Abstract
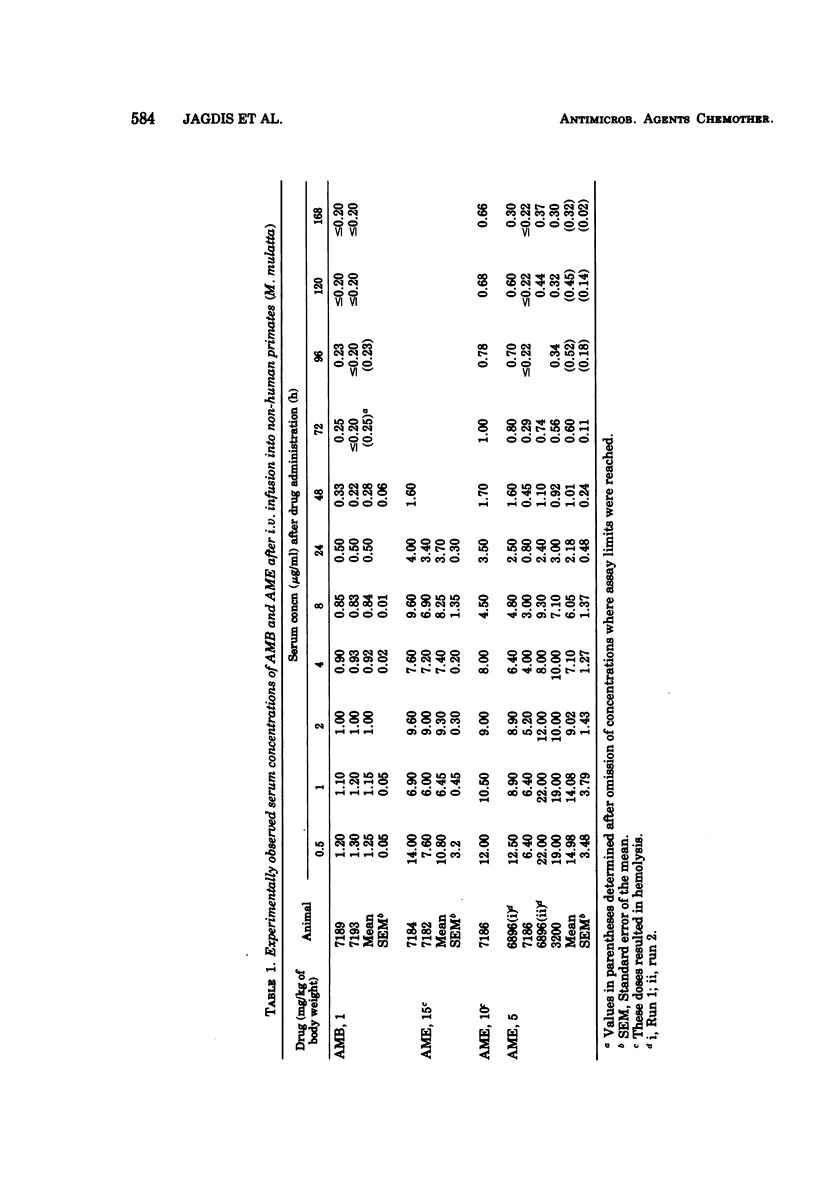
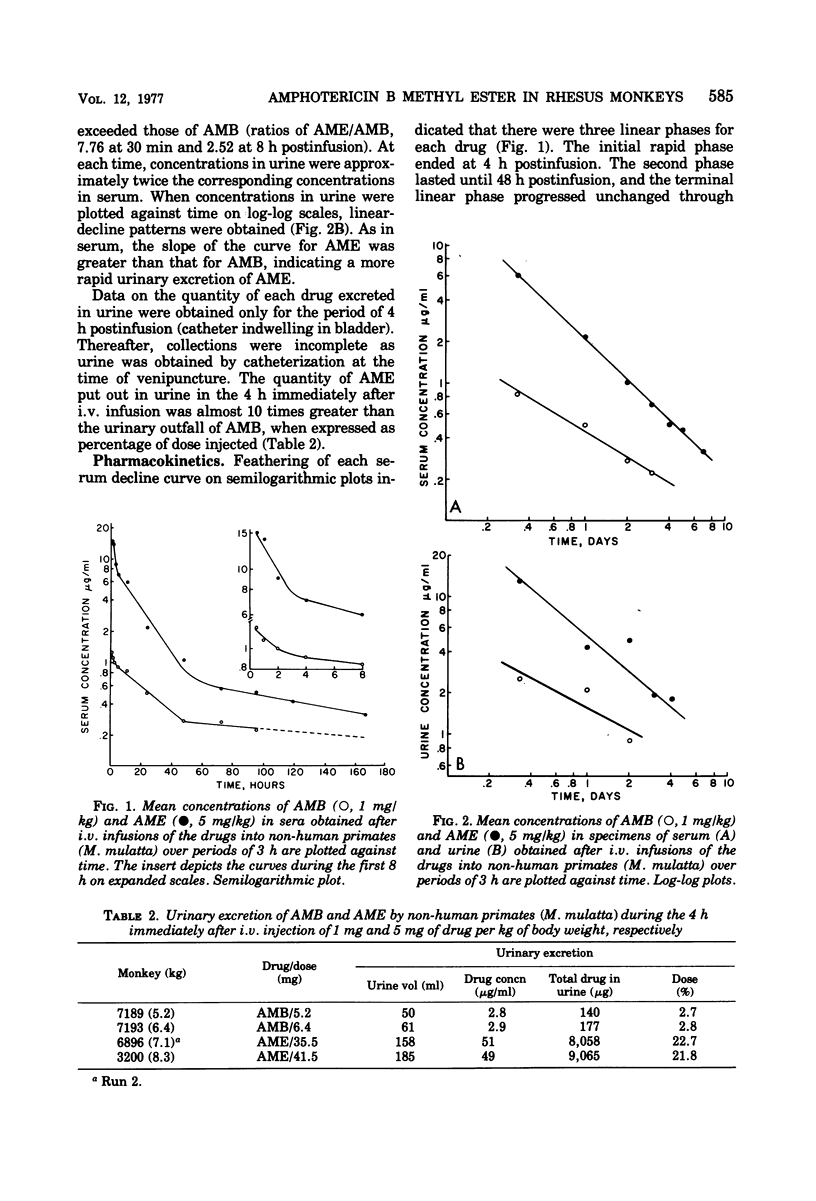
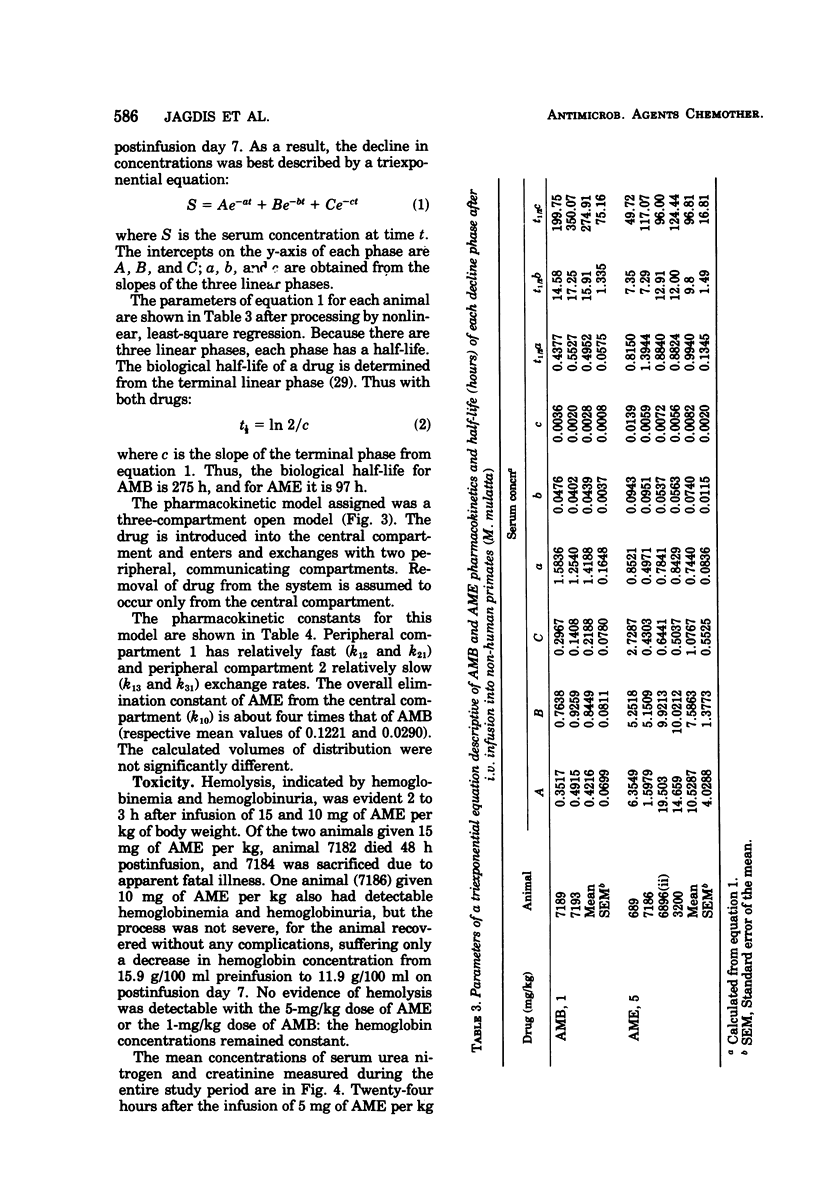
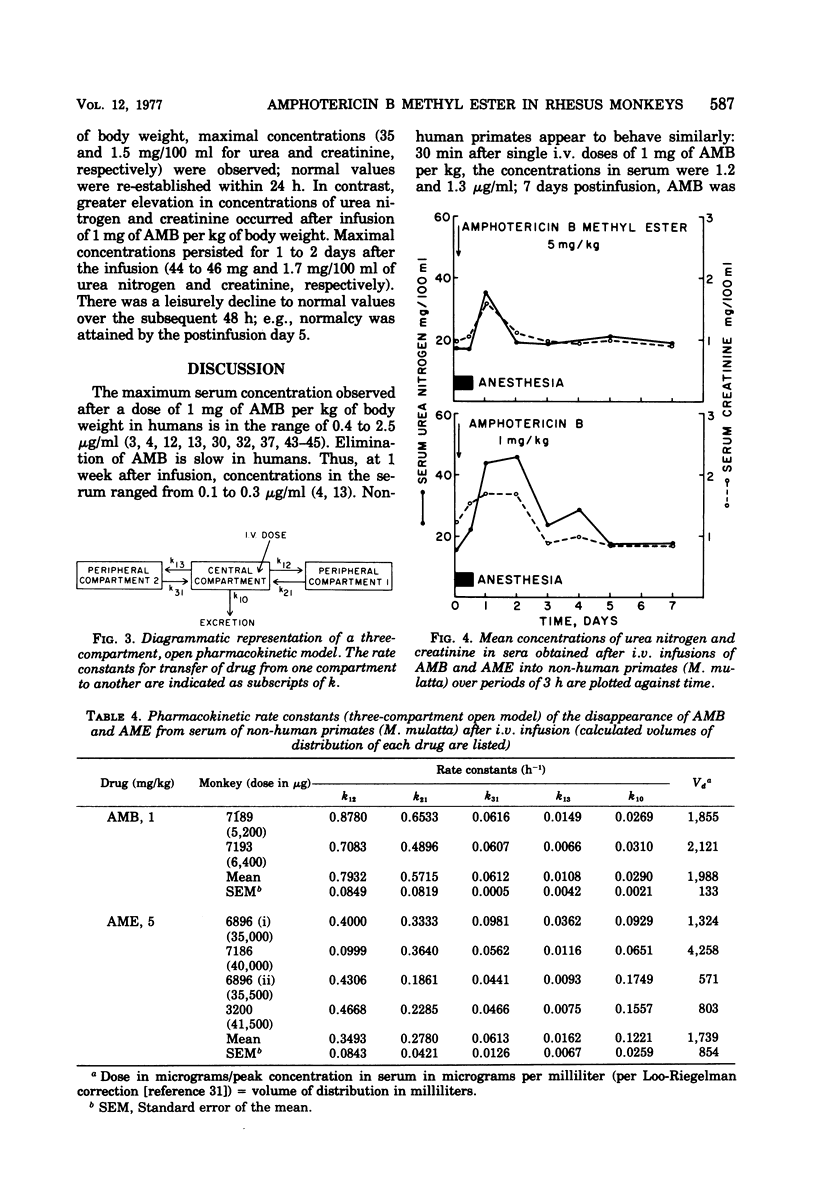
The pharmacokinetics of amphotericin B methyl ester hydrochloride (AME) and commercial deoxycholate-stabilized amphotericin B (AMB) were compared after single doses of 5 mg and 1 mg/kg of body weight, respectively, given intravenously in a period of 3 h to adult female rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta). By bioassay, the concentrations of AME were 12.2 to 7.2 times higher in the serum and 7.8 to 2.5 times higher in the urine during the 8 h after infusion. The decline in concentrations of the drugs in sera was consistent with a three-compartment, open pharmacokinetic model; rate constants of transfer of the drugs between the compartments and volumes of distribution were calculated. The overall rate of elimination from the central compartment (the bloodvascular space) was about four times greater for AME than for AMB. Serum urea nitrogen and creatinine concentrations were mildly and transiently increased after infusion of AME, whereas the more severe azotemia that followed infusion of AMB persisted for 5 days. AME was less toxic and achieved a greater urinary outfall than AMB. As the antifungal activity of AME is comparable to that of AMB by testing in vitro, further study is warranted.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDRIOLE V. T., KRAVETZ H. M. The use of amphotericin B in man. JAMA. 1962 Apr 28;180:269–272. doi: 10.1001/jama.1962.03050170001001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AOKAWA K., MATSUSHITA M. [Hemolytic study of amphotericin B]. Chiryo. 1962 Dec 1;44:2305–2308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battock D. J., Grausz H., Bobrowsky M., Littman M. L. Alternate-day amphotericin B therapy in the treatment of rhinocerebral phycomycosis (mucormycosis). Ann Intern Med. 1968 Jan;68(1):122–137. