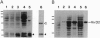Abstract
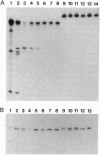
Virulence proteins VirD1 and VirD2 are subunits of a relaxosome-like protein complex that mediates conjugational transfer of a Ti plasmid segment, the T-DNA, from Agrobacterium into higher plants. The VirD1-VirD2 complex binds to 25-bp repeats at the borders of the T-DNA and catalyzes sequence-specific nicking of the conjugative DNA strand (the T-strand) at the third base of these repeats. Nuclear localization signals present in VirD2 target the T-strand to plant cell nuclei. In addition, VirD2 probably plays a role in the high-frequency integration of the T-DNA into the plant genome by illegitimate recombination. Whereas Agrobacterium transformation of dicots is very efficient, T-DNA integration in most monocots can barely be detected. To develop an artificial T-DNA delivery system for monocots, a technique for efficient in vitro production of T-strand DNAs was established by using VirD1 and VirD2 proteins purified from overexpressing Escherichia coli strains. The topoisomerase-like VirD2 enzyme was shown to mediate precise, sequence-specific cleavage of T-DNA border sequences carried by single-stranded DNA templates, even in the absence of VirD1 protein. During this reaction, VirD2 remains covalently bound to the 5' end of artificial T-strand DNAs. In contrast, VirD2, alone or in complex with VirD1, fails to nick linear double-stranded DNA templates in vitro.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albright L. M., Yanofsky M. F., Leroux B., Ma D. Q., Nester E. W. Processing of the T-DNA of Agrobacterium tumefaciens generates border nicks and linear, single-stranded T-DNA. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1046–1055. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1046-1055.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharjee M. K., Meyer R. J. A segment of a plasmid gene required for conjugal transfer encodes a site-specific, single-strand DNA endonuclease and ligase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Mar 11;19(5):1129–1137. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.5.1129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchner J., Rudolph R. Renaturation, purification and characterization of recombinant Fab-fragments produced in Escherichia coli. Biotechnology (N Y) 1991 Feb;9(2):157–162. doi: 10.1038/nbt0291-157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vos G., Zambryski P. Expression of Agrobacterium nopaline-specific VirD1, VirD2, and VirC1 proteins and their requirement for T-strand production in E. coli. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1989 Mar-Apr;2(2):43–52. doi: 10.1094/mpmi-2-043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depicker A., De Wilde M., De Vos G., De Vos R., Van Montagu M., Schell J. Molecular cloning of overlapping segments of the nopaline Ti-plasmid pTiC58 as a means to restriction endonuclease mapping. Plasmid. 1980 Mar;3(2):193–211. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(80)90109-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürrenberger F., Crameri A., Hohn B., Koukolíková-Nicola Z. Covalently bound VirD2 protein of Agrobacterium tumefaciens protects the T-DNA from exonucleolytic degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9154–9158. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filichkin S. A., Gelvin S. B. Formation of a putative relaxation intermediate during T-DNA processing directed by the Agrobacterium tumefaciens VirD1,D2 endonuclease. Mol Microbiol. 1993 May;8(5):915–926. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01637.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gheysen G., Villarroel R., Van Montagu M. Illegitimate recombination in plants: a model for T-DNA integration. Genes Dev. 1991 Feb;5(2):287–297. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.2.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera-Estrella A., Chen Z. M., Van Montagu M., Wang K. VirD proteins of Agrobacterium tumefaciens are required for the formation of a covalent DNA--protein complex at the 5' terminus of T-strand molecules. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4055–4062. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03299.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard E. A., Winsor B. A., De Vos G., Zambryski P. Activation of the T-DNA transfer process in Agrobacterium results in the generation of a T-strand-protein complex: Tight association of VirD2 with the 5' ends of T-strands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4017–4021. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koncz C., Martini N., Mayerhofer R., Koncz-Kalman Z., Körber H., Redei G. P., Schell J. High-frequency T-DNA-mediated gene tagging in plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8467–8471. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matson S. W., Nelson W. C., Morton B. S. Characterization of the reaction product of the oriT nicking reaction catalyzed by Escherichia coli DNA helicase I. J Bacteriol. 1993 May;175(9):2599–2606. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.9.2599-2606.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayerhofer R., Koncz-Kalman Z., Nawrath C., Bakkeren G., Crameri A., Angelis K., Redei G. P., Schell J., Hohn B., Koncz C. T-DNA integration: a mode of illegitimate recombination in plants. EMBO J. 1991 Mar;10(3):697–704. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07999.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto S., Toyoda-Yamamoto A., Ito K., Takebe I., Machida Y. Localization and orientation of the VirD4 protein of Agrobacterium tumefaciens in the cell membrane. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Aug;228(1-2):24–32. doi: 10.1007/BF00282443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pansegrau W., Balzer D., Kruft V., Lurz R., Lanka E. In vitro assembly of relaxosomes at the transfer origin of plasmid RP4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6555–6559. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pansegrau W., Lanka E. Common sequence motifs in DNA relaxases and nick regions from a variety of DNA transfer systems. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 25;19(12):3455–3455. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.12.3455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogowsky P. M., Powell B. S., Shirasu K., Lin T. S., Morel P., Zyprian E. M., Steck T. R., Kado C. I. Molecular characterization of the vir regulon of Agrobacterium tumefaciens: complete nucleotide sequence and gene organization of the 28.63-kbp regulon cloned as a single unit. Plasmid. 1990 Mar;23(2):85–106. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(90)90028-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherzinger E., Lurz R., Otto S., Dobrinski B. In vitro cleavage of double- and single-stranded DNA by plasmid RSF1010-encoded mobilization proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 11;20(1):41–48. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J., John M., Wieneke U., Krüssmann H. D., Schell J. Expression of the nodulation gene nodA in Rhizobium meliloti and localization of the gene product in the cytosol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9581–9585. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stachel S. E., Timmerman B., Zambryski P. Activation of Agrobacterium tumefaciens vir gene expression generates multiple single-stranded T-strand molecules from the pTiA6 T-region: requirement for 5' virD gene products. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):857–863. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04831.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel A. M., Das A. Mutational analysis of Agrobacterium tumefaciens virD2: tyrosine 29 is essential for endonuclease activity. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;174(1):303–308. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.1.303-308.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang K., Stachel S. E., Timmerman B., VAN Montagu M., Zambryski P. C. Site-Specific Nick in the T-DNA Border Sequence as a Result of Agrobacterium vir Gene Expression. Science. 1987 Jan 30;235(4788):587–591. doi: 10.1126/science.235.4788.587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters V. L., Hirata K. H., Pansegrau W., Lanka E., Guiney D. G. Sequence identity in the nick regions of IncP plasmid transfer origins and T-DNA borders of Agrobacterium Ti plasmids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1456–1460. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanofsky M. F., Porter S. G., Young C., Albright L. M., Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. The virD operon of Agrobacterium tumefaciens encodes a site-specific endonuclease. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):471–477. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90604-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambryski P. Basic processes underlying Agrobacterium-mediated DNA transfer to plant cells. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:1–30. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]