Abstract
This study investigates the relationship of promoter methylation in tumor suppressor genes with copy-number aberrations (CNA) and with tumor markers in breast cancer (BCs). The study includes 98 formalin fixed paraffin-embedded BCs in which promoter methylation of 24 tumour suppressor genes were assessed by Methylation-Specific Multiplex Ligation-dependent Probe Amplification (MS-MLPA), CNA of 20 BC related genes by MLPA and ER, PR, HER2, CK5/6, CK18, EGFR, Cadherin-E, P53, Ki-67 and PARP expression by immunohistochemistry (IHC). Cluster analysis classed BCs in two groups according to promoter methylation percentage: the highly-methylated group (16 BCs), containing mostly hyper-methylated genes, and the sparsely-methylated group (82 BCs) with hypo-methylated genes. ATM, CDKN2A, VHL, CHFR and CDKN2B showed the greatest differences in the mean methylation percentage between these groups. We found no relationship of the IHC parameters or pathological features with methylation status, except for Catherin-E (p = 0.008). However the highly methylated BCs showed higher CNA proportion than the sparsely methylated BCs (p < 0.001, OR = 1.62; IC 95% [1.26, 2.07]). CDC6, MAPT, MED1, PRMD14 and AURKA showed the major differences in the CNA percentage between the two groups, exceeding the 22%. Methylation in RASSF1, CASP8, DAPK1 and GSTP1 conferred the highest probability of harboring CNA. Our results show a new link between promoter methylation and CNA giving support to the importance of methylation events to establish new BCs subtypes. Our findings may be also of relevance in personalized therapy assessment, which could benefit the hyper methylated BC patients group.
Keywords: Breast cancer, promoter methylation, copy number aberrations, immunochemistry
Introduction
Breast cancer (BC) is the most common cancer in women. Every year about one million women worldwide are diagnosed with BC [1]. Consequently, this pathology has been extensively investigated in terms of histopathology, immunohistochemistry (IHC) and genetic disorders. Carcinogenesis is the result of accumulating genetic alterations as mutations, copy number aberrations (CNA) and, recently, it has also been demonstrated that epigenetic alterations such as promoter methylation in tumor suppressor genes can drive to tumor development [2]. Epigenetic is defined as changes in gene expression that are not due to any alteration in the DNA sequence [3]. They are mediated by several molecular mechanisms including histone modifications, small non-coding RNAs and gene promoter methylation in CpG islands [4]. The understanding of these mechanisms is playing a relevant role in the diagnosis, prognosis and in the design of new treatment strategies.
Epigenetic deregulation, particularly altered DNA methylation patterns, is known to play a key role in the altered gene expression profiles found in all human cancers. The last advances in genome-wide approaches have contributed to BC molecular classification [5]. At this regard, methylation profiles have been widely studied in BC, finding different methylation patterns between normal breast and BC [6,7]. Furthermore, methylation profiles are also associated with BC immunohistochemical features [8,9] and they are able to differentiate new BC subtypes, not previously identified by conventional IHC [10].
Promoter alterations are also associated with follow-up parameters in BC. Thus, Xu et al [11] studied the methylation status of BRCA1, APC and p16 in 800 archival retrieved BC and analyzed their relationship with mortality and disease free survival, finding that mortality is associated with p16 promoter methylation, and that the number of methylated genes increases with the BC mortality risk [11].
Although the relevance of epigenetics in carcinogenesis is well established, little is known about the mechanism involved, particularly the relationship between DNA methylation in BC and molecular aberrations commonly detected in cancer. At this regard, recent advances in genome-wide approaches have contributed to BC molecular classification, finding that luminal B subtype is usually associated with chromosomal gains and promoter hyper-methylation [12].
We consider that it is necessary to deepen in the understanding of the molecular mechanisms involved in carcinogenesis in order to develop a personalized medicine based on the design of specific therapeutic agents. Therefore, this study aims to investigate the implications of DNA methylation of tumor suppressor gene promoters with CNA of genes related with BC, and with pathological and immunohistochemical parameters.
Material and methods
Patients
The study includes 98 formalin fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) BCs in which promoter methylation, CNA and IHC were assessed. The pathological and IHC features of these patients are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1.