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-68-1-122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bindschadler D. D., Bennett J. E. A pharmacologic guide to the clinical use of amphotericin B. J Infect Dis. 1969 Oct;120(4):427–436. doi: 10.1093/infdis/120.4.427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner D. P., Mechlinski W., Schaffner C. P. Polyene macrolide derivatives. 3. Biological properties of polyene macrolide ester salts. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1972 Apr;25(4):261–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruzzese T., Cambieri M., Recusani F. Synthesis and biological properties of alkyl esters of polyene antibiotics. J Pharm Sci. 1975 Mar;64(3):462–463. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600640327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler W. T., Cotlove E. Increased permeability of human erythrocytes induced by amphotericin B. J Infect Dis. 1971 Apr;123(4):341–350. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.4.341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W. C., Sud I. J., Chou D. L., Feingold D. S. Selective toxicity of the polyene antibiotics and their methyl ester derivatives. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jan 24;74(2):480–487. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90329-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman H. A., Hamilton J. D., Gutman R. A. Amphotericin B therapy in an anephric patient. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Sep;4(3):302–305. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.3.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields B. T., Jr, Bates J. H., Abernathy R. S. Amphotericin B serum concentrations during therapy. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Jun;19(6):955–959. doi: 10.1128/am.19.6.955-959.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher P. B., Goldstein N. I., Bonner D. P., Mechlinski W., Bryson V., Schaffner C. P. Toxicity of amphotericin B and its methyl ester toward normal and tumor cell lines. Cancer Res. 1975 Aug;35(8):1996–1999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadebusch H. H., Pansy F., Klepner C., Schwind R. Amphotericin B and amphotericin B methyl ester ascorbate. I. Chemotherapeutic activity against Candida albicans, Cryptococcus neoformans, and Blastomyces dermatitidis in mice. J Infect Dis. 1976 Nov;134(5):423–427. