. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90604-A. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Nielsen AT, Dolganov NA, Rasmussen T, Otto G, Miller MC, Felt SA, Torreilles S, Schoolnik GK. A bistable switch and anatomical site control Vibrio cholerae virulence gene expression in the intestine. PLoS Pathog. 2010;6(9):e1001102. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Heidelberg JF, Eisen JA, Nelson WC, Clayton RA, Gwinn ML, Dodson RJ, Haft DH, Hickey EK, Peterson JD, Umayam L, Gill SR, Nelson KE, Read TD, Tettelin H, Richardson D, Ermolaeva MD, Vamathevan J, Bass S, Qin H, Dragoi I, Sellers P, McDonald L, Utterback T, Fleishmann RD, Nierman WC, White O. DNA sequence of both chromosomes of the cholera pathogen Vibrio cholerae. Nature. 2000;406(6795):477–483. doi: 10.1038/35020000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Borgeaud S, Blokesch M. Overexpression of the tcp gene cluster using the T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system and natural transformation-mediated genetic engineering of Vibrio cholerae. PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53952. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Khlebnikov A, Risa O, Skaug T, Carrier TA, Keasling JD. Regulatable arabinose-inducible gene expression system with consistent control in all cells of a culture. J Bacteriol. 2000;182(24):7029–7034. doi: 10.1128/JB.182.24.7029-7034.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Keene ON. The log transformation is special. Stat Med. 1995;14(8):811–819. doi: 10.1002/sim.4780140810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Raibaud O, Schwartz M. Positive control of transcription initiation in bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:173–206. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.001133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Campbell EA, Muzzin O, Chlenov M, Sun JL, Olson CA, Weinman O, Trester-Zedlitz ML, Darst SA. Structure of the bacterial RNA polymerase promoter specificity sigma subunit. Mol Cell. 2002;9(3):527–539. doi: 10.1016/S1097-2765(02)00470-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Shultzaberger RK, Chen Z, Lewis KA, Schneider TD. Anatomy of Escherichia coli σ70 promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(3):771–788. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Solovyev V, Salamov A: Automatic Annotation of Microbial Genomes and Metagenomic Sequences. In Metagenomics and its Applications in Agriculture, Biomedicine and Environmental Studies (Ed. R.W. Li), Nova Science Publishers 2011, pp 61-78
- 67.Lee DJ, Minchin SD, Busby SJ. Activating transcription in bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2012;66:125–152. doi: 10.1146/annurev-micro-092611-150012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Antonova ES, Bernardy EE, Hammer BK. Natural competence in Vibrio cholerae is controlled by a nucleoside scavenging response that requires CytR-dependent anti-activation. Mol Microbiol. 2012;86(5):1215–1231. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