Pathological and immunohistochemical parameters in breast cancer and breast cancer cluster methylated groups
| All Samples | Cluster Groups | x2 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
||||||||
| Parameter/Event | Event (%) | n | Highly methylated | Sparsely methylated | Adjusted p | ||||
|
|
|||||||||
| Event (%) | n | Event (%) | n | ||||||
| Pathological characteristics | T | 1 | 56 (58) | 97 | 10 (62) | 16 | 46 (57) | 81 | ns |
| 2 | 41 (42) | 97 | 6 (38) | 16 | 35 (43) | 81 | |||
| N | 0 | 63 (67) | 94 | 11 (69) | 16 | 52 (67) | 78 | ns | |
| 1 | 31 (33) | 94 | 5 (31) | 16 | 26 (33) | 78 | |||
| Histological Type | CDI | 88 (90) | 98 | 13 (81) | 16 | 75 (91) | 82 | ns | |
| CLI | 6 (6) | 98 | 3 (19) | 16 | 3 (4) | 82 | |||
| Other | 4 (4) | 98 | 0 (0) | 16 | 4 (5) | 82 | |||
| HG | 1 | 19 (20) | 94 | 4 (29) | 14 | 15 (19) | 80 | ns | |
| 2 | 37 (39) | 94 | 4 (29) | 14 | 33 (41) | 80 | |||
| 3 | 38 (40) | 94 | 6 (43) | 14 | 32 (40) | 80 | |||
| Tumor Stage | < III | 79 (82) | 96 | 14 (88) | 16 | 65 (81) | 80 | ns | |
| ≥ III | 17 (18) | 96 | 2 (12) | 16 | 15 (19) | 80 | |||
| Immunohistochemistry | ER | pos | 68 (70) | 97 | 11 (69) | 16 | 57 (70) | 81 | ns |
| PR | pos | 57 (59) | 97 | 6 (38) | 16 | 51 (63) | 81 | ns | |
| HER2 | pos | 20 (21) | 96 | 4 (25) | 16 | 16 (20) | 80 | ns | |
| Cadherin-E | pos | 84 (95) | 88 | 10 (77) | 13 | 74 (99) | 75 | 0.008 | |
| Ki-67 | high | 43 (47) | 92 | 5 (36) | 14 | 38 (49) | 78 | ns | |
| CK5/6 | pos | 18 (20) | 89 | 2 (18) | 14 | 16 (21) | 78 | ns | |
| EGFR | pos | 12 (14) | 85 | 0 (0) | 10 | 12 (16) | 75 | ns | |
| CK18 | pos | 80 (91) | 88 | 9 (75) | 12 | 71 (93) | 76 | ns | |
| P53 | pos | 43 (57) | 75 | 3 (30) | 12 | 40 (62) | 65 | ns | |
| PARP | pos | 67 (82) | 82 | 9 (82) | 11 | 58 (82) | 71 | ns | |
T: Tumor stage (T1 < 2 cm; T2 ≥ 2 cm); N: Node involvement (N0: Absence; N1: Presence); HG: Histological grade; CDI: Invasive ductal Carcinoma; CLI: Invasive lobular Carcinoma; ER: Estrogen receptor; PR: Progesterone receptor; HER2: Erythroblastic leukemia viral oncogene homolog 2 receptor; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; PARP: Poly-ADP-Ribose-Polymerase; pos: Positivity; %: percentage of positives; n: total number of cases; adjusted p: Holm’s adjusted χ2 p-value associated to the differences between the cluster groups; ns: not significant.
All patients signed an informed consent elaborated by the Health Department following the recommendations of the Declaration of Human Rights, the Conference of Helsinki [http://www.wma.net/en/30publications/10policies/b3/index.html] and institutional regulations that was approved by the Hospital Ethics Committee.
Molecular studies
DNA was isolated from FFPE using Deparaffinization Solution and QuiAmp DNA Investigation Kit (Quiagen, Hilden, Germany). DNA quantity and quality was measured spectrophotometrically using NanoDrop 2000c (ThermoFisher).
Methylation studies were performed with the Methylation-Specific Multiplex Ligation Dependent Probe Amplification (MS-MLPA) technique [13]. We used ME001 Tumour Suppressor Mix 1 Kit (MRC Holland, Amsterdam, The Netherlands) [14]. This kit contains probes addressed to detect the methylation status in tumour suppressor gene promoters that are frequently silenced by methylation in cancer such as TIMP3, APC, CDKN2A, MLH1, ATM, RARB, CDKN2B, HIC1, CHFR, BRCA1, CASP8, CDKN1B, PTEN, BRCA2, CD44, RASSF1, DAPK1, VHL, ESR1, TP73, FHIT, IGSF4, CDH13 and GSTP1.
To detect CNA we also employed the MLPA technique [15] with the P078B1 Breast Tumour Kit (MRC Holland, Amsterdam, The Netherlands) [16]. This kit includes probes to detect CNA of HER2, BIRC5, MYC, TOP2A, ESR1, MTDH, CCND1, CCNE1, EGFR, EMSY, ADAM9, IKBKB, CDH1, CDC6, CPD, FGFR1, MED1, MAPT, PRMD14 and AURKA which are frequently altered in BC.
The amplicons generated on MS-MLPA and MLPA were analysed by capillary electrophoresis on an AB3130 Capillary Sequencer (Applied Biosystems) according to MLPA protocol, and fragment analysis was performed using Coffalyser.net software (MRC Holland, Amsterdam, The Netherlands). MLPA and MS-MLPA results were evaluated as previously reported [14,17].
Immunohistochemistry
IHC was performed using tissue microarray (TMA). The slides were immuno-stained using primary antibodies against Ki-67, ER, PR, HER2, CK5/6, CK18, EGFR, Cadherin-E and P53, all from (DAKO, Glostrup, Denmark) and PARP from (ABCAM, Cambridge, UK). ER and PR expression was evaluated according to Allred scoring system [18]. HER2 expression was scored according to Hercep Test criteria [19]. In 2+ HER2 expression samples fluorescent in situ hybridization was also performed [20]. For EGFR and Cadherin-E expression, the same criteria as for HER-2 were applied [20-22]. Ki-67 and P53 expression was evaluated according to St Gallen International Expert Consensus [20,23]. The criteria followed to assign CK5/6 and CK18 positivity was their cytoplasmic detection in more than 5% of cells. To evaluate PARP expression, nuclear staining percentage over 5% was considered positive. Finally, in order to define invasive BC subtypes we followed St. Gallen International Expert Consensus [20,24].
Statistical analysis
Data were summarized by their mean and standard deviation and their median and 1st and 3rd quartiles (continuous variables) and by relative and absolute frequencies (categorical variables).
Unsupervised hierarchical analysis [25] was performed for clustering the samples according to the methylation grade, trying to achieve maximal homogeneity for each group and the highest difference between the groups.
Chi-square test applying Holm’s correction [26] was used to compare pathological and IHC features between cluster groups.
The number of genes with CNA out of the total number of genes studied was computed for each individual creating a new variable. This new variable was used as a dependent variable in a binomial generalized linear model with methylation group as predictor. We also used the lasso (“least absolute shrinkage and selection operator”) procedure [27] to find which specific genes were most probably associated with these total CNA between both groups. 10-fold cross validation was used to select the regularization parameter for the lasso. All statistical analyses were performed using the R software (version 3.1.0) [http://www.R-project.org/].