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.5.423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibaldi M., Weintraub H. Some considerations as to the determination and significance of biologic half-life. J Pharm Sci. 1971 Apr;60(4):624–626. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600600430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeprich P. D., Huston A. C. Susceptibility of coccidioides immitis, Candida albicans, and Cryptococcus neoformans to amphotericin B, flucytosine, and clotrimazole. J Infect Dis. 1975 Aug;132(2):133–141. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.2.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howarth W. R., Tewari R. P., Solotorovsky M. Comparative in vitro antifungal activity of amphotericin B and amphotericin B methyl ester. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Jan;7(1):58–63. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.1.58. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsuchen C. C., Feingold D. S. Selective membrane toxicity of the polyene antibiotics: studies on natural membranes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Sep;4(3):316–319. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.3.316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KINSKY S. C. COMPARATIVE RESPONSES OF MAMMALIAN ERYTHROCYTES AND MICROBIAL PROTOPLASTS TO POLYENE ANTIBIOTICS AND VITAMIN A. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Aug;102:180–188. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90169-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keim G. R., Jr, Poutsiaka J. W., Kirpan J., Keysser C. H. Amphotericin B methyl ester hydrochloride and amphotericin B: comparative acute toxicity. Science. 1973 Feb 9;179(4073):584–585. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4073.584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keim G. R., Sibley P. L., Yoon Y. H., Kulesza J. S., Zaidi I. H., Miller M. M., Poutsiaka J. W. Comparative toxicological studies of amphotericin B methyl ester and amphotericin B in mice, rats, and dogs. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Oct;10(4):687–690. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.4.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LECHEVALIER H., BOROWSKI E., LAMPEN J. O., SCHAFFNER C. P. Water-soluble N-acetyl derivatives of heptaene macrolide antifungal antibiotics: microbiological studies. Antibiot Chemother (Northfield) 1961 Oct;11:640–647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTMAN M. L., HOROWITZ P. L., SWADEY J. G. Coccidioidomycosis and its treatment with amphotericin B. Am J Med. 1958 Apr;24(4):568–592. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(58)90297-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOURIA D. B. Some aspects of the absorption, distribution, and excretion of amphotericin B in man. Antibiotic Med Clin Ther (New York) 1958 May;5(5):295–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampen J. O. Amphotericin B and other polyenic antifungal antibiotics. Am J Clin Pathol. 1969 Aug;52(2):138–146. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/52.2.138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence R. M., Hoeprich P. D. Comparison of amphotericin B and amphotericin B methyl ester: efficacy in murine coccidioidomycosis and toxicity. J Infect Dis. 1976 Feb;133(2):168–174. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.2.168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loo J. C., Riegelman S. Assessment of pharmacokinetic constants from postinfusion blood curves obtained after I.V. infusion. J Pharm Sci. 1970 Jan;59(1):53–55. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600590107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mechlinski W., Schaffner C. P. Polyene macrolide derivatives. I. N-acylation and esterification reactions with amphotericin B. