Abstract
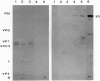
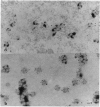
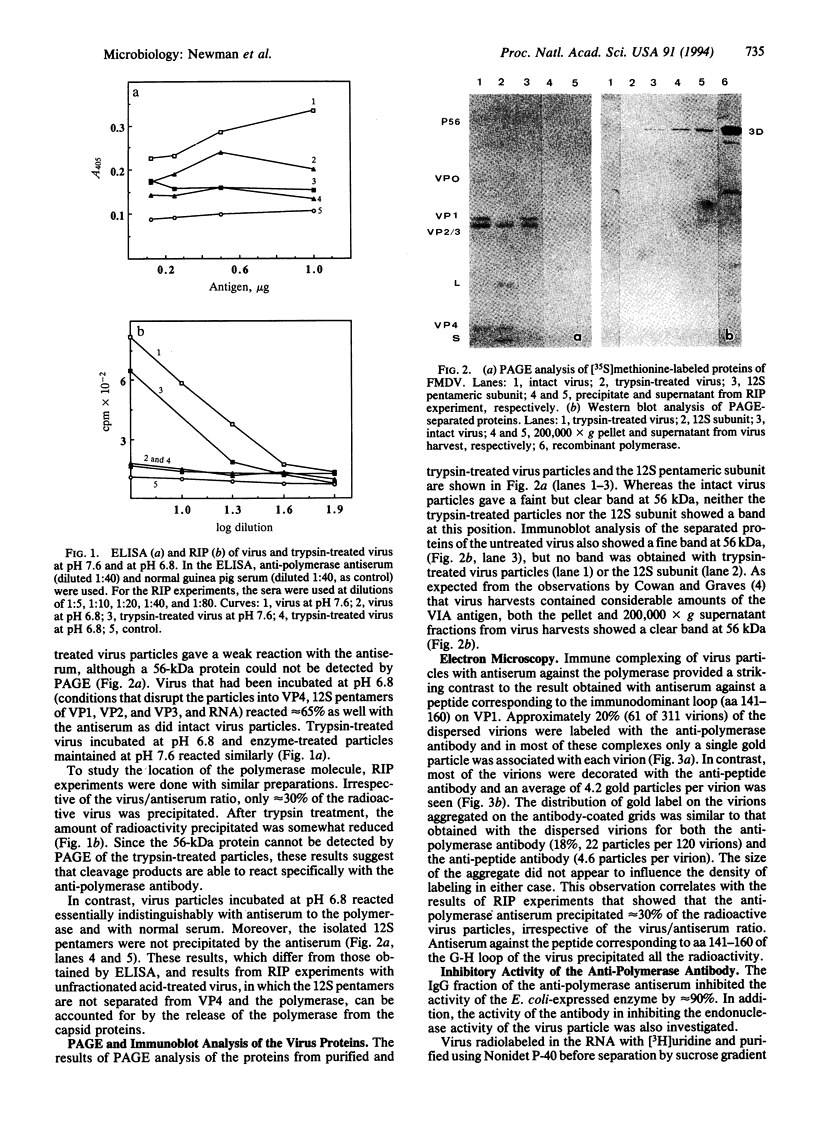
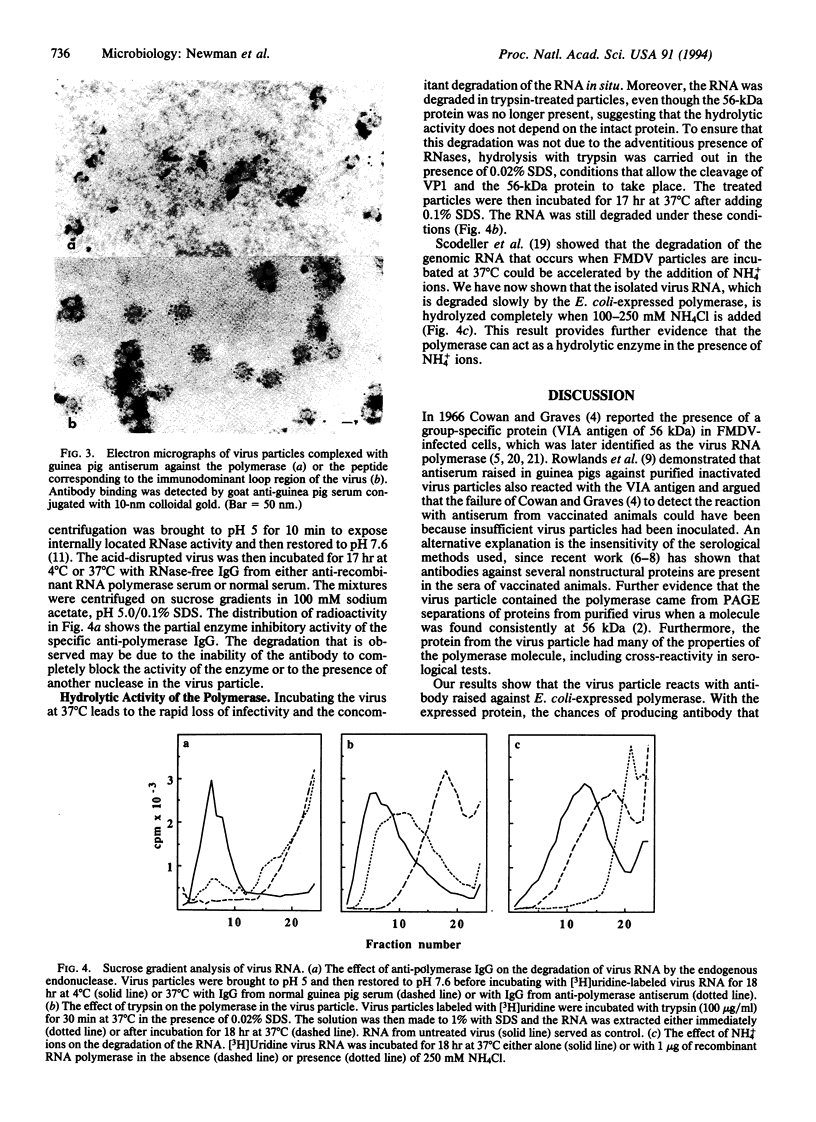
An antibody against the Escherichia coli-expressed RNA polymerase of foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV) reacts with the virus in ELISA and radioimmunoprecipitation experiments and with a protein of the disrupted virus particle in an immunoblot analysis. Treatment of the virus with trypsin, which cleaves capsid protein VP1 and a 56-kDa polypeptide present in trace amount in the particles, reduces the level of the reaction in ELISA and radioimmunoprecipitation and eliminates the immunoblot reaction. Electron microscopy showed that only approximately 20% of the virus particles reacted with the anti-polymerase antibody, whereas most reacted with an antibody against the immunodominant G-H loop of the virus. In the presence of ammonium ions, the expressed polymerase degrades the RNA of the virus into molecules sedimenting at approximately 12 S, indicating that it can act as a hydrolytic as well as a polymerizing enzyme. Moreover, the RNA in trypsin-treated virus particles is degraded when incubated at 37 degrees C, suggesting that the cleaved 56-kDa protein still possesses hydrolytic activity. In addition, the anti-polymerase antibody, which inhibits the polymerase activity of the E. coli-expressed protein, also partially inhibits the hydrolytic activity of the previously described endonuclease of the virus particle, suggesting that this enzyme is identical with the polymerase or forms part of it.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BROWN F., CARTWRIGHT B. PURIFICATION OF RADIOACTIVE FOOT-AND-MOUTH DISEASE VIRUS. Nature. 1963 Sep 21;199:1168–1170. doi: 10.1038/1991168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN F., HYSLOP N. S., CRICK J., MORROW A. W. THE USE OF ACETYLETHYLENEIMINE IN THE PRODUCTION OF INACTIVATED FOOT-AND-MOUTH DISEASE VACCINES. J Hyg (Lond) 1963 Sep;61:337–344. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400039620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN F., STEWART D. L. Studies with infective ribonucleic acid from tissues and cell cultures infected with the virus of foot-and-mouth disease. Virology. 1959 Apr;7(4):408–418. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(59)90069-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger H. G., Straub O. C., Ahl R., Tesar M., Marquardt O. Identification of foot-and-mouth disease virus replication in vaccinated cattle by antibodies to non-structural virus proteins. Vaccine. 1990 Jun;8(3):213–216. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(90)90048-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown F., Wild T. F. The effect of heat on the structure of foot-and-mouth disease virus and the viral ribonucleic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 May 19;119(2):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90188-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan K. M., Graves J. H. A third antigenic component associated with foot-and-mouth disease infection. Virology. 1966 Nov;30(3):528–540. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90128-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denoya C. D., Scodeller E. A., Vasquez C., La Torre J. L. Foot and mouth disease virus. II. Endoribonuclease activity within purified virions. Virology. 1978 Aug;89(1):67–74. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90040-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denoya C. D., Scodeller E. A., Vasquez C., La Torre J. L. Ribonuclease activities associated with purified foot and mouth disease virus. Arch Virol. 1978;57(2):153–159. doi: 10.1007/BF01315676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Torre J. L., Grubman M. J., Baxt B., Bachrach H. L. The structural polypeptides of aphthovirus are phosphoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7444–7447. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laporte J., Lenoir G. Structural proteins of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Gen Virol. 1973 Aug;20(2):161–168. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-20-2-161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe P. A., Brown F. Isolation of a soluble and template-dependent foot-and-mouth disease virus RNA polymerase. Virology. 1981 May;111(1):23–32. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90650-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neitzert E., Beck E., de Mello P. A., Gomes I., Bergmann I. E. Expression of the aphthovirus RNA polymerase gene in Escherichia coli and its use together with other bioengineered nonstructural antigens in detection of late persistent infections. Virology. 1991 Oct;184(2):799–804. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90456-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman J. F., Cartwright B., Doel T. R., Brown F. Purification and identification of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Gen Virol. 1979 Nov;45(2):497–507. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-45-2-497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polatnick J., Arlinghaus R. B. Foot-and-mouth disease virus-induced ribonucleic acid polymerase in baby hamster kidney cells. Virology. 