Abstract
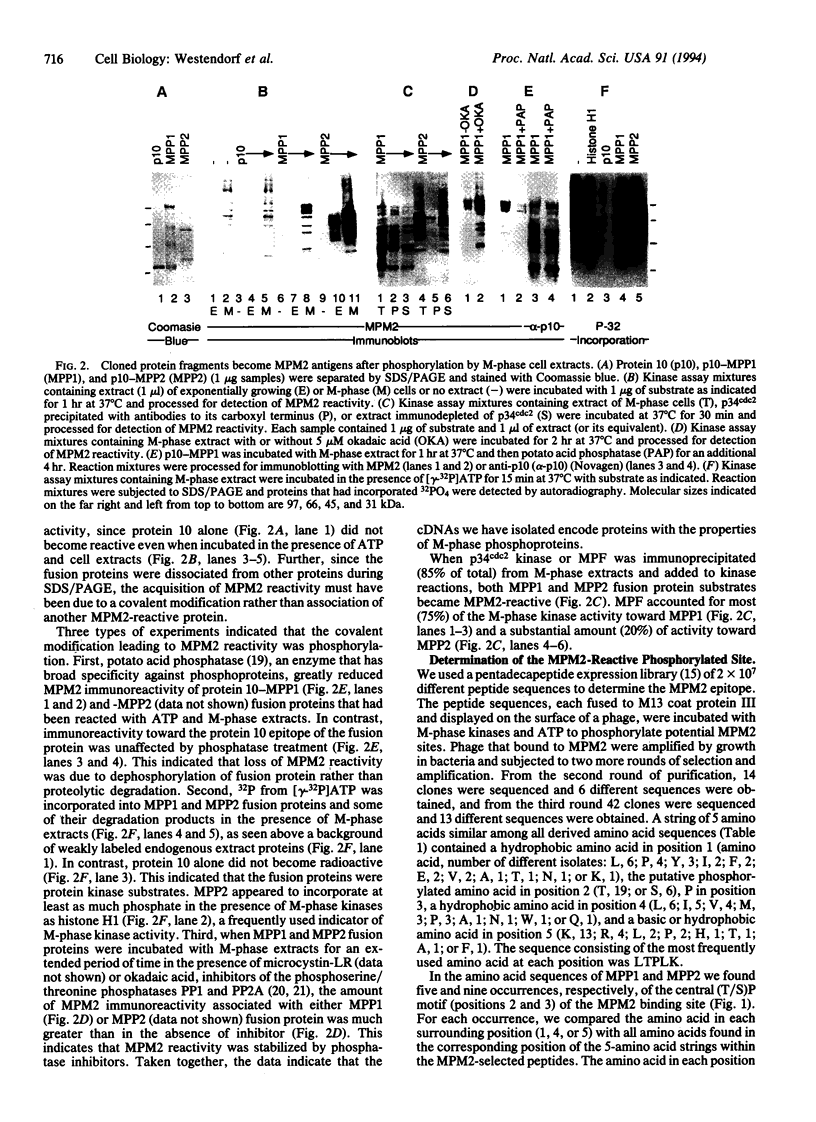
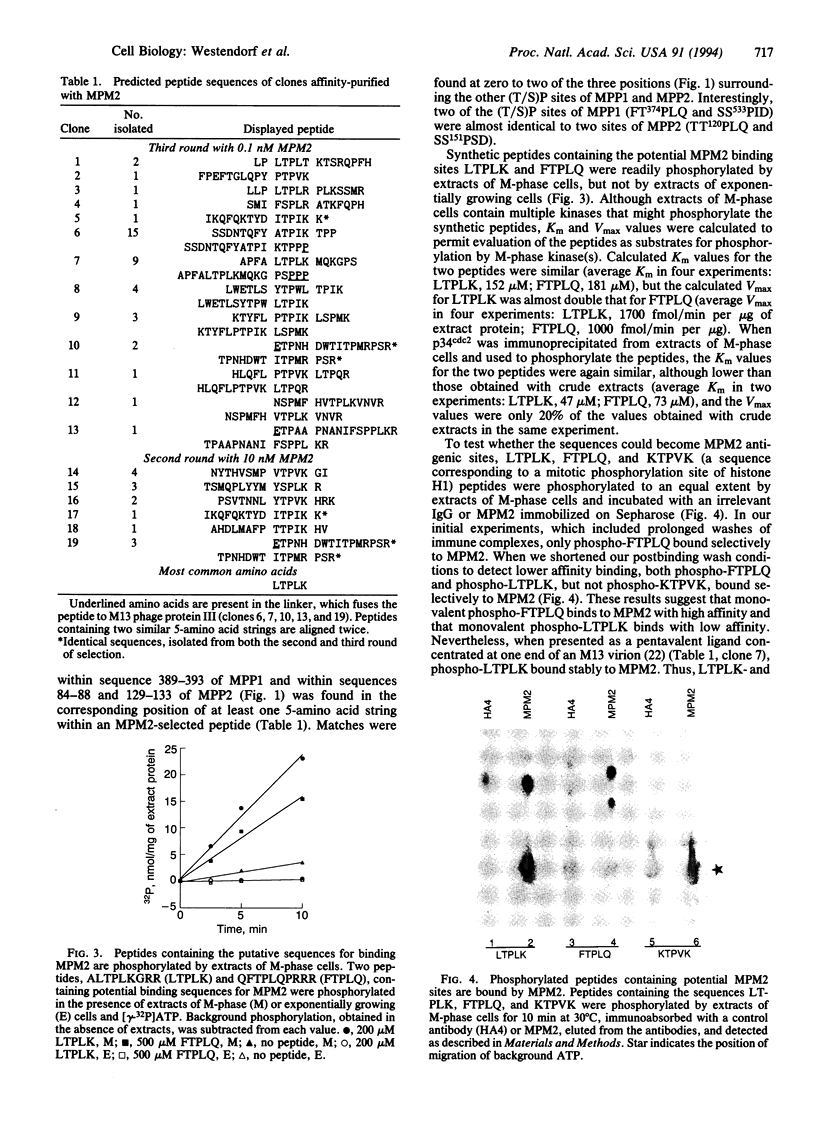
The MPM2 monoclonal antibody binds to a phospho amino acid-containing epitope present on more than 40 proteins of M-phase eukaryotic cells. We have developed a technique for cloning cDNAs encoding MPM2-reactive phosphoproteins from bacteriophage lambda expression libraries. Proteins from phage plaques were absorbed to nitrocellulose filters, phosphorylated by M-phase kinases, and screened for MPM2 binding. Partial-length cDNAs encoding two MPM2-reactive proteins termed MPM2-reactive phosphoproteins 1 and 2 (MPP1 and MPP2) were isolated. The deduced MPP1 and MPP2 amino acid sequences are not closely related to any previously described proteins. To determine which amino acid stretches contained the MPM2 epitope, sequences from a 15 amino acid peptide expression library were selected for binding to MPM2 after phosphorylation by M-phase kinases. A string of five amino acids was similar among all selected peptides, and the sequence reflecting the most frequent amino acid at each position was Leu-Thr-Pro-Leu-Lys (LTPLK). MPP1 and MPP2 proteins, respectively, contained five and nine sites closely related to LTPLK, including two that were common to both proteins, (F/T)TPLQ and SSP(I/S)D. Peptides containing LTPLK and FTPLQ were strongly phosphorylated by M-phase, but not interphase, cytosolic kinases, and the phosphorylated peptides were bound by MPM2. Thus, we have identified M-phase-specific phosphorylation sites bound by MPM2 and two putative M-phase phosphoproteins containing these sites.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Casnellie J. E. Assay of protein kinases using peptides with basic residues for phosphocellulose binding. Methods Enzymol. 1991;200:115–120. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)00133-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers T. C., Langan T. A. Purification and characterization of growth-associated H1 histone kinase from Novikoff hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):16940–16947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark-Lewis I., Sanghera J. S., Pelech S. L. Definition of a consensus sequence for peptide substrate recognition by p44mpk, the meiosis-activated myelin basic protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15180–15184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Holmes C. F., Tsukitani Y. Okadaic acid: a new probe for the study of cellular regulation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Mar;15(3):98–102. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90192-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., King C. S. Dephosphorylation or antibody binding to the carboxy terminus stimulates pp60c-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4467–4477. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis F. M., Tsao T. Y., Fowler S. K., Rao P. N. Monoclonal antibodies to mitotic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):2926–2930. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.2926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devlin J. J., Panganiban L. C., Devlin P. E. Random peptide libraries: a source of specific protein binding molecules. Science. 1990 Jul 27;249(4967):404–406. doi: 10.1126/science.2143033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant R. A., Lin T. C., Konigsberg W., Webster R. E. Structure of the filamentous bacteriophage fl. Location of the A, C, and D minor coat proteins. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 10;256(1):539–546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T., Mitchison T. J. Cell cycle control of higher-order chromatin assembly around naked DNA in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;115(6):1479–1489. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.6.1479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuang J., Ashorn C. L. At least two kinases phosphorylate the MPM-2 epitope during Xenopus oocyte maturation. J Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;123(4):859–868. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.4.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuang J., Zhao J., Wright D. A., Saunders G. F., Rao P. N. Mitosis-specific monoclonal antibody MPM-2 inhibits Xenopus oocyte maturation and depletes maturation-promoting activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4982–4986. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKintosh C., Beattie K. A., Klumpp S., Cohen P., Codd G. A. Cyanobacterial microcystin-LR is a potent and specific inhibitor of protein phosphatases 1 and 2A from both mammals and higher plants. FEBS Lett. 1990 May 21;264(2):187–192. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80245-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P. Universal control mechanism regulating onset of M-phase. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):503–508. doi: 10.1038/344503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottaviano Y., Gerace L. Phosphorylation of the nuclear lamins during interphase and mitosis. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):624–632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmley S. F., Smith G. P. Antibody-selectable filamentous fd phage vectors: affinity purification of target genes. Gene. 1988 Dec 20;73(2):305–318. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90495-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. K., Smith G. P. Searching for peptide ligands with an epitope library. Science. 1990 Jul 27;249(4967):386–390. doi: 10.1126/science.1696028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suprynowicz F. A., Gerace L. A fractionated cell-free system for analysis of prophase nuclear disassembly. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2073–2081. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tombes R. M., Peloquin J. G., Borisy G. G. Specific association of an M-phase kinase with isolated mitotic spindles and identification of two of its substrates as MAP4 and MAP1B. Cell Regul. 1991 Nov;2(11):861–874. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.11.861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandre D. D., Davis F. M., Rao P. N., Borisy G. G. Phosphoproteins are components of mitotic microtubule organizing centers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4439–4443. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandré D. D., Centonze V. E., Peloquin J., Tombes R. M., Borisy G. G. Proteins of the mammalian mitotic spindle: phosphorylation/dephosphorylation of MAP-4 during mitosis. J Cell Sci. 1991 Apr;98(Pt 4):577–588. doi: 10.1242/jcs.98.4.577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. Y. Antibodies for phosphotyrosine: analytical and preparative tool for tyrosyl-phosphorylated proteins. Anal Biochem. 1988 Jul;172(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90403-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]