Results
We detected methylation in the 24 promoters studied for the majority of samples studied (Table 2). The mean methylation percentage for each promoter ranged from 1.0 (CD44) to 37.5 (RASSF1). On average, we found a total of 5.97 (median: 5.0; Q1: 3.25; Q3: 8.0) promoter methylated genes per patient.
Table 2.
Methylation status intensity in tumor suppressor genes in breast cancer
| All Samples | Cluster Groups | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Gene Promoters | n = 98 | Highly Methylated n = 16 | Sparsely Methylated n = 82 | Differences of the means | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| ¥ ± SD | (% MS) | ¥ ± SD | (% MS) | ¥ ± SD | (% MS) | Highly-Sparsely | ||
| APC | 36.3 ± 27.4 | 83 | 53.8 ± 28.0 | 94 | 32.9 ± 26.1 | 80 | 20.8 | |
| ATM | 15.7 ± 23.9 | 46 | 56.7 ± 20.3 | 100 | 7.6 ± 14.4 | 35 | 49.0 | |
| BRCA1 | 5.7 ± 16.2 | 15 | 13.5 ± 25.7 | 38 | 4.2 ± 13.3 | 11 | 9.3 | |
| BRCA2 | 3.2 ± 11.5 | 12 | 12.7 ± 25.3 | 25 | 1.4 ± 4.5 | 10 | 11.3 | |
| CASP8* | 7.1 ± 13.2 | 31 | 16.8 ± 15.9 | 69 | 5.2 ± 11.8 | 23 | 11.6 | |
| CD44 | 1.0 ± 7.2 | 2 | 2.4 ± 9.5 | 6 | 0.7 ± 6.7 | 1 | 1.6 | |
| CDH13 | 26.1 ± 21.9 | 78 | 36.1 ± 22.5 | 81 | 24.2 ± 21.3 | 77 | 11.9 | |
| CDKN1B | 6.4 ± 18.6 | 15 | 33.1 ± 35.2 | 56 | 1.2 ± 4.3 | 7 | 32.0 | |
| CDKN2A | 14 ± 23.1 | 45 | 51.1 ± 33.2 | 81 | 6.7 ± 10.4 | 38 | 44.4 | |
| CDKN2B | 3.5 ± 11.7 | 11 | 17.3 ± 23.6 | 44 | 0.8 ± 4.0 | 5 | 16.5 | |
| CHFR | 9.1 ± 18.9 | 26 | 38.5 ± 25.9 | 88 | 3.3 ± 9.9 | 13 | 35.2 | |
| DAPK1* | 9.6 ± 19.5 | 24 | 34.6 ± 27.6 | 69 | 4.8 ± 12.8 | 16 | 29.9 | |
| ESR1 | 3.3 ± 14.2 | 8 | 15.9 ± 31.8 | 25 | 0.8 ± 3.9 | 5 | 15.2 | |
| FHIT | 4.3 ± 15.1 | 10 | 22.8 ± 31.1 | 44 | 0.7 ± 3.6 | 4 | 22.1 | |
| GSTP1* | 16.3 ± 26.9 | 40 | 28.4 ± 38.8 | 44 | 13.9 ± 23.5 | 39 | 14.6 | |
| HIC1 | 5.9 ± 20.1 | 12 | 31.4 ± 41.1 | 44 | 0.9 ± 3.9 | 6 | 30.4 | |
| IGSF4 | 3.2 ± 10.8 | 10 | 13.1 ± 20.9 | 31 | 1.2 ± 5.9 | 6 | 11.9 | |
| MLH1 | 3.9 ± 10.5 | 15 | 15.9 ± 16.6 | 62 | 1.6 ± 6.9 | 6 | 14.4 | |
| PTEN | 3.9 ± 7.8 | 26 | 9.4 ± 14.3 | 38 | 2.8 ± 5.3 | 23 | 6.6 | |
| RARB | 2.7 ± 10.0 | 8 | 3.8 ± 10.7 | 12 | 2.4 ± 9.9 | 7 | 1.3 | |
| RASSF1* | 37.5 ± 28.5 | 79 | 49.2 ± 35.0 | 81 | 35.3 ± 26.7 | 78 | 14.0 | |
| TIMP3 | 3.9 ± 12.7 | 12 | 5.8 ± 16.3 | 12 | 3.6 ± 12 | 12 | 2.2 | |
| TP73 | 4.0 ± 14.1 | 13 | 18.5 ± 30.5 | 31 | 1.2 ± 3.9 | 10 | 17.3 | |
| VHL | 8.1 ± 23.8 | 13 | 41.3 ± 44.7 | 50 | 1.6 ± 6.8 | 6 | 39.7 | |
|
| ||||||||
| TOTAL METHYLATED GENES PER PATIENT | Mean (SD) | 5.97 (3.7) | 12.1 (2.9) | 4.8 (2.5) | ||||
| Median (Q1-Q3) | 5.0 (3.25-8.0) | 11.5 (10.0-15.0) | 4.0 (3.0-6.0) | |||||
¥Mean methylation percentage; % MS: Percentage of Methylated samples; SD: Standard deviation; In bold are indicated genes that show major differences between highly and sparsely methylated; groups;
genes whose methylation is associated with an increased percentage of CNA in the tumors.
We found CNA, gains or losses, for the twenty studied genes in the majority of the BCs (Table 3). The incidence of CNA ranged from the 7% (ESR1) to 52% (MED1) and remained above 39% for MYC, FGFR1, BIRC5, CCND1, HER2 and MED1. On average, we found a 31.0% (median: 30.0%; Q1: 20.0%; Q3: 40.0%) of total aberrations per patient.
Table 3.
