Abstract
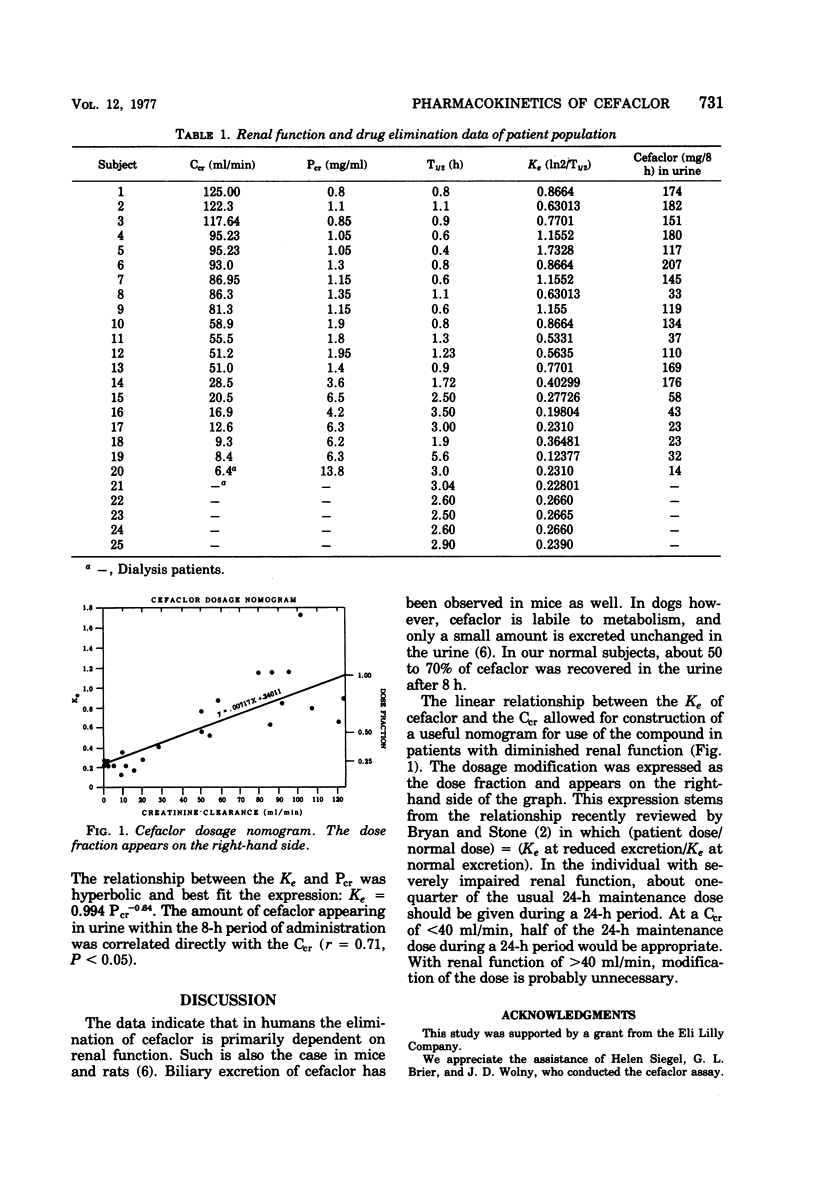
We studied the pharmacokinetics of cefaclor, a new cephalosporin antibiotic, in normal subjects and subjects with chronic renal failure. Cefaclor was largely, but not entirely, eliminated by the kidneys. The cefaclor half-life in normal subjects was 40 to 60 min; in subjects with essentially no renal function, it increased to 3 h. In normal subjects, 50 to 70% of a 250-mg dose was excreted in the urine within 8 h. The linear relationship between the elimination constant and creatinine clearance allowed the construction of a useful dosage modification nomogram.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bryan C. S., Stone W. J. Antimicrobial dosage in renal failure: a unifying nomogram. Clin Nephrol. 1977 Feb;7(2):81–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammer R. B., Preston D. A., Turner J. R., Hawley L. C. Rapid detection of ampicillin-resistant Haemophilus influenzae and their susceptibility to sixteen antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Jul;8(1):91–94. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.1.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy G. Pharmacokinetics in renal disease. Am J Med. 1977 Apr;62(4):461–465. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(77)90397-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTINEZ E., DOOLAN P. D. Determination of creatinine in small quantities of plasma. Observations on two methods. Clin Chem. 1960 Jun;6:233–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan H. R., Due S. L., Kau D. L., Quay J. F., Miller W. Metabolism of (14C) cefaclor, a cephalosporin antibiotic, in three species of laboratory animals. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Oct;10(4):630–638. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.4.630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


