Abstract
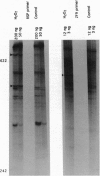
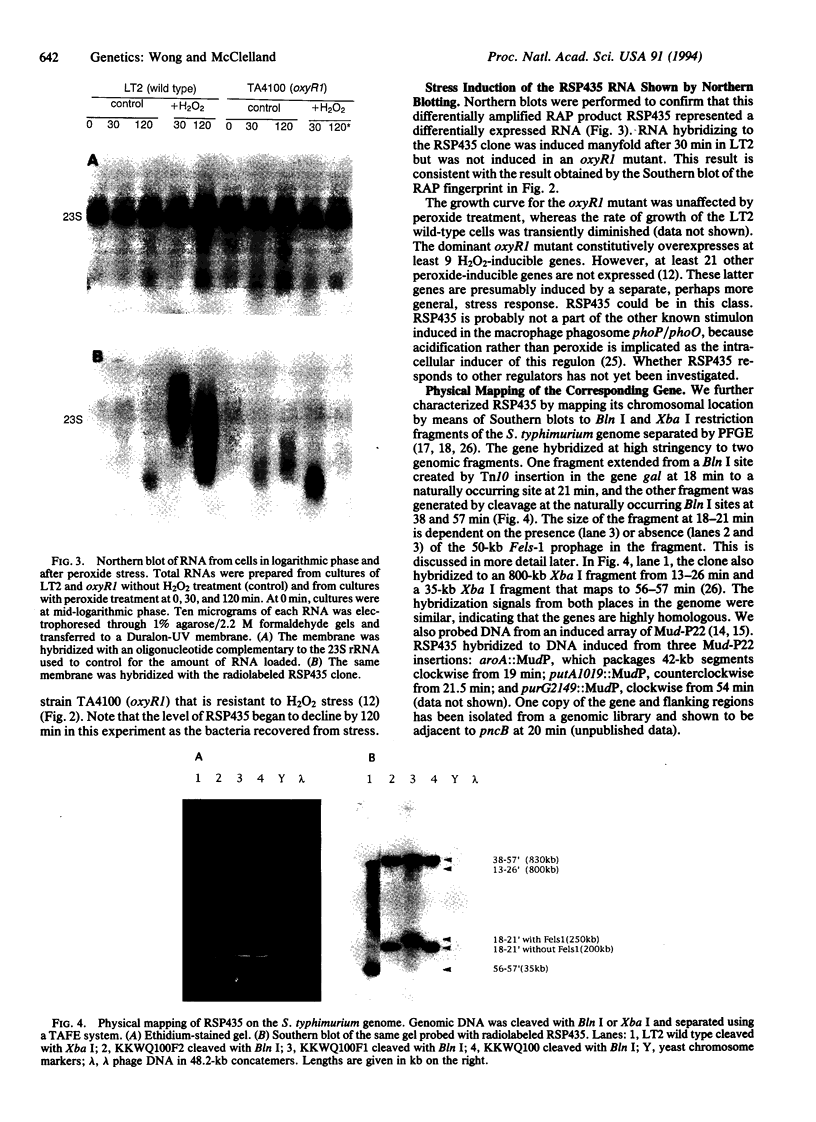
Fingerprinting of RNA by arbitrarily primed PCR (RAP) can be used to identify conditionally expressed genes in prokaryotes. Differential gene expression in Salmonella typhimurium LT2 in response to peroxide treatment was examined as a system in which to demonstrate this strategy. This treatment models the induction of bacterial protective proteins that may occur when mammalian phagocytes use peroxide to fight S. typhimurium infection. To identify genes inducible by hydrogen peroxide stress, total RNA from peroxide-treated and untreated bacterial cultures were RAP fingerprinted with six different arbitrarily selected primers. A 435-base RAP product that was differentially amplified by RAP using the reverse sequencing primer was cloned and sequenced. Northern blot analysis confirmed that the RNA corresponding to this clone, RSP435, was induced when bacteria were treated with hydrogen peroxide. The RNA was not induced in an oxyR1 mutant that constitutively expressed a subset of hydrogen peroxide-inducible genes. Using pulsed-field gel electrophoresis and dot blot hybridization to an array of induced Mud-P22 integrations, the gene corresponding to RSP435 was mapped to two places, one between 19 and 21.5 min and one between 56 and 57 min. Thus, two similar or identical stress-inducible genes were found in different parts of the genome. Identification, cloning, and mapping of the conditionally expressed RSP435 cDNA were performed entirely by physical means, demonstrating that the strategy should complement genetic methods for many prokaryotic or archaebacterial systems and should be applicable to organisms in which genetic methods are difficult to perform or have not yet been developed.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Affolter M., Parent-Vaugeois C., Anderson A. Curing and induction of the Fels 1 and Fels 2 prophages in the Ames mutagen tester strains of Salmonella typhimurium. Mutat Res. 1983 Aug;110(2):243–262. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(83)90143-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alpuche Aranda C. M., Swanson J. A., Loomis W. P., Miller S. I. Salmonella typhimurium activates virulence gene transcription within acidified macrophage phagosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10079–10083. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann B. J. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 8. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Jun;54(2):130–197. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.2.130-197.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson N. R., Goldman B. S. Rapid mapping in Salmonella typhimurium with Mud-P22 prophages. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(5):1673–1681. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.5.1673-1681.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bliska J. B., Galán J. E., Falkow S. Signal transduction in the mammalian cell during bacterial attachment and entry. Cell. 1993 Jun 4;73(5):903–920. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90270-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J. Plasmid vectors for the selection of promoters. Gene. 1984 Feb;27(2):151–160. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90136-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao G. J., Sarkar N. Poly(A) RNA in Escherichia coli: nucleotide sequence at the junction of the lpp transcript and the polyadenylate moiety. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7546–7550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christman M. F., Morgan R. W., Jacobson F. S., Ames B. N. Positive control of a regulon for defenses against oxidative stress and some heat-shock proteins in Salmonella typhimurium. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):753–762. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80056-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanish J., McClelland M. Activity of DNA modification and restriction enzymes in KGB, a potassium glutamate buffer. Gene Anal Tech. 1988 Sep-Oct;5(5):105–107. doi: 10.1016/0735-0651(88)90005-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang P., Pardee A. B. Differential display of eukaryotic messenger RNA by means of the polymerase chain reaction. Science. 1992 Aug 14;257(5072):967–971. doi: 10.1126/science.1354393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S. L., Sanderson K. E. A physical map of the Salmonella typhimurium LT2 genome made by using XbaI analysis. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(5):1662–1672. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.5.1662-1672.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahan M. J., Slauch J. M., Mekalanos J. J. Selection of bacterial virulence genes that are specifically induced in host tissues. Science. 1993 Jan 29;259(5095):686–688. doi: 10.1126/science.8430319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Root R. K., Cohen M. S. The microbicidal mechanisms of human neutrophils and eosinophils. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 May-Jun;3(3):565–598. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.3.565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E., Roth J. R. Linkage map of Salmonella typhimurium, edition VII. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Dec;52(4):485–532. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.4.485-532.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmieger H. Phage P22-mutants with increased or decreased transduction abilities. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;119(1):75–88. doi: 10.1007/BF00270447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh J., McClelland M. Fingerprinting genomes using PCR with arbitrary primers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7213–7218. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.24.7213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. G., Kubelik A. R., Livak K. J., Rafalski J. A., Tingey S. V. DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6531–6535. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. K., Kwan H. S. Transcription of glpT of Escherichia coli K12 is regulated by anaerobiosis and fnr. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992 Jul 1;73(1-2):15–18. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(92)90574-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. K., McClelland M. A BlnI restriction map of the Salmonella typhimurium LT2 genome. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(5):1656–1661. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.5.1656-1661.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. K., McClelland M. Dissection of the Salmonella typhimurium genome by use of a Tn5 derivative carrying rare restriction sites. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(11):3807–3811. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.11.3807-3811.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. K., Suen K. L., Kwan H. S. Transcription of pfl is regulated by anaerobiosis, catabolite repression, pyruvate, and oxrA: pfl::Mu dA operon fusions of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):4900–4905. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.4900-4905.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto N. The origin of bacteriophage P221. Virology. 1967 Nov;33(3):545–547. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90132-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youderian P., Sugiono P., Brewer K. L., Higgins N. P., Elliott T. Packaging specific segments of the Salmonella chromosome with locked-in Mud-P22 prophages. Genetics. 1988 Apr;118(4):581–592. doi: 10.1093/genetics/118.4.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]