Incidence of abnormalities (gains or losses) in breast cancers
| All Samples | Cluster Groups | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
||||
| Gene | Chr | n = 98 | Highly Methylated n = 16 | Sparsely Methylated n = 82 | Difference of Abnormalities |
|
|
|
||||
| Abnormalities | Abnormalities | Abnormalities | Highly-Sparsely (%) | ||
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | |||
| ESR1 | 06q25 | 7 (7) | 0 (0) | 7 (9) | -9 |
| EGFR | 07p11 | 15 (15) | 3 (19) | 12 (15) | 4 |
| FGFR1 | 08p12 | 40 (41) | 4 (25) | 36 (44) | -19 |
| ADAM9 | 08p11 | 26 (27) | 5 (31) | 21 (26) | 5 |
| IKBKB | 08p11 | 34 (35) | 7 (44) | 27 (33) | 11 |
| PRDM14 | 08q13 | 36 (37) | 9 (56) | 27 (33) | 23 |
| MYC | 08q24 | 39 (40) | 8 (50) | 31 (38) | 12 |
| MTDH | 08q22 | 33 (34) | 8 (50) | 25 (30) | 20 |
| CCND1 | 11q13 | 44 (45) | 7 (44) | 37 (45) | -1 |
| EMSY | 11q13 | 36 (37) | 6 (38) | 30 (37) | 1 |
| CDH1 | 16q22 | 18 (18) | 5 (31) | 13 (16) | 15 |
| CPD | 17q11 | 19 (19) | 4 (25) | 15 (18) | 7 |
| MED1 | 17q11 | 51 (52) | 12 (75) | 39 (48) | 27 |
| HER2 | 17q12 | 47 (48) | 9 (56) | 38 (46) | 10 |
| CDC6 | 17q21 | 35 (36) | 10 (62) | 25 (30) | 32 |
| TOP2A | 17q21 | 16 (16) | 3 (19) | 13 (16) | 3 |
| MAPT | 17q21 | 35 (36) | 10 (62) | 25 (30) | 32 |
| BIRC5 | 17q25 | 44 (45) | 8 (50) | 36 (44) | 6 |
| CCNE1 | 19q12 | 13 (13) | 4 (25) | 9 (11) | 14 |
| AURKA | 20q13 | 19 (19) | 6 (38) | 13 (16) | 22 |
|
| |||||
| TOTAL CNA PER PATIENT | Mean (%) | 31.0 | 40.0 | 29.2 | |
| Median (%) (Q1-Q3) | 30 (20-40) | 42.5 (30.0-50.0) | 30.0 (16.3-40.0) | ||
Chr: chromosome location; CNA: Copy Number Aberration; Bold character indicate the genes that show major differences between highly and sparsely methylated groups.
Unsupervised clustering of promoters methylation percentage split the BCs into two groups (Figure 1), the first one (placed on the left) was named highly-methylated group and contained 16 BCs, many of them harboring hyper or moderately methylated genes. The second group (placed on the right) was called sparsely-methylated group, and contained 82 BCs mostly showing no or low methylation degree. Methylation status in both clusters is displayed in Table 2 and represented in a heatmap (Figure 1). All promoters showed higher mean methylation percentage in the highly-methylated group (Figure 2A, Table 2). ATM, CDKN2A, VHL and CHFR were the ones that presented the widest differences in the mean methylation percentage between the two established groups with methylation percentages of 49.0%, 44.4%, 39.7% and 35.2%, respectively. We found on average 12.1 (median: 11.5; Q1: 10.0; Q3: 15.0) promoter methylated genes in the highly-methylated cluster and 4.8 (median: 4.0; Q1: 3.0; Q3: 6.0) in the sparsely-methylated cluster.
Figure 1.
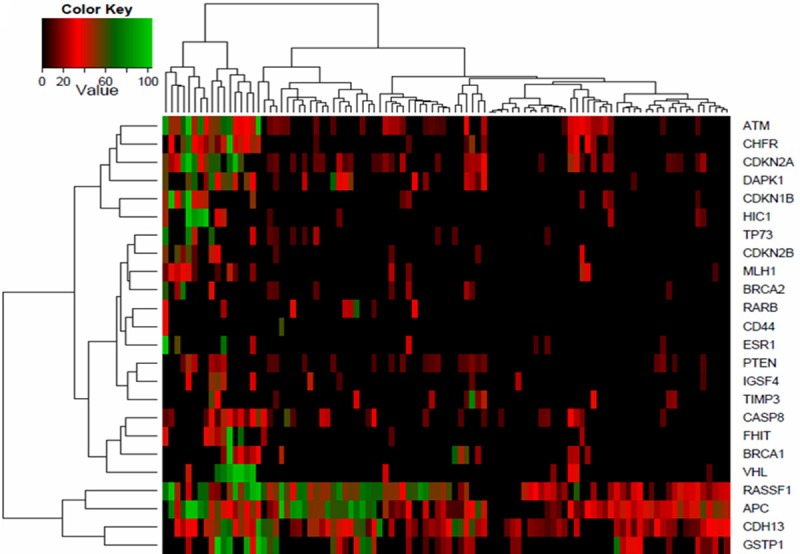
Clustering diagram of breast cancer methylation profile of 24 tumor suppressor genes. The heatmap depicts the percentage of promoter methylation (black, low methylation; red, medium methylation and green, high methylation).
Figure 2.
