Abstract
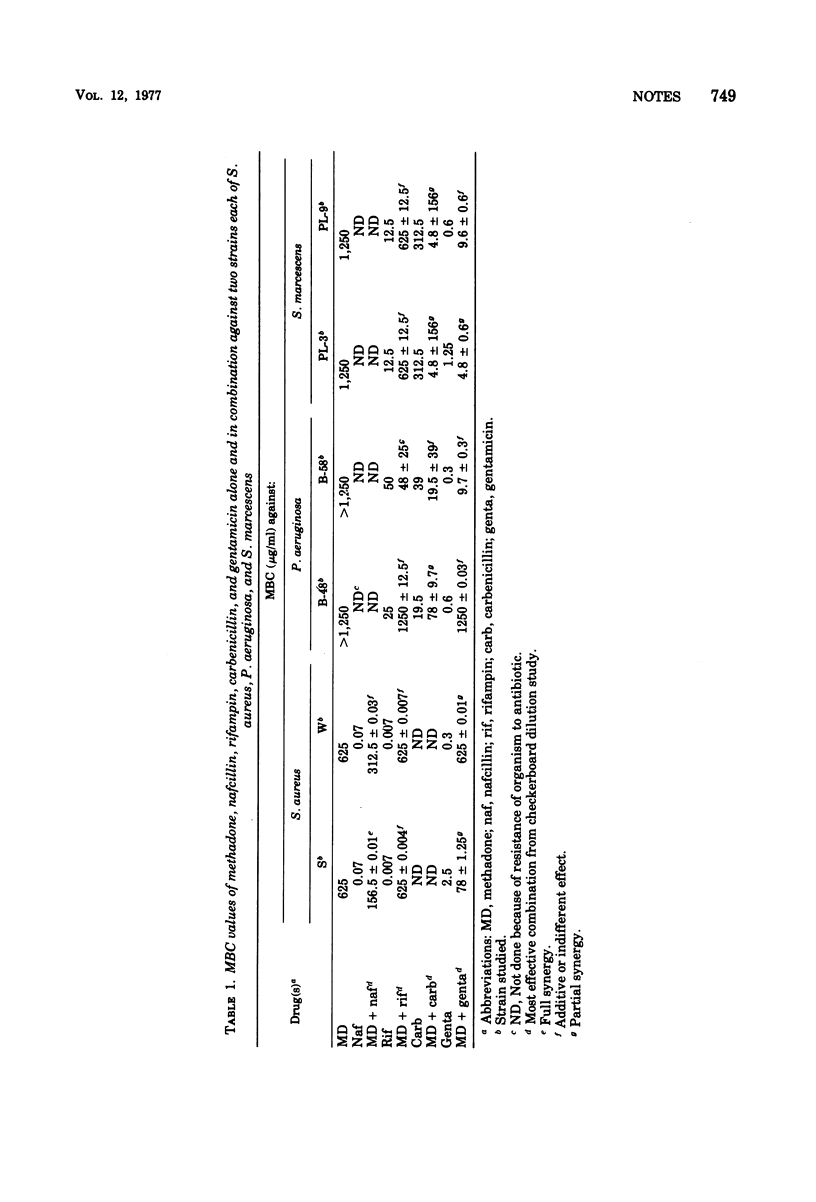
We studied the effect of methadone, alone and in combination with antimicrobial agents, on two strains each of Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Serratia marcescens isolated from blood streams of parenteral drug abusers with bacterial endocarditis. Methadone has its own antibacterial effect, although at supraphysiological concentrations, and is even synergistic with antimicrobial agents against some organisms. Thus, methadone does not interfere with the antibacterial effects of antibiotics in vitro.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gispen W. H., Krivoy W. A., de Wied D., Zimmermann E. Effect of rifampicin on development of tolerance to analgesic actions. Life Sci. 1975 Jul 15;17(2):247–251. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90510-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreek M. J., Garfield J. W., Gutjahr C. L., Giusti L. M. Rifampin-induced methadone withdrawal. N Engl J Med. 1976 May 13;294(20):1104–1106. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197605132942008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLowry J. D., Jaqua M. J., Selepak S. T. Detailed methodology and implementation of a semiautomated serial dilution microtechnique for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Jul;20(1):46–53. doi: 10.1128/am.20.1.46-53.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills J., Drew D. Serratia marcescens endocarditis: a regional illness associated with intravenous drug abuse. Ann Intern Med. 1976 Jan;84(1):29–35. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-84-1-29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuazon C. U., Cardella T. A., Sheagren J. N. Staphylococcal endocarditis in drug users. Clinical and microbiologic aspects. Arch Intern Med. 1975 Dec;135(12):1555–1561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


