Abstract
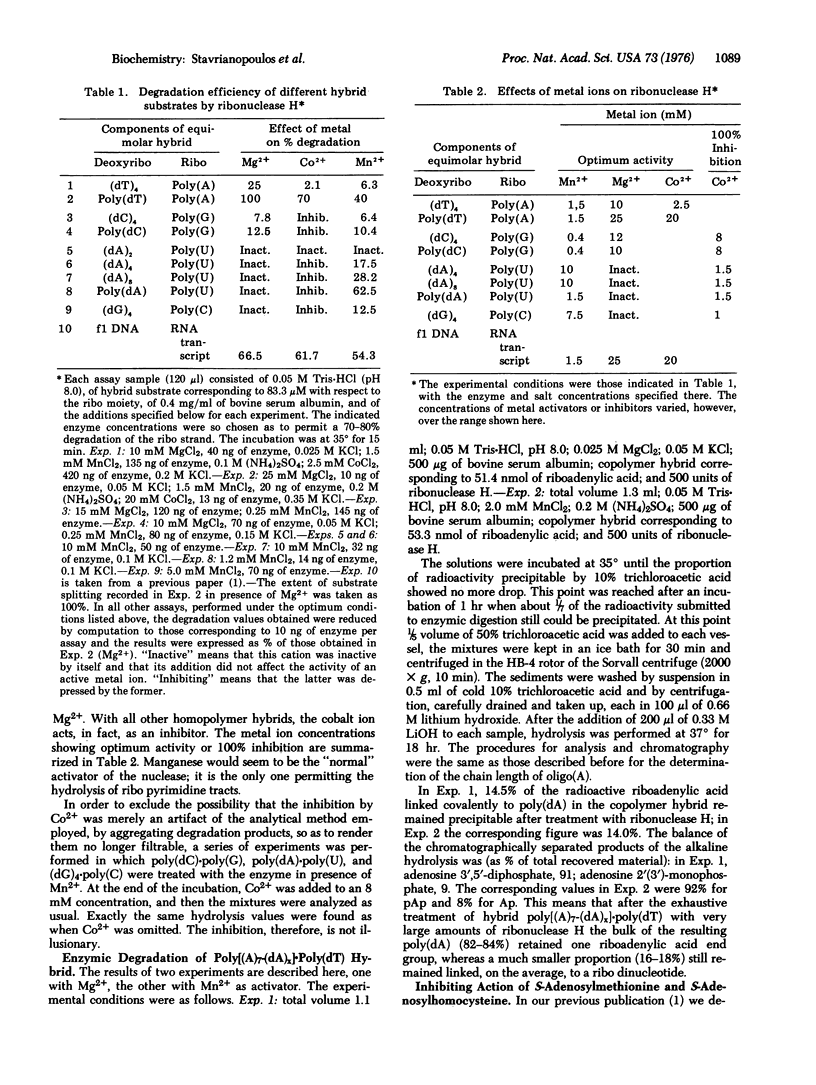
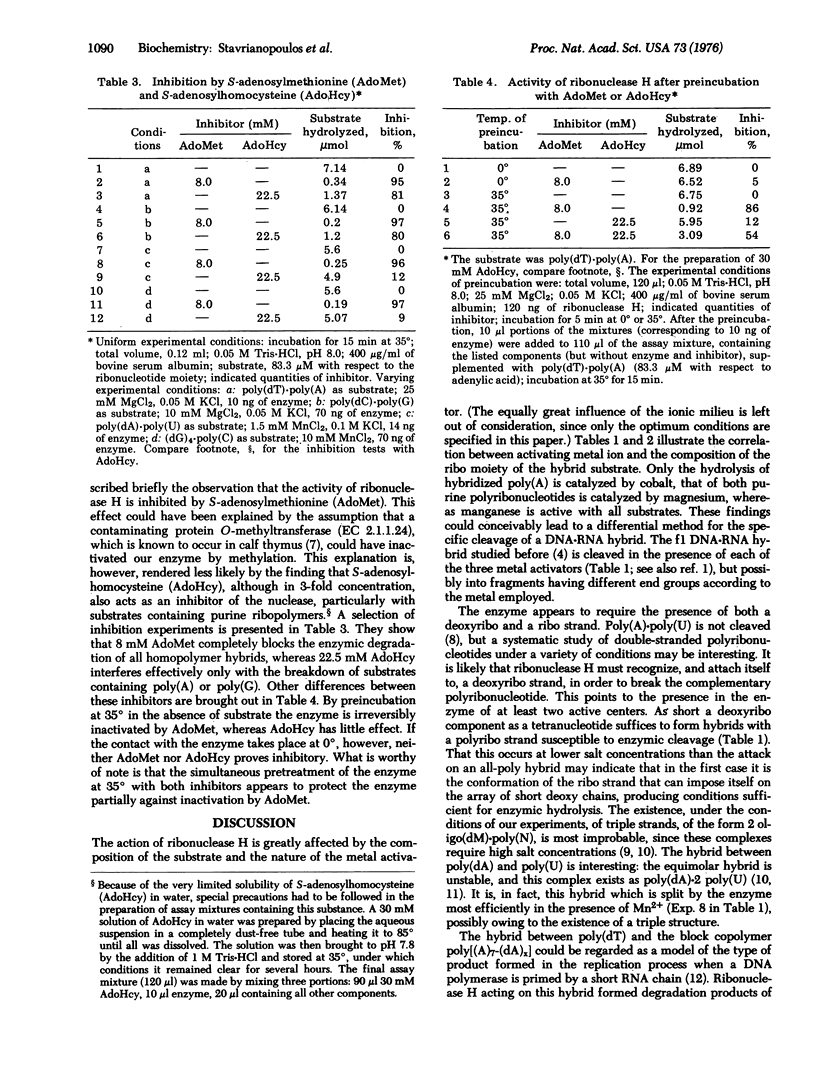
When the action of highly purified specimens of ribonuclease H (hybrid nuclease; RNA-DNA hybrid ribonucleotidohydrolase; EC 3.1.4.34) of calf thymus on a wide selection of homopolymer hybrids was studied, the extent, and even the occurrence, of hydrolysis was found to be governed by the interplay of several factors: the composition of the ribo strand, the length of the deoxyribo strand, and the nature of the activating metal. Mn2+ activates the enzymic cleavage of all hybrid combinations, Mg2+ only of those containing purine ribo strands, Co2+ only of poly(A) hybrids. A 1:1 hybrid of phage f1 DNA and RNA is, however, split in the presence of any of these activators. Hybrids with deoxyribo tetranucleotides can still be cleaved, but not with dinucleotides. The behavior of hybrids containing covalently linked runs of ribo and deoxyribopolynucleotides was studied with the hybrid poly(dT)-poly(A)7-(dA)X]. This hybrid is attacked by ribonuclease H so that the bulk of the resulting poly(dA) still retains one covalently linked riboadenylic acid end group, whereas a small proportion carries a ribo dinucleotide. Inhibition studies showed that ribonuclease H is inactivated irreversibly by pretreatment with S-adenosylmethionine at 35 degrees, but not at 0 degrees. S-Adenosylhomocysteine also is inhibitory, but not irreversibly; also it is essentially limited to the inhibition of the cleavage of purine ribo strands. When the enzyme is exposed simultaneously to both inhibitors, irreversible inactivation is diminished considerably.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- FELSENFELD G., RICH A. Studies on the formation of two- and three-stranded polyribonucleotides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Dec;26(3):457–468. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90091-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber F. E., Chargaff E. Studies on the specificity of the enzymic synthesis of polyribonucleotides. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Nov;2(4):433–441. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1967.tb00156.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausen P., Stein H. Ribonuclease H. An enzyme degrading the RNA moiety of DNA-RNA hybrids. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Jun;14(2):278–283. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00287.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamaluddin M., Kim S., Paik W. K. Studies on the kinetic mechanism of S-adenosylmethionine: protein O-methyltransferase of calf thymus. Biochemistry. 