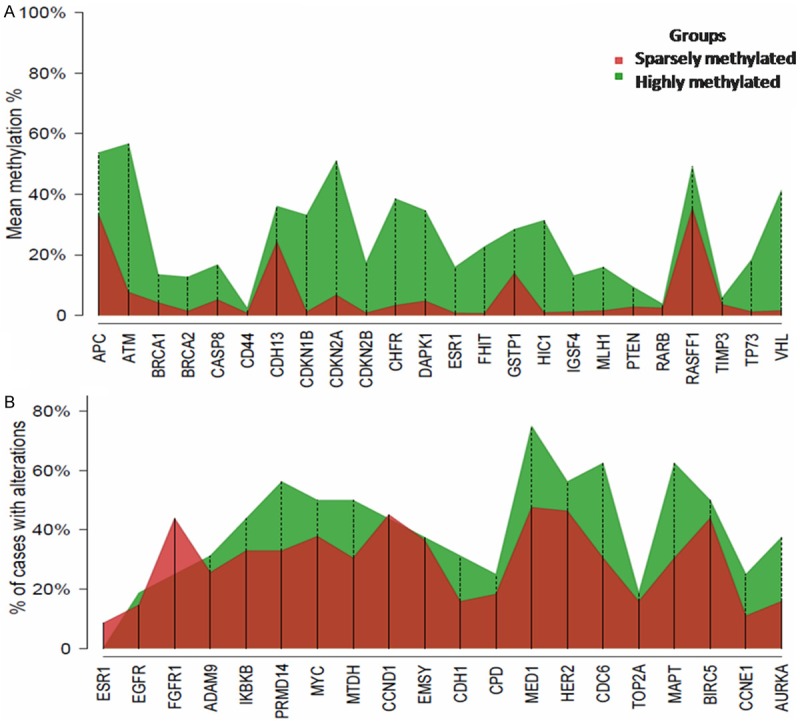
Percentage of promoter methylation (Panel A) for each gene and proportion of BCs with genetic aberrations (Panel B) by methylation group.
With regard to the methylation percentage, we differentiated three groups (Figure 1); The first group contained ATM, CHFR, CDKN2A and DAPK1, was placed in the upper four rows of the heatmap and differentiated a 16 highly-methylated BCs; the second was formed by RASSF1, APC, CDH13 and GSTP1, placed in the lower part of the heatmap, and showed a high methylation percentage in nearly all samples; finally, the central cluster included the remaining 16 genes showing low methylation degree.
We did not find statistical differences for the pathological and IHC features between the highly and the sparsely-methylated groups, except for Cadherin-E which was less expressed in the highly methylated samples (p = 0.008; Table 1).
We found a strong association between the total proportion of CNA detected in each BC sample and the corresponding methylation status. Hence, the highly-methylated group BCs showed a higher proportion CNAs than the sparsely-methylated group BCs. The total CNA mean percentage per sample was 40.0% (median: 42.5%; Q1: 30.0%; Q3: 50.0%) and 29.2% (median: 30.0%; Q1: 16.3%; Q3: 40.0%), in the highly and sparsely-methylated cluster, respectively (Table 3, Figure 3). This was confirmed applying a binomial model which showed that highly-methylated BCs was statistically linked with a higher probability of harboring genetic abnormalities (p < 0.001, OR = 1.62; IC 95% [1.26, 2.07]).
Figure 3.
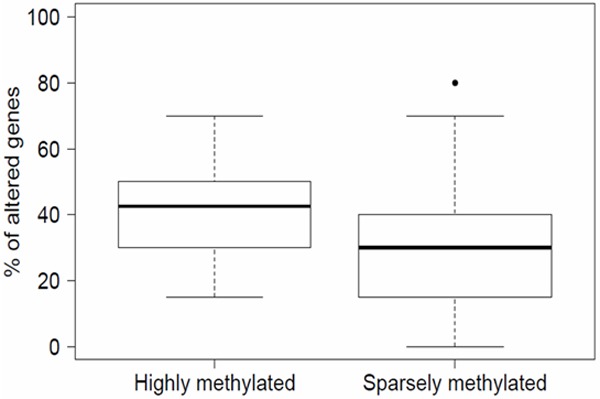
Proportion of genetic aberrations by methylation status. BCs in the highly-methylated group show a greater proportion of genetic aberrations than BCs in the sparsely-methylated group.
The proportion of BCs with aberrations for each gene in the methylated groups varied between the studied genes (Figure 2B, Table 3). Hence, ESR1, FGFR1 and CCND1 showed a higher proportion of abnormalities in the sparsely-methylated group. The remaining 17 genes presented a higher proportion of aberrations in the highly-methylated group. CDC6, MAPT, MED1, PRDM14, and AURKA showed the highest CNA percentage in the highly methylated group with a mean difference between groups of 32%, 32%, 27%, 23% and 22%, respectively.
We also analyzed the methylated genes that were more specifically associated with CNA in the two methylation groups. This study was performed by applying lasso analysis to the total patient series, using 10-fold cross validation. The analysis selected the genes RASSF1, CASP8, DAPK1 and GSTP1 as those whose methylation status showed higher probability of having CNA.
Discussion
It is well known that promoter methylation is related with gene expression and tumor subtypes, which suggest that altered methylation signatures in BC could play an important role in phenotype establishment [2].
In the present study we detected methylation in all promoters, although the methylation percentage varied greatly among the genes. At this regard our results for BRCA1, RASSF1, RARB and CDKN2B were similar with those previously reported [28-30]. However, for the remaining genes we observed a great disparity [31] that could be attributed to the variability in the methylation assays, sample types (FFPE samples or fresh tumor), different CpG islands studied, etc. [31].
Our CNA results are in full agreement with those reported by Moelans et al [16] in a series of 104 BC using MLPA assays. They found similar gain percentages for EGFR, FGFR, IKBKB, PRMD14, HER2, CCND1, CDH1, CCNE1 and AURKA. Here, we observed that MED1, HER2, BIRC5, CCND1, MYC and FGFR1 showed the highest CNA incidences. In this regard, abnormalities in MED1, HER2 and BIRC5, like many other genes located in chromosome 17 [32], could have a role in cancer initiation, progression or in targeted therapy such as HER2 amplifications in BC.