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1972 Apr;25(4):256–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monji N., Bonner D. P., Hashimoto Y., Schaffner C. P. Studies on the absorption, distribution and excretion of radioactivity after intravenous and intraperitoneal administration of 14C-methyl ester of amphotericin B. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1975 Apr;28(4):317–324. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.28.317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEWCOMER V. D., STERNBERG T. H., WRIGHT E. T., REISNER R. M. Current status of amphotericin B in the treatment of the systemic fungus infections. J Chronic Dis. 1959 Apr;9(4):353–374. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(59)90056-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newberry W. M. Drug treatment of the systemic mycoses. Semin Drug Treat. 1972 Winter;2(3):313–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAFFNER C. P., BOROWSKI E. Biologically active N-acyl derivatives of polyene macrolide antifungal antibiotics. Antibiot Chemother (Northfield) 1961 Nov;11:724–732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEABURY J. H., DASCOMB H. E. Experience with amphotericin B for the treatment of systemic mycoses. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1958 Dec;102(6):960–976. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1958.00260230106014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner C. P., Mechlinski W. Polyene macrolide derivatives. II. Physical-chemical properties of polyene macrolide esters and their water soluble salts. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1972 Apr;25(4):259–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westlake W. J. Use of statistical methods in evaluation of in vivo performance of dosage forms. J Pharm Sci. 1973 Oct;62(10):1579–1589. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600621002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