1975 Feb 25;14(4):694–698. doi: 10.1021/bi00675a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato K. I., Gonçalves J. M., Houts G. E., Bollum F. J. Deoxynucleotide-polymerizing enzymes of calf thymus gland. II. Properties of the terminal deoxynucleotidyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jun 10;242(11):2780–2789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller W. RNA-primed DNA synthesis in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1560–1564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leis J. P., Berkower I., Hurwitz J. Mechanism of action of ribonuclease H isolated from avian myeloblastosis virus and Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):466–470. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paik W. K., Kim S. Protein methylase I. Purification and properties of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1968 May 10;243(9):2108–2114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich A. A HYBRID HELIX CONTAINING BOTH DEOXYRIBOSE AND RIBOSE POLYNUCLEOTIDES AND ITS RELATION TO THE TRANSFER OF INFORMATION BETWEEN THE NUCLEIC ACIDS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960 Aug;46(8):1044–1053. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.8.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley M., Maling B. Physical and chemical characterization of two- and three-stranded adenine-thymine and adenine-uracil homopolymer complexes. J Mol Biol. 1966 Sep;20(2):359–389. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90069-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stavrianopoulos J. G., Chargaff E. Purification and properties of ribonuclease H of calf thymus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):1959–1963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stavrianopoulos J. G., Karkas J. D., Chargaff E. DNA polymerase of chicken embryo: purification and properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1781–1785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stavrianopoulos J. G., Karkas J. D., Chargaff E. Mechanism of DNA replication by highly purified DNA polymerase of chicken embryo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2609–2613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stavrianopoulos J. G., Karkas J. D., Chargaff E. Nucleic acid polymerases of the developing chicken embryo: a DNA polymerase preferring a hybrid template. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2207–2211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



