Abstract
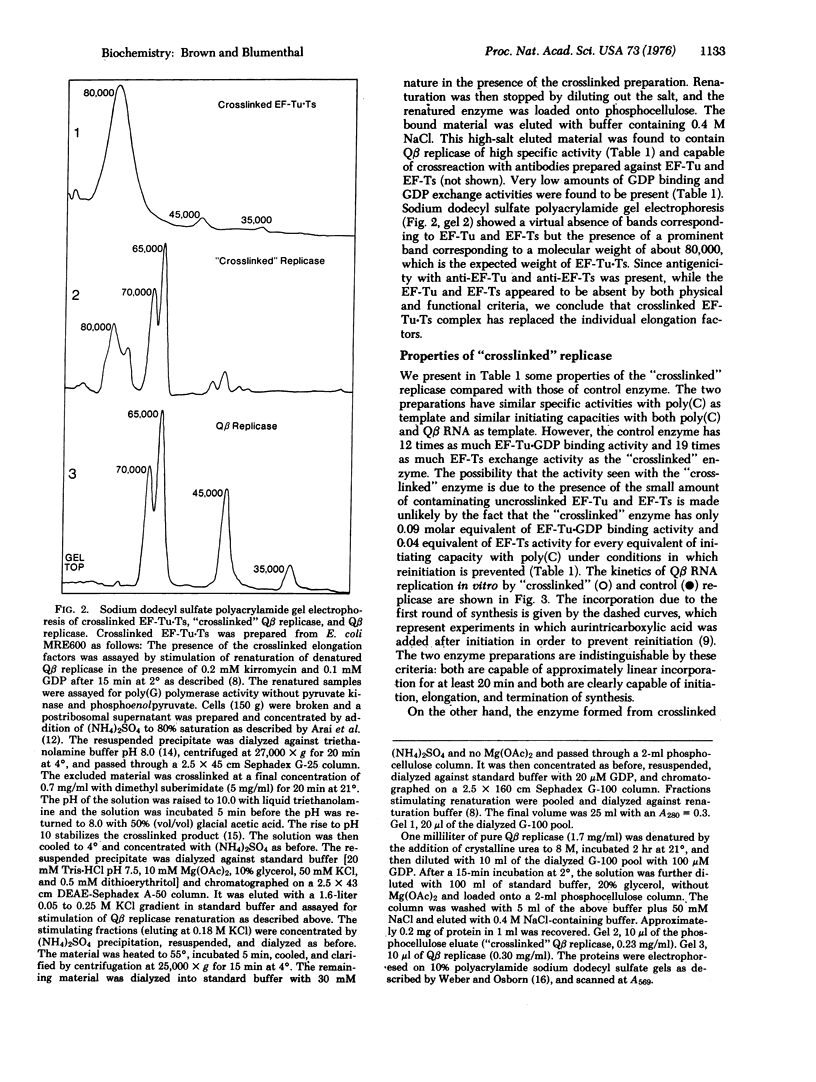
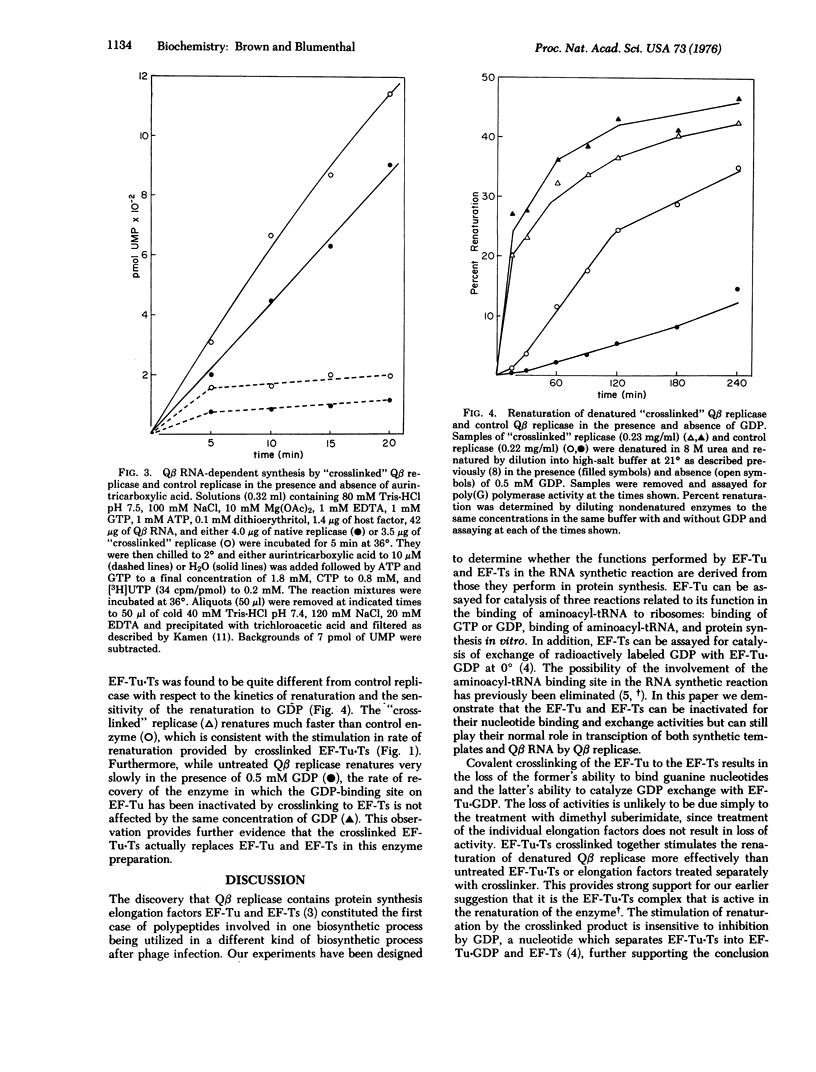
Escherichia coli phage Qbeta RNA replicase, an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RNA-dependent RNA nucleotidyltransferase), is a tetramer composed of one phage-coded polypeptide and three host-supplied polypeptides which are known to function in the biosynthesis of proteins in the uninfected host. Two of these polypeptides, protein synthesis elongation factors EF-Tu and EF-Ts, can be covalently crosslinked with dimethyl suberimidate to form a complex which lacks the ability to catalyze the known host functions catalyzed by the individual elongation factors. Using a previously developed reconstitution system we have examined the effects of crosslinking the EF-Tu-Ts complex on reconstituted replicase activity. Renaturation is significantly more efficient when exogenously added native EF-Tu-Ts is crosslinked than when it is not. Crosslinked EF-Tu-Ts can be purified from a crude crosslinked postribosomal supernatant by its ability to replace EF-Tu and EF-Ts in the renaturation of denatured Qbeta replicase. A sample of Qbeta replicase with crosslinked EF-Tu-Ts replacing the individual elongation factors was prepared. Although it lacked EF-Tu and EF-Ts activities, it could initiate transcription of both poly(C) and Qbeta RNA normally and had approximately the same specific activity as control enzyme. Denatured Qbeta replicase formed with crosslinked EF-Tu-Ts was found to renature much more rapidly than untreated enzyme and, in contrast to normal replicase, its renaturation was not inhibited by GDP. The results demonstrate that EF-Tu and EF-Ts function as complex in Qbeta replicase and do not perform their known protein biosynthetic function in the RNA synthetic reaction.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arai K. I., Kawakita M., Kaziro Y. Studies on polypeptide elongation factors from Escherichia coli. II. Purification of factors Tu-guanosine diphosphate, Ts, and Tu-Ts, and crystallization of Tu-guanosine diphosphate and Tu-Ts. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):7029–7037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- August J. T., Banerjee A. K., Eoyang L., Franze de Fernandez M. T., Hori K., Kuo C. H., Rensing U., Shapiro L. Synthesis of bacteriophage Q-beta RNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:73–81. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1968.033.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal T., Landers T. A. Renaturation of a multisubunit multiactivity enzyme complex: recovery of phage Qbeta RNA replicase, EF-Tu, and EF-Ts activities after denaturation in urea. Biochemistry. 1976 Jan 27;15(2):422–425. doi: 10.1021/bi00647a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal T., Landers T. A. The inhibition of nucleic acid-binding proteins by aurintricarboxylic acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Dec 10;55(3):680–688. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91198-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal T., Landers T. A., Weber K. Bacteriophage Q replicase contains the protein biosynthesis elongation factors EF Tu and EF Ts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 May;69(5):1313–1317. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.5.1313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browne D. T., Kent S. B. Formation of non-amidine products in the chemical modification of horse liver alcohol dehydrogenase with imido esters. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Nov 3;67(1):133–138. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90293-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamen R. A new method for the purification of Q RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 23;262(1):88–100. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90221-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamen R. Characterization of the subunits of Q-beta replicase. Nature. 1970 Nov 7;228(5271):527–533. doi: 10.1038/228527a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo M., Gallerani R., Weissmann C. Subunit structure of Q-beta replicase. Nature. 1970 Nov 7;228(5271):525–527. doi: 10.1038/228525a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landers T. A., Blumenthal T., Weber K. Function and structure in ribonucleic acid phage Q beta ribonucleic acid replicase. The roles of the different subunits in transcription of synthetic templates. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 25;249(18):5801–5808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas-Lenard J. Protein biosynthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1971;40:409–448. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.40.070171.002205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. L., Weissbach H. Interactions between the elongation factors: the displacement of GPD from the TU-GDP complex by factor Ts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Mar 27;38(6):1016–1022. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90341-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann C., Billeter M. A., Goodman H. M., Hindley J., Weber H. Structure and function of phage RNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1973;42:303–328. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.42.070173.001511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Blumenthal T. Phage Q-beta ribonucleic acid replicase. Subunit relationships determined by intramolecular cross-linking. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 10;250(5):1829–1832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