1967 Apr;31(4):601–608. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90188-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polatnick J. Effect of salts and other agents on foot-and-mouth disease virus poly (U) polymerase activity. Arch Virol. 1985;84(3-4):269–275. doi: 10.1007/BF01378979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowlands D. J., Cartwright B., Brown F. Evidence for an internal antigen in foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Gen Virol. 1969 Jun;4(4):479–487. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-4-4-479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan M. D., Belsham G. J., King A. M. Specificity of enzyme-substrate interactions in foot-and-mouth disease virus polyprotein processing. Virology. 1989 Nov;173(1):35–45. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90219-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sangar D. V., Rowlands D. J., Cavanagh D., Brown F. Characterization of the minor polypeptides in the foot-and-mouth disease particle. J Gen Virol. 1976 Apr;31(1):35–46. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-31-1-35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sankar S., Porter A. G. Expression, purification, and properties of recombinant encephalomyocarditis virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):2993–3000. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.2993-3000.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scodeller E. A., Lebendiker M. A., Dubra M. S., Crespo O. A., Basarab O., La Torre J. L., Vasquez C. Inactivation of foot-and-mouth disease virus vaccine strains by activation of virus-associated endonuclease. J Gen Virol. 1984 Sep;65(Pt 9):1567–1573. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-9-1567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesar M., Berger H. G., Marquardt O. Serological probes for some foot-and-mouth disease virus nonstructural proteins. Virus Genes. 1989 Sep;3(1):29–44. doi: 10.1007/BF00301985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward R. L. Mechanism of poliovirus inactivation by ammonia. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):299–305. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.299-305.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziola B. R., Scraba D. G. Structure of the Mengo virion. I. Polypeptide and ribonucleate components of the virus particle. Virology. 1974 Feb;57(2):531–542. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90192-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]