Cluster analysis revealed that the methylation profile of 24 tumor suppressor gene promoters enabled the differentiation of two BCs sets, the highly and sparsely-methylated BCs. Of these 24 genes ATM, CDKN2A, VHL and CHFR were the ones that showed the highest differences between the mean methylation percentages of the groups. These particular genes are mainly involved in cell cycle regulation and are associated with poor prognosis and tumor progression. Specifically, for ATM, it is widely reported that mutation carriers present an increased risk of BC development [33]. On the other hand, the association of CDKN2A, methylation and BC development has been broadly studied; however the results are still controversial [34]. pVHL is the central component of an ubiquitin ligase complex, that interacts with HIF protein. In its absence, as it would be the case of VHL methylation, HIF becomes stabilized and is free to induce the expression of its target genes, many of which are relevant in the angiogenesis process, cell growth or cell survival regulation [35]. And, CHFR has been found poorly expressed in BC cell lines and its reduced expression was reactivated with the use of demethylating agents [36]. In addition, its reduced expression was associated with an increase of aneuploidy [37].
We found that samples belonging to the highly methylated group showed less Cadherin-E expression. This fact would confer to this group of samples an advantage in the dedifferentiation and invasiveness [38], although no association with these pathological features was here found.
Samples in the highly methylated group presented higher CNA. This finding identifies a subgroup of tumors that combines epigenetic and genetic aberrations. The major differences in the CNA percentage between the two groups were found in CDC6, MAPT, AURKA, PRDM14 and MED1. These genes are implicated in carcinogenesis [39-43] and are frequently amplified in BC. CDC6 is essential for DNA replication and mitosis regulation [42], and AURKA is crucial for proper chromosomes segregation during mitosis [41]. These genes are associated with poor differentiated tumors and reduced survival.
Here we found that of 24 studied genes CASP8, GSTP1, RASSF1 and DAPK1 promoter methylation were the most specifically related with CNA in the BC. To our knowledge, there are no reports relating the methylation status with copy number variations in cancer, and more specifically in BC. The hitherto existing reports related methylation events with genetic instability in colorectal cancer, [44] suggesting that methylation might play an important role in chromosomal segregation processes during the clonal evolution of tumors. Furthermore it has been reported that genetic silencing caused by methylation of genes involved in apoptosis, metabolism detoxification, and cell cycle regulation [45-47] may be a factor that could impair the prognosis of these BCs.
Of the four methylated genes, GSTP1 plays an essential role in carcinogenesis detoxification and its absence leads to toxic accumulation in the cell and cancer progression [45]. GSTP1 may act as a caretaker and its methylation could lead to additional somatic genome alterations promoting tumor growth [48]. On other hand, CASP8 plays a relevant role in the induction of apoptosis by external death signals or in response to DNA damage. Its epigenetic silencing caused by DNA promoter methylation leads to an increased risk of tumor formation and cancer progression [46,47]. DAPK1, a pro-apoptotic serine/threonine protein kinase gene is also essential for the execution of the apoptotic process [49], so its silencing by methylation is also related with an increased risk of BC development. Consequently, CASP8 and DAPK1 methylation could contribute to BC progression and to the maintenance of cells carrying genetic abnormalities. Finally, epigenetic RASSF1 silencing has also been widely reported in BC. RASSF1 protein acts at level of G1/S-phase cell cycle progression regulating cyclin D1 protein accumulation [50]. When the RASSF1 protein is not expressed there is an imbalance in favor of cell division. Therefore these cells can continue dividing increasing genetic instability instead of arresting the cell cycle. Likewise, it has been observed in knockout mice that re-expression of RASFF1 inhibits tumorigenesis [51].
In summary, our results support that tumor suppressor genes promoter methylation is associated with genetic aberrations. Furthermore, the methylation profile of tumor suppressor genes identifies two types of BCs, being the highly-methylated associated with a greater number of aberrations in genes involved in development, progression and response to therapy in BC. Finally, our results reveal a new link between methylation and CNA which gives support to the importance of methylation events to establish new subtypes of BCs. Our findings may be of significance in personalized therapy assessment that could benefit the hyper-methylated BC patients group.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank to the Carlos III Health Institute for having granted this project PI10/00347. We also would like to thank to the Health Research Institute La Fe for having granted Rosa Murria Estal which made possible her participation in the study. We should thank the effort to perform this work to the pathologists, Francisco Javier Seguí Ivañez (University Hospital of Alicante) and Ana García Martínez (University Hospital La Fe). We also should thank to the molecular biologist José Antonio López Guerrero (Valencia Institute of Oncology); to the laboratory technicians Gema Pérez Simó (University Hospital La Fe) and Estefania Rojas Calvente (University Hospital of Alicante) and to Jacobo Martinez Santamaría, Mercedes Goicoechea Sáez and Dolores Salas Trejo (General department of public health, Conselleria de Sanitat, Generalitat Valenciana). Finally we would like to acknowledge the patients enrolled in this study and the Biobank of the General University Hospital of Alicante and the biobank for the biomedical research and public health of the Comunidad Valenciana (IBSP-CV) as part of the Valenciana Biobank Network (RVB) and the National Biobank.
Disclosure of conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
References
- 1.Bouchalova K, Cizkova M, Cwiertka K, Trojanec R, Hajduch M. Triple negative breast cancer current status and prospective targeted treatment based on HER1 (EGFR), TOP2A and C-MYC gene assessment. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2009;153:13–18. doi: 10.5507/bp.2009.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Holm K, Hegardt C, Staaf J, Vallon-Christersson J, Jönsson G, Olsson H, Borg A, Ringnér M. Molecular subtypes of breast cancer are associated with characteristic DNA methylation patterns. Breast Cancer Res. 2010;12:R36. doi: 10.1186/bcr2590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Esteller M. Epigenetics in cancer. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:1148–1159. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra072067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Jovanovic J, Rønneberg JA, Tost J, Kristensen V. The epigenetics of breast cancer. Mol Oncol. 2010;4:242–254. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2010.04.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Roa JC, Anabalón L, Tapia O, Martínez J, Araya JC, Villaseca M, Guzmán P, Roa I. Promoter methylation profile in breast cancer. Rev Med Chil. 2004;132:1069–1077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bardowell SA, Parker J, Fan C, Crandell J, Perou CM, Swift-Scanlan T. Differential methylation relative to breast cancer subtype and matched normal tissue reveals distinct patterns. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013;142:365–380. doi: 10.1007/s10549-013-2738-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Radpour R, Kohler C, Haghighi MM, Fan AX, Holzgreve W, Zhong XY. Methylation profiles of 22 candidate genes in breast cancer using high-throughput MALDI-TOF mass array. Oncogene. 2009;28:2969–2978. doi: 10.1038/onc.2009.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Sun Z, Asmann YW, Kalari KR, Bot B, Eckel-Passow JE, Baker TR, Carr JM, Khrebtukova I, Luo S, Zhang L, Schroth GP, Perez EA, Thompson EA. Integrated analysis of gene expression, CPG island methylation, and gene copy number in breast cancer cells by deep sequencing. PLoS One. 2011;6:e17490. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kajabova V, Smolkova B, Zmetakova I, Sebova K, Krivulcik T, Bella V, Kajo K, Machalekova K, Fridrichova I. RASSF1A promoter methylation levels positively correlate with estrogen receptor expression in breast cancer patients. Transl Oncol. 2013;6:297–304. doi: 10.1593/tlo.13244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Rhee JK, Kim K, Chae H, Evans J, Yan P, Zhang BT, Gray J, Spellman P, Huang TH, Nephew KP, Kim S. Integrated analysis of genome-wide DNA methylation and gene expression profiles in molecular subtypes of breast cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41:8464–8474. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Xu X, Gammon MD, Zhang Y, Cho YH, Wetmur JG, Bradshaw PT, Garbowski G, Hibshoosh H, Teitelbaum SL, Neugut AI, Santella RM, Chen J. Gene promoter methylation is associated with increased mortality among women with breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010;121:685–692. doi: 10.1007/s10549-009-0628-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Cancer Genome Atlas Network. Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 2012;490:61–70. doi: 10.1038/nature11412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Anders O, Nygren H, Ameziane N, Duarte HMB, Vijzelaar R, Waisfisz Q, Hess CJ, Schouten JP, Errami A. Methylation-Specific MLPA (MS-MLPA): simultaneous detection of CpG methylation and copy number changes of up to 40 sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005;33:e128. doi: 10.1093/nar/gni127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Henken FE, Wilting SM, Overmeer RM, van Rietschoten JG, Nygren AO, Errami A, Schouten JP, Meijer CJ, Snijders PJ, Steenbergen RD. Sequential gene promoter methylation during HPV-induced cervical carcinogenesis. Brit J Cancer. 2007;97:1457–1464. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6604055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Schouten JP, McElgunn CJ, Waaijer R, Zwijnenburg D, Diepvens F, Pals G. Relative quantification of 40 nucleic acid sequences by multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002;30:e57. doi: 10.1093/nar/gnf056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Moelans CB, de Weger RA, Monsuur HN, Vijzelaar R, van Diest PJ. Molecular profiling of invasive breast cancer by multiplex ligation dependent probe amplification-based copy number analysis of tumor suppressor and oncogenes. Mod Pathol. 2010;23:1029–1039. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2010.84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Bunyan DJ, Eccles DM, Sillibourne J, Wilkins E, Thomas NS, Shea-Simonds J, Duncan PJ, Curtis CE, Robinson DO, Harvey JF, Cross NC. Dosage analysis of cancer predisposition genes by multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification. Br J Cancer. 2004;91:1155–1159. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Hammond ME, Hayes DF, Dowsett M, Allred DC, Hagerty KL, Badve S, Fitzgibbons PL, Francis G, Goldstein NS, Hayes M, Hicks DG, Lester S, Love R, Mangu PB, McShane L, Miller K, Osborne CK, Paik S, Perlmutter J, Rhodes A, Sasano H, Schwartz JN, Sweep FC, Taube S, Torlakovic EE, Valenstein P, Viale G, Visscher D, Wheeler T, Williams RB, Wittliff JL, Wolff AC. American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists guideline recommendations for immunohistochemical testing of estrogen and progesterone receptors in breast cancer. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2010;134:e48–72. doi: 10.5858/134.7.e48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Milanezi F, Carvalho S, Schmitt FC. EGFR/HER2 in breast cancer: a biological approach for molecular diagnosis and therapy. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2008;8:417–434. doi: 10.1586/14737159.8.4.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Goldhirsch A, Wood WC, Coates AS, Gelber RD, Thürlimann B, Senn HJ. Strategies for subtypes-dealing with the diversity of breast cancer: highlights of the St. Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2011. Ann Oncol. 2011;22:1736–1747. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdr304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Tang Y, Zhu L, Li Y, Ji J, Li J, Yuan F, Wang D, Chen W, Huang O, Chen X, Wu J, Shen K, Loo WT, Chow LW. Overexpression of epithelial growth factor receptor (EGFR) predicts better response to neo-adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with triple-negative breast cancer. J Transl Med. 2012;10:S4. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-10-S1-S4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Gillett CE, Miles DW, Ryder K, Skilton D, Liebman RD, Springall RJ, Barnes DM, Hanby AM. Retention of the expression of E-cadherin and catenins is associated with shorter survival in grade III ductal carcinoma. J Pathol. 2001;193:433–441. doi: 10.1002/path.831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Cheang MC, Chia SK, Voduc D, Gao D, Leung S, Snider J, Watson M, Davies S, Bernard PS, Parker JS, Perou CM, Ellis MJ, Nielsen TO. Ki67 index, HER2 status, and prognosis of patients with luminal B breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2009;101:736–750. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djp082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Nielsen TO, Hsu FD, Jensen K, Cheang M, Karaca G, Hu Z, Hernandez-Boussard T, Livasy C, Cowan D, Dressler L, Akslen LA, Ragaz J, Gown AM, Gilks CB, van de Rijn M, Perou CM. Immunohistochemical and clinical characterization of the basal-like subtype of invasive breast carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:5367–5374. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-0220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ward JH. Hierarchical Grouping to Optimize an Objective Function. J Am Statist Assoc. 1963;58:236–244. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Holm S. A simple sequentially rejective multiple test procedure. Scand J Statist. 1979;6:65–70. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Tibshirani R. Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso. J R Statist Soc B. 1996;58:267–288. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Parrella P, Poeta ML, Gallo AP, Prencipe M, Scintu M, Apicella A, Rossiello R, Liguoro G, Seripa D, Gravina C, Rabitti C, Rinaldi M, Nicol T, Tommasi S, Paradiso A, Schittulli F, Altomare V, Fazio VM. Nonrandom distribution of aberrant promoter methylation of cancer-related genes in sporadic breast tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:5349–5354. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-0555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Shinozaki M, Hoon DS, Giuliano AE, Hansen NM, Wang HJ, Turner R, Taback B. Distinct hypermethylation profile of primary breast cancer is associated with sentinel lymph node metastasis. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:2156–2162. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-1810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Purnomosari D. Molecular analysis of early onset Indonesian breast cancer. Doctoral Thesis. The Netherlands: Utrecht University; 2006. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Brooks J, Cairns P, Zeleniuch-Jacquotte A. Promoter methylation and the detection of breast cancer. Cancer Cause Control. 2009;20:1539–1550. doi: 10.1007/s10552-009-9415-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Zhang W, Yu Y. The important molecular markers on chromosome 17 and their clinical impact in breast cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2011;12:5672–5683. doi: 10.3390/ijms12095672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ahmed M, Rahman N. ATM and breast cancer susceptibility. Oncogene. 2006;25:5906–5911. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Wang L, Tang L, Xie R, Nie W, Chen L, Guan X. P16 promoter hypermethylation is associated with increased breast cancer risk. Mol Med Rep. 2012;6:904–908. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2012.1001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kim WY, Kaelin WG. Role of VHL gene mutation in human cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004;22:4991–5004. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2004.05.061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Erson AE, Petty EM. CHFR-associated early G2/M checkpoint defects in breast cancer cells. Mol Carcinog. 2004;39:26–33. doi: 10.1002/mc.10161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Privette LM, González ME, Ding L, Kleer CG, Petty EM. Altered expression of the early mitotic checkpoint protein, CHFR, in breast cancers: implications for tumor suppression. Cancer Res. 2007;67:6064–6074. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-4109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Frixen UH, Behrens J, Sachs M, Eberle G, Voss B, Warda A, Ltehner D, Bircluneier W. E-Cadherin mediated cell-cell adhesion prevents invasiveness of human carcinoma cells. J Cell Biol. 1991;113:173–185. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.1.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Luoh SW. Amplification and expression of genes from the 17q11 approximately q12 amplicon in breast cancer cells. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2002;136:43–47. doi: 10.1016/s0165-4608(01)00657-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Rouzier R, Rajan R, Wagner P, Hess KR, Gold DL, Stec J, Ayers M, Ross JS, Zhang P, Buchholz TA, Kuerer H, Green M, Arun B, Hortobagyi GN, Symmans WF, Pusztai L. Microtubule-associated protein tau: a marker of paclitaxel sensitivity in breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:8315–8320. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0408974102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Fu J, Biang M, Jiang Q, Zhang C. Roles of Aurka kinases in mitosis and tumorigenesis. Mol Cancer Res. 2007;5:1–10. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-06-0208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Bolardo L, Méndez J. CDC6: from DNA replication to cell cycle checkpoints and oncogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 2008;29:237–243. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgm268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Nishikawa N, Toyota M, Suzuki H, Honma T, Fujikane T, Ohmura T, Nishidate T, Ohe-Toyota M, Maruyama R, Sonoda T, Sasaki Y, Urano T, Imai K, Hirata K, Tokino T. Gene amplification and overexpression of PRDM14 in breast cancers. Cancer Res. 2007;67:9649–9657. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-4111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Lengauer C, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B. DNA methylation and genetic instability in colorectal cancer cells. PNAS. 1997;94:2545–2550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.6.2545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Esteller M, Corn PG, Urena JM, Gabrielson E, Baylin SB, Herman JG. Inactivation of glutathione S-transferase P1 gene by promoter hypermethylation in human neoplasia. Cancer Res. 1998;58:4515–4518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Esteller M. Epigenetic gene silencing in cancer: the DNA hypermethylome. Hum Mol Genet. 2007;16:R50–R59. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddm018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Wu Y, Alvarez M, Slamon DJ, Koeffler P, Vadgama JV. Caspase 8 and maspin are downregulated in breast cancer cells due to CpG site promoter methylation. BMC Cancer. 2010;10:32. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Saxena A, Dhillon VS, Shahid M, Khalil HS, Rani M, Prasad DAS T, Hedau S, Hussain A, Naqvi RA, Deo SV, Shukla NK, Das BC, Husain SA. GSTP1 methylation and polymorphism increase the risk of breast cancer and the effects of diet and lifestyle in breast cancer patients. Exp Ther Med. 2012;4:1097–1103. doi: 10.3892/etm.2012.710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Levy-Strumpf N, Kimchi A. Death associated proteins (DAPs): from gene identification to the analysis of their apoptotic and tumor suppressive functions. Oncogene. 1998;17:3331–3340. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1202588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Shivakumar L, Minna J, Sakamaki J, Pestell R, White M. The RASSF1A tumor suppressor blocks cell cycle progression and inhibits cyclin D1 accumulation. Mol Cell Biol. 2002;22:4309–4318. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.12.4309-4318.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Dammann R, Li C, Yoon J, Chin P, Bates S, Pfeifer GP. Epigenetic inactivation of a RAS association domain family protein from the lung tumour suppressor locus 3p21.3. Nat Genet. 2000;25:315–319. doi: 10.1038/